Math tips and tricks Division 1 ( ECS – Grade 3)
advertisement
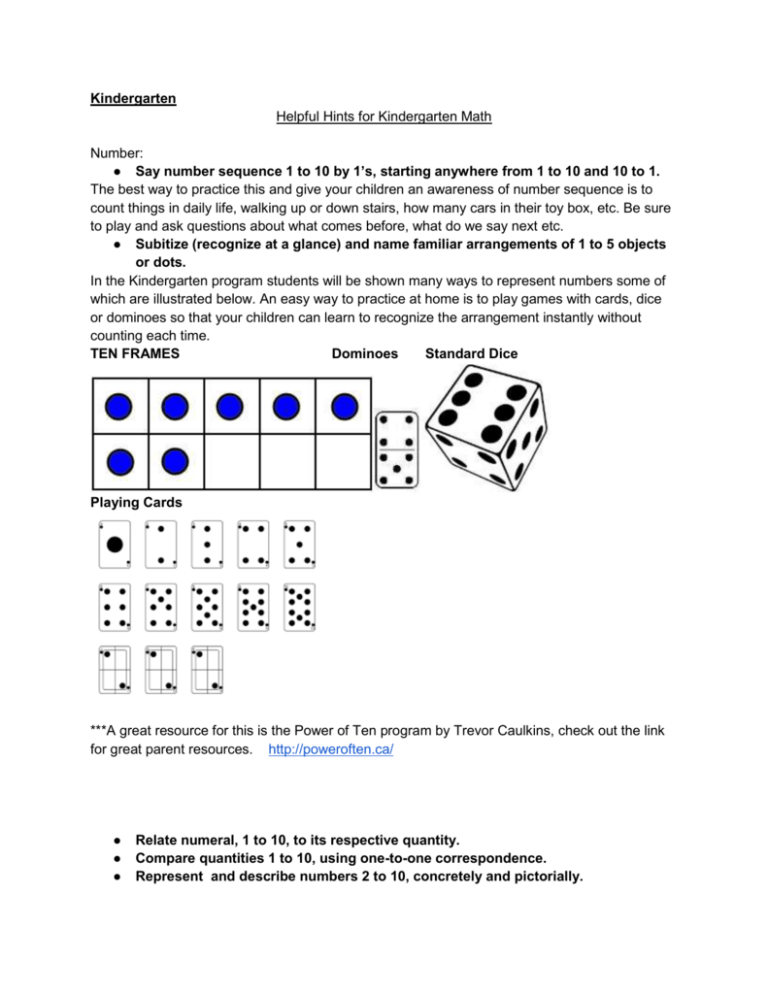
Kindergarten Helpful Hints for Kindergarten Math Number: ● Say number sequence 1 to 10 by 1’s, starting anywhere from 1 to 10 and 10 to 1. The best way to practice this and give your children an awareness of number sequence is to count things in daily life, walking up or down stairs, how many cars in their toy box, etc. Be sure to play and ask questions about what comes before, what do we say next etc. ● Subitize (recognize at a glance) and name familiar arrangements of 1 to 5 objects or dots. In the Kindergarten program students will be shown many ways to represent numbers some of which are illustrated below. An easy way to practice at home is to play games with cards, dice or dominoes so that your children can learn to recognize the arrangement instantly without counting each time. TEN FRAMES Dominoes Standard Dice Playing Cards ***A great resource for this is the Power of Ten program by Trevor Caulkins, check out the link for great parent resources. http://poweroften.ca/ ● ● ● Relate numeral, 1 to 10, to its respective quantity. Compare quantities 1 to 10, using one-to-one correspondence. Represent and describe numbers 2 to 10, concretely and pictorially. Have your children sort items into groups of a given quantity. ie. “Show me five buttons, macaroni, beans,etc. Ask them to identify which group is larger, which group has more, which group has less? Have students demonstrate understanding of how to show numbers: 3, Patterns and Relations: ● demonstrate an understanding of a repeating pattern(two or three elements)by: ● identifying,reproducing,extending,creating, patterns using manipulatives, sounds and actions. Identify: red,blue,red,blue (a,b,a,b) What comes next? Can you make your own pattern? ● Sort a set of objects based on a single attribute, and explain the sorting rule. Students will be able to create groups based on attributes like size, shape, color, object, etc. Shape and Space(Measurement): ● Use direct comparison to compare two objects based on a single attribute, such as length, height, mass, weight, volume, capacity. Shape and Space: (3-D objects and 2-D shapes) ● Sort 3-D objects,using a single attribute. ● Build and describe 3-D objects. Helpful Hints for Grade 1 Math PATTERNING Students will be able to repeat and extend the following patterns: AB, AAB, ABB, AABB, ABC example: AB patterns Students will be able to sort by different attributes (size, colour,shape, etc) NUMBER SENSE Students will be able to: - count to 100 by 1s between any two given numbers. - skip counting by 2s 5s and 10s (2, 4, 6, 8… 20) (5, 10, 15, 20….100) (10, 20, 30, 40…100) - recognize at a glance (subitize) 1-10 objects or dots (on a TEN FRAME or a DICE) TEN FRAME: ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION Students will be able to: - add to sums of 20 (5+9=14) - subtract using numbers less than 20 (18-7=11) - recognize an equal symbol, an addition symbol, and a subtraction symbol - place those symbols in a number sentence correctly (5 + 2 = 7) - use fact families (see below) MEASUREMENT Students will be able to: - understand terms such as longer/shorter, as tall as, more/less, heavier/lighter - compare masses of objects using simple scales and balances 2D AND 3D SHAPES Students will be able to: - sort and compare objects or shapes according to 1 attribute (number of sides, have curves) - describe objects and shapes - identify 2D and 3D shapes Grade 2 Math Tips and Tricks Power of Ten The Power of Ten is a program that helps students build number sense and visualize numbers in different ways. Program Click here to link to the Power of Ten website to find out more about this program and to learn math games to play with your family. Games Click here for information and videos about specific Power of Ten games. Or - click on link to go to the games on the power of ten website http://poweroften.ca/category/games/ Download/print your own Power of Ten cards here http://nosecreek.rockyview.ab.ca/our-school/programs/power-often/Power%20of%20ten%20cards.pdf/view Grade 2 students ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● count to 100 in many different ways (e.g., count by 5s starting at 35 and going to 100) compare and order numbers to 100 and know whether a number is even or odd show, describe and compare quantities to 100, using objects, pictures and numbers understand and apply strategies for addition and subtraction facts to 18 recall addition and subtraction facts to 10 add and subtract numbers to 100 talk about how they solve problems connect numbers, shapes and time frames to everyday life (e.g., relate the number of days to a week) recognize and create repeating and increasing patterns construct 2-D shapes and 3-D objects use graphs to communicate information measure using nonstandard tools such as a hand span Addition and Subtraction Strategies - students will learn a variety of methods for adding and subtracting numbers to 18. See below for some of the language we will be using in grade 2. In grade two we will be solving word problems. Below are key words to help students decide whether the question is an addition problem or a subtraction problem. Addition and Subtraction Strategies (2 digit) In grade two we will be adding and subtracting numbers to 100. While many of us use and were only taught the traditional addition method (“carrying the one”) and subtraction method (“borrowing”) these are in fact not always the most efficient or accurate methods of solving problems. When using this method students lose the understanding of what each number represents, students learn to follow a memorized set of steps. For example, when asked what the one in the following problem means, many students will respond that it stands for “1.” This is incorrect. 1 36 + 49 ----------------85 That one actually stands for ten! My goal by the end of this year is to teach students to be able to add and subtract numbers comfortably in a variety of ways. In doing this, students will have a deeper understanding of the number sense. This will lead to increased understanding moving forward to multiplication and division. We will be using several strategies for addition and subtraction that may seem unfamiliar, but which will teach students that numbers can be taken apart and combined in many different ways. Estimation Skills Estimation is ... finding a number that is close enough to the right answer. ● You are not trying to get the exact right answer ● In life you use estimation when what you want, is something that is good enough (because you are usually in a hurry!) You want a “smart guess” that is close to what the exact answer is. Referents - Referents are looking at what a smaller group looks like and then using it to help you make a smart guess. So for example when guessing how many shapes are in the picture below you would look at / count out what a group of 5 or 10 looks like and use that visual to decide about how many there would be all together. Seeing what a group of 5 or 10 looks like (using the number 5 or 10 as your referant) should help you see how many are in the larger group. See this link for examples of how to estimate and practice activities. http://www.mathsisfun.com/numbers/estimation.html Increasing Patterns An increasing pattern happens when something is added (to each element) each time. You can have a growing pattern with pictures, objects, shapes, and even numbers. Examples: 1, 4, 7, 10… Decreasing Patterns An decreasing pattern happens when something is taken away (from each element) each time. You can have a decreasing pattern with pictures, objects, shapes, and even numbers. Examples: 10, 8, 6, 4 ... Grade Three Welcome parents. We hope this is helpful in communicating with your child and becoming more familiar with the language and strategies of math. If you cannot find a term or strategy, try the online glossary below. http://www.learnalberta.ca/content/memg/1_A/index.html Addition and Subtraction Mental Math Basic mental math strategies to provide solutions for facts to 18. ● doubles; eg. for 6+8, think 7+7 ● doubles plus one; eg. 6+6, think 6+6+1 ● doubles take away one; eg. for 6+7, think 7+7 -1 ● doubles plus two; eg. for 6+8, think 6+6+2 ● doubles take away two; eg. for 6+8, think 8+8 -2 ● making 10; eg for 6+8, think 6+4 +4, OR 8+2+4 ● commutative property; eg. for 3+9, think 9+3 ● addition for subtraction; eg. for 13-7, think 7+ ? = 13 In class, we will use the following strategies: 1. Traditional Stacking (“The Way We Learned”) ● this is the way most of us learned math ● add the tens and then add the ones 2. Adding Ten First 28 + 39 = 50 + 17 =67 3. Doubles (using basic facts) When adding two numbers, double one of the numbers 4. Using a number line to add 2 and 3 digit numbers ------------------------------------------------------------- 5. Chunking: Adding 2 digit numbers . 6. Adding 3 digit numbers 7.Adding 2 digit numbers on a number line Adding and subtracting using a hundreds Chart. Subtraction: Traditional Method (Stacking): For 2 digit and 3 digit numbers << Now, I'm going to make my stripes taller... You'll see why in a second! The first thing to do is to subtract the ones... But, there's a big problem! But, no worries... We can fix it! What we're going to do is borrow from the tens column. (Also called regrouping!) Place Value Students will need to concretely, pictorialy, symbolically represent numbers to 1,000. One way to do this, is using place value charts. These can be made at home easily to help practice. Triangle Flash Cards. Triangles are seen everywhere and grade threes learn about their strength in science this year. In math, we use them for flash cards and to explain related facts. Kids learn to always put the large number at the top. It works for addition/subtraction and multiplication/division. They can be made at home, or drawn on paper. These are easy to make by cutting the corners off of paper sheets. Students need to model up to 5x5=25. They learn strategies to solve up to 9x9=81, but knowing the basic lower facts is is important. Addition/subtraction facts up to 20 will help with more complicated functions later. Estimation Rule: “Five or more, let it soar. Four or less, let it rest.” (if a number is a five or more, round it up. If the number is four or less, round down.) In grade 3, we learn numbers from 1-100, so we typically round to the nearest tens place value. 1. Front end estimating (Subtraction) A. 74 - 32 = _______ B. 70 - 30 = __40___ (the tens place value is the only value subtracted) 2. Front end estimating (addition) A. 24 + 32 = ______ B. 20 + 30 = ___50_ (the tens place value is the only value added) Rounding by ones value (the way we learned it) A. 74 - 36 = _______ (round 36 to 40 and 74 to 70) B. 70 - 40 = __30___ Same process applies for addition. Multiplication and Division Strategies: Repeated addition and subtraction Strategies: Using Arrays to divide Games: Power of ten games to help with multiplication facts. These are games that are often played to assist with numbers sense. DOUBLE Set up one 20-card deck of Power of Ten cards, stacked in a face-down pile. 1. The dealer turns over the top card from the deck. 2. The first player to say the correct answer to ‘double’ wins the card. 3. Another card is turned over and the process is repeated until all cards have been turned over. 4. The player with the most cards at the end wins. DOUBLE DOUBLE Set up one 20-card deck of Power of Ten cards, stacked in a face-down pile. 1. The dealer turns over the top card from the deck. 2. The first player to say the correct answer to ‘double the double’ wins the card (this is the same as multiplying by four). 3. Another card is turned over and the process is repeated until all cards have been turned over. 4. The player with the most cards at the end wins. Patterns When using a hundreds chart to add or subtract by 10, counting up or down will give help find patterns. Pattern Rule: Start at 53, add 3 each time to 98. We do the same type of patterns using numbers to 1000. For example ,start at 445 add 5 each time to 470. Fractions Used: Geometric Shapes: Students will need to know that a Polygon is a shape that is closed with straight lines only. Red are regular, Green are irregular 2D. 3D Shapes: These shapes are identified by faces, edges, and Data Analysis their number of vertices. Tally Marks Bar Graph Line Plot