Semantics: - Yilmaz Kilicaslan

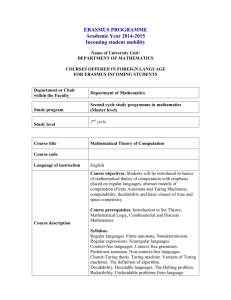
Formal Languages and Abstract Machines
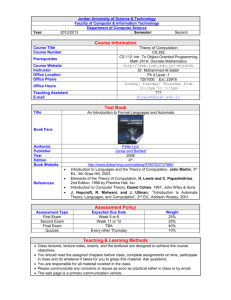
Course Description
Yılmaz Kılıçaslan
20 September 2012
Prerequisites
To know at least one of the logic programming languages (Artificial Intelligence and Logic
Programming).
Objectives
The main objective of the course is to study Computation Theory as one of the major theories of Computer Science in terms of types and levels of formal languages and abstract machines.
Also, to have a look at compiler programs and to develop natural language processing applications within the theoretical framework to be set up are determined as secondary objectives of the course.
Syllabus
The course begins with a discussion of the development of machines throughout the history.
Afterwards, Gödel’s Incompleteness Theorem and Turing’s Uncomputability Theorem are examined as theories determining the limits of axiomatic logic. Then, languages and corresponding machines are classified according to the Chomsky hierarchy from simple to complex and studied in turn with applications. The formal language techniques learnt in the course are applied to the morphological, syntactic and semantic dimensions of natural languages with particular emphasis in Turkish. Furthermore, the tools for the lexical and syntactic analysis of programming languages are examined within the formal languages paradigms studied in the course.
The topics to be covered are as follows:
Historical development of machines
Gödel’s Incompleteness Theorem
Turing’s Uncomputability Theorem
Chomsky Hierarchy
Regular Languages
Context-Free Languages
Context-Sensitive Languages
Recurisively Enumerable Languages
Regular Expressions
Finite-State Automata
Non-Deterministic Finite-State Automata
Two-Way Finite-State Automata
Push-Down Automata
Turing Machines
Schedule
The contents of lectures are scheduled as shown in the following table:
WEEK
1
2
3
4
5
6
10
11
12
7
8
9
TOPIC
Historical Development of Machines, Limits of Logic and Computation
Scaling Formal Languages and Abstarct Machines from Simple to Complex
Finite-State Automata
Morphological Analysis of Turkish
Regular Languages
Regular Expressions
Midterm Exam
Push-Down Automata
Context-Free Grammars
Context-Sensitive Grammars
Turing Machines
Final Exam
Intellectual Development
The aim of the course is to make students grasp computer science in its interaction with mathematics and formal language theory. The most important gain which the course may offer is to enable our students close to graduation to approach their profession through the perspective of computer science.
Activities
The course consists of three hours lectures each week. The theoretical content of the course will be offered with practices to be carried out in tandem.
References
Hopcroft, J.E. and Ullman J.D. (1979). Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and
Computation (1st ed.). Addison-Wesley.
Gazdar, G. and Mellish C. (1989). Natural Language Processing in Prolog. Addison-
Wesley.
Yarımağan, Ü. (2011). Özdevinirler (Otomatlar) Kuramı ve Biçimsel Diller (İkinci
Basım). Akademi Yayıncılık.