Unit C Review Questions
advertisement

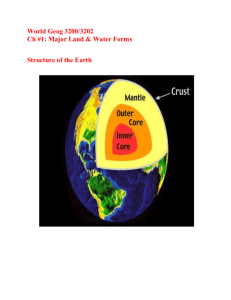
Unit C Review Questions 1. Students will fill in this chart while watching “Geomorphology.” Era Period Time Frame (Millions of Years Before Present) Environmental Conditions Events and Life Forms 4500 volcanic, hot to 590 Precambrian Cambrian 590 to sea 500 Ordovician/ Silurian 500 to sea 410 life begins in sea algae, bacteria, primitive worms Devonian Carboniferous Mesozoic 410 to warm, shallow 360 sea shallow 360 to tropical 290 seas Permian huge swamps, 290 to but largely 250 marine Triassic 250 to supercontinent none explosion of life increase in atmospheric oxygen jellyfish crustaceans snails none ammonoides (ammonites) crinoids eurypterids water scorpions corals Paleozoic Societal Connection (Fossil Fuels) predatory fish large carbonate reefs carbonate shells giant dragonflies fin-backed reptiles large reptiles none much of Alberta’s oil and gas deposits first oil discovere d from this time period none oil and 210 Jurassic (Pangaea) 210 to marine, shore, 140 continental early dinosaurs dinosaurs ruled dinosaurs continue to roam T-Rex triceratops duck-bill dinosaurs flowering plants snakes Rocky Mountain building starts major extinction caused by asteroid impact and cooling climate Cretaceous 140 to inland sea 65 Tertiary 65 to 1.7 Cenozoic Quaternary warm, swampy forests transitioning to cooler grasslands ice ages, ice 1.7 to sheets, present glaciers gas oil and gas oil sands oil and gas coal rise of mammals dominance of grasses and grazing mammals mammoths 80 000 years ago last ice age begins none none 2. Students will fill in this table to summarize the important concepts of Unit C. One possible set of answers is shown. Concept Explanation Earth’s history has occurred challenges of over billions of investigating years and is changes to recorded all Earth’s crustal across the planet plates in sedimentary rocks thousands of metres thick. evolution of geological process theories Over the past 300 years, new theories have developed and Connection to Technology and/or Society Examples most rocks and fossils from early in Earth’s history destroyed by rock cycle uniformitarianism versus catastrophism development of plate tectonic theory new technological advances—groundpenetrating radar, GPS satellites, radiometric-dating techniques help scientists overcome challenges computer modelling mass spectrometer seismometers continue to change in light of new evidence. development of radiometric dating and dating Earth’s age various theories concerning climate change energy released by earthquakes Seismic waves travel out in all directions from the epicentre. P-waves S-waves surface waves layers for Earth’s internal structure The internal structure of Earth is composed of layers. inner core outer core mantle crust Crustal plates float and move plate tectonics on Earth’s mantle. sea-floor spreading subduction driving force for plate tectonics Convection currents push and pull on Earth’s tectonic plates. Juan de Fuca Plate being subducted under North American Plate determining absolute age This is determined by finding the age in years of rocks or fossils. radiometric dating uranium carbon fossilization Information about once-living organisms is preserved in layers of sedimentary rock. moulds imprints tracks trails burrows actual remains determining relative age This is a matter of determining which rock layer or fossil is older or younger. principle of superposition evidence of past climates Rock features and composition mud cracks GPS ground-penetrating radar satellite imaging computer modelling uncertainty concerning theories about climate changes affects public policy technology used to track earthquakes lives saved by earthquake predictions seismic waves used to probe internal structure of Earth predictions of volcanic eruptions save lives GPS used to track, predict plate movement lava lamp also works using the concept of convection new technologies— mass spectrometer fossil fuels Alberta’s main energy source presence of fossils in drill-core samples—a useful indicator of petroleum used to correlate drill cores for oil exploration understanding climate in rocks can indicate the characteristics of climate. atmosphere’s composition affected by life forms Organisms exchange gases with the atmosphere. evidence of repeated glaciations in Alberta Glaciations occur when ice sheets advance to cover much of Canada, and then they retreat. ice cores show evidence of warming, cooling several theories about causes of climate change exist Continental ice sheets and glaciers reveal the records of annual snowfall. Several cold periods in Earth’s history each contained repeated glaciations. salt deposits limestone marine fossils oxygen-18: oxygen-16 ratios from ocean sediments cyanobacteria help provide oxygen to early atmosphere exponential increase in atmospheric CO2 from burning fossil fuels drumlins eskers kames kettles till deposits Vostok ice core from Antarctica record of 420 000 years climate and atmospheric composition plate tectonics affect continent position, ocean currents Milankovitch theory variations in solar radiation (sunspots) changes in atmospheric composition (carbon dioxide) enhanced greenhouse effect changes of past helps scientists predict changes in future and determine extent and nature of human impacts on climate human-induced enhanced greenhouse effect sharp peaks of Alberta’s mountains largely due to glaciation much of Alberta’s drinking water from glaciers Vostok ice core used to support theories about causes of climate change—used to make predictions concerning climate change theories about causes of climate change form foundation for models used to predict future climate change—public policy based on scientific data concerning degree of human influence on global climate 3. James Hutton is credited with the theory of uniformitarianism. 4. The theory of uniformitarianism argues that Earth’s history of change can be explained in terms of geological processes still in operation. 5. The layers listed in order from oldest to youngest are C, B, and A. 6. The law of superposition had to be applied to answer question 5. 7. First, the layers of sedimentary rock (now tilted) were laid down at the bottom of an ancient ocean. They were then tilted by tectonic processes. After a period of erosion, the tilted layers were covered by glacial till during the last glaciation. Water erosion later cut out the outcropping. 8. 9. 10. 11. Fossil 1 is younger than fossil 2, according to the law of superposition. The Tertiary Period is part of the Cenozoic Era. Layer C is between 140 and 65 million years old. The boundary between layers A and B is called an unconformity. The presence of boulders and gravel in layer A suggests the unconformity was caused by glaciation. 12. Parent material: 93% According to the decay curve, 0.10 half-lives have elapsed. Age = (0.10 half-lives)(7.04 × 108 a/half-lives) Age = 7.0 × 107 a or 70 million years old Layer C is 70 million years old. 13. The date determined in question 12 is absolute. 14. Layer A is glacial till that was likely deposited during the last glaciation. 15. The last glaciation ended approximately 10 000 years ago, so it was likely deposited shortly before that time. 16. a. b. c. 17. 18. 19. 20. 7 3 5 d. e. f. 1 4 6 g. h. i. 8 2 9 D A A Answers will vary but could include one of the following: The organism is buried rapidly by fine material before the remains are subjected to the effects of scavengers and decomposition. The organism must be in an environment that is favourable to preservation when it dies (low oxygen, smothered in tree sap, freezing, etc.). 21. Answers will vary but could include the following: Various rock units correlate with each other (must give examples such as sandstone layers or lava flows). The ages of the volcanic lava match. The pattern of magnetic reversals (paleomagnetism) matches. The overall pattern of rock units correlate well, from lava flow downward. 22. Answers will vary but could include the following: The rate of sea-floor spreading was faster during the reversed period. The period of magnetic reversal lasted longer than the normally magnetized period. 23. The geological columns are almost identical until the top of the 20 million-year-old lava flows. The rock units then begin to differ. The top lava flow is 20 million years old, so the separation would have started after the lava flows formed. 24. a. b. Graph II Graph III c. Graph I 25. Each of these topics has a controversial aspect to the suggested connection between climate, human activity, and culture. Students should be encouraged to identify sources that support—as well as sources that challenge—the validity of these connections. 26. Students will evaluate their time lines according to the scoring rubric presented in the textbook. Science 20 © 2006, Alberta Education