Year 11 Physics Half Yearly Revision Problems Solution
advertisement
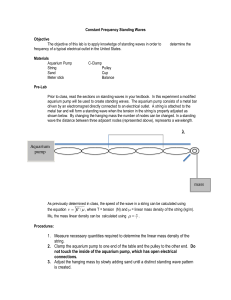
Year 11 Physics Half Yearly Revision Problems Solution 1. A sound wave travelling at a speed of 340 m/s has a wavelength of 2.25 m. What is the pitch of the wave? 𝒗 = 𝒇𝝀 𝒇= 𝒗 𝟑𝟒𝟎𝒎 ⋅ 𝒔−𝟏 = = 𝟏𝟓𝟏𝑯𝒛 𝝀 𝟐. 𝟐𝟓𝒎 2. Two torches, A and B, are shone on a person from different directions. The torches are of the same design and are using the same type of new batteries, so can be treated as the same light source. If torch A is 5 times further away than torch B, how many times brighter will the person measure torch B to be? 𝐈∝ 𝟐𝟓 𝟏 𝟏 𝐝𝟐 𝐈=𝐤× 𝟏 𝐝𝟐 = 𝐤 𝐝𝟐 𝐤 = 𝐈𝐝𝟐 𝐈𝐀 𝐝𝟐𝐀 = 𝐈𝐁 𝐝𝟐𝐁 𝐈𝐁 𝐈𝐀 = 𝐝𝟐𝐀 𝐈𝐁 𝐝𝟐𝐁 𝐈𝐀 = (𝟓𝐝𝐁 )𝟐 𝐝𝟐𝐁 = 𝟐𝟓𝐝𝟐𝐁 𝐝𝟐𝐁 = = 𝟐𝟓 𝐭𝐢𝐦𝐞𝐬 𝐛𝐫𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭𝐞𝐫 3. α, β and γ radiation travel between two parallel charged plates. If the positive plate is at the top of the page and the negative plate is at the bottom and the radiation enters from the left, sketch the path of each type of radiation through the electric field. 4. A vibrating string is fixed at two points. a) Sketch the first (fundamental), second and third harmonics of vibrating string and label the nodes and antinodes. b) If the distance between the two fixed points is 90cm, calculate the wavelength of the first, second and third harmonics. Express your answers in the standard units for distance 𝝀𝟏 = 𝟏. 𝟖𝒎 𝝀𝟐 = 𝟎. 𝟗𝒎 𝝀𝟑 = 𝟎. 𝟔𝒎 c) What must be changed to produce different harmonics? The tension of the string or the distance between the two fixed points. d) The tension is adjusted to produce a standing wave with a pitch of Middle D (first harmonic = 294 Hz) in the above string. Calculate the speed of the standing wave in the string. 𝒗 = 𝒇𝝀 = 𝟐𝟗𝟒𝑯𝒛 × 𝟏. 𝟖𝒎 = 𝟓𝟐𝟗. 𝟐 𝒎 ⋅ 𝒔−𝟏 e) Without further adjusting the tension, a standing wave of pitch Middle A (first harmonic = 440 Hz) is produced in the above string by pressing down hard on the string to shorten its length. How far from the fixed end should the person place his finger to produce Middle A? 𝒗 = 𝒇𝝀 𝝀 𝟐 𝒗 𝟓𝟐𝟗.𝟐 𝒎⋅𝒔−𝟏 𝒇 𝟒𝟒𝟎𝑯𝒛 𝝀= = = 𝟏. 𝟐𝟎𝒎 𝑭𝒐𝒓 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒇𝒊𝒓𝒔𝒕 𝒉𝒂𝒓𝒎𝒐𝒏𝒊𝒄, 𝝀 = 𝟐𝑳 𝑳= = 𝟎. 𝟔𝟎𝒎 Therefore, the person should place his finger 0.30m from the fixed end. 5. A transverse wave has an amplitude of 5cm and a wavelength of 3cm. a) Sketch a labelled displacement-distance graph of the wave. Include the labels for crest, trough, amplitude and wavelength. b) If the wave is a light wave travelling through a vacuum, calculate its frequency. 𝒗 = 𝒇𝝀 𝒗 𝟑.𝟎𝟎×𝟏𝟎𝟖 𝒎⋅𝒔−𝟏 𝝀 𝟎.𝟎𝟑𝒎 𝒇= = = 𝟏 × 𝟏𝟎𝟏𝟎 𝑯𝒛 c) In which part of the electromagnetic spectrum would the wave be? microwave 𝟏 𝟏 𝒇 𝟏×𝟏𝟎𝟏𝟎 𝑯𝒛 d) Calculate the period of the wave. 𝑻 = = = 𝟏 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟏𝟎 𝒔 e) How many cycles of the wave would pass by a fixed point is 12 seconds? The period is the time for one complete cycle. 𝒕 𝟏𝟐𝒔 𝒏𝒖𝒎𝒃𝒆𝒓 𝒐𝒇 𝒄𝒚𝒄𝒍𝒆𝒔 𝒊𝒏 𝒂 𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒊𝒐𝒅 𝒐𝒇 𝒕𝒊𝒎𝒆 = = = 𝟏. 𝟐 × 𝟏𝟎𝟏𝟏 𝒄𝒚𝒄𝒍𝒆𝒔 −𝟏𝟎 𝑻 𝟏 × 𝟏𝟎 𝒔 6. What does CRO stand for? Cathode Ray Oscilloscope 7. Which property of waves is responsible for producing echoes? Reflection 8. Describe the relationship between particle motion and the direction of energy propagation in transverse and longitudinal waves. perpendicular for transverse and parallel for longitudinal 9. How can experiments be made more valid? Take steps to control errors 10. How can experiments be made more reliable? Repeat measurements 11. What type of interference occurs in each of the following situations? a) At the nodes of standing waves destructive interference b) At the antinodes of standing waves constructive interference c) In headphones utilising active noise cancelation technology destructive interference d) Two waves in phase travelling from opposite directions meet constructive interference e) At the dark bands produced by the superposition of two light sources destructive interference 12. Sketch and label a longitudinal wave.