TrigonometryFinalExamGuide
advertisement

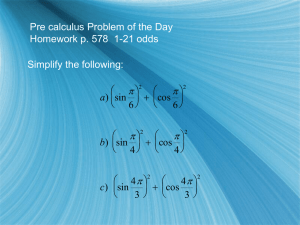
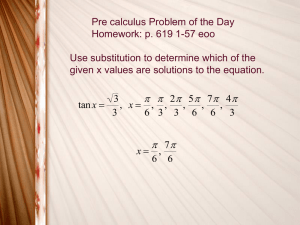
Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide General Study Tips: •rework all tests and take-home quizzes, example problems from class, and tests in online test archive •memorize formulas and names of formulas, and the cases to which you apply them Topics to Know: Algebra •manipulate fractions, including complex fractions •rationalize denominators •factor •apply the square root theorem, zero product property, and quadratic formula Basic Trig Topics (Ch. 5): • evaluate without a calculator all six trig functions of any angle in radians or degrees having a 0, 30, 45, 60, or 90 reference angle •evaluate without a calculator all six trig functions of any angle, given one of the six trig function values and the quadrant •apply concepts of cofunction and like reference angles to evaluate trig functions given angles that are complements or have the same reference angle but are in different quadrants •convert between radians and degrees •angles of elevation and depression •linear speed, angular speed, and arc length Graphing: •graph all 6 basic trig functions • find amplitude and period •rewrite all equations by factoring to find horizontal shift (-c/b) •apply horizontal and vertical shifts •graph sum and difference of basic trig and linear functions Identities (Ch. 6): •evaluate trig functions of a given angle using sum, difference, half, and double angle identities •simplify expressions using identities •evaluate double, half, sum, and difference identities of an angle, given trig functions of one or more original angles and the quadrant(s) •evaluate inverse trig functions and compositions of inverse functions •solve trig equations for both all real values of the variable and for all values of the variable in a given interval •prove trigonometric identities Solving Triangles (Ch. 7) •identify type of triangle (SSS,SAS,SSA,ASA,AAS) •solve any triangle given at least one side and two other measures •solve word problems involving the Law of Sines and Law of Cosines •find the area of any triangle Vectors (Ch. 7) •perform arithmetic operations with vectors (scalar multiplication and vector addition/subtraction) •find the magnitude and direction angle of any vector •write vectors in component form and in terms of 𝑖⃗ and 𝑗⃗ •find a unit vector in the direction of any vector •find the dot product of two given vectors •find the angle between two vectors •solve word problems involving a mass on an incline •solve word problems involving heading of boats and airplanes Trigonometric Form of Complex Numbers (Ch. 7) •convert between standard form and trigonometric form •determine the modulus and argument of a given complex number •multiply and divide complex numbers in trigonometric form Trig Functions of an Acute Angle 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝜃 sin 𝜃 = cos 𝜃 = tan 𝜃 = ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝜃 ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝜃 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝜃 csc 𝜃 = sec 𝜃 = cot 𝜃 = ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝜃 ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝜃 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝜃 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝜃 Converting Between Degree & Radian Measure To convert from degree to radian measure, multiply by To convert from radian to degree measure, multiply by 𝜋 180° 180° 𝜋 Arc Length and Angular Speed Variables 𝑠 = 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑑 or 𝑎𝑟𝑐 𝑙𝑒𝑛𝑔𝑡ℎ (𝑖𝑛𝑐ℎ𝑒𝑠, 𝑘𝑖𝑙𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠, 𝑒𝑡𝑐) 𝑡 = 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 (𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑠, 𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑢𝑡𝑒𝑠, ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑟𝑠, 𝑑𝑎𝑦𝑠, 𝑒𝑡𝑐) 𝜃 = 𝑎𝑚𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑟𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 or 𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑙𝑢𝑑𝑒𝑑 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 (𝑑𝑒𝑔𝑟𝑒𝑒𝑠, 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠, 𝑟𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠, 𝑟𝑒𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠, 𝑒𝑡𝑐) 𝑟 = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠 𝑜𝑟 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑟𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 (𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠, 𝑖𝑛𝑐ℎ𝑒𝑠, 𝑒𝑡𝑐) 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 v = linear speed = 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑎𝑚𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑟𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝜔 = 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑟 𝑠𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑 = 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 Formulas 𝑠 θ 𝑠 = 𝑟𝜃 , 𝑣= , ω= , 𝑣 = 𝑟ω 𝑡 t Dimensional analysis conversion factors 5280 𝑓𝑡 12 𝑖𝑛 2𝜋 𝜋 60 𝑚𝑖𝑛 60 𝑠𝑒𝑐 , , , , , , 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑖𝑟 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑠 1 𝑚𝑖 1 𝑓𝑡 1 𝑟𝑒𝑣 180° 1 ℎ𝑟 1 𝑚𝑖𝑛 Example problem: A car travels at 60 miles per hour. Its wheels have a 24-inch diameter. What is the angular speed of a point on the rim of a wheel in revolutions per minute? Solution: 𝑣 = 60 𝑚𝑖 1 ℎ𝑟 , = 12 𝑖𝑛 , 𝜔 = ? Equation relating these variables: 𝑣 = 𝑟𝜔 𝑣 1 60 𝑚𝑖 1 1 ℎ𝑟 5280 𝑓𝑡 12 𝑖𝑛 1 𝑟𝑒𝑣 2640 𝑟𝑒𝑣 𝜔= =𝑣∙ = ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ = 𝑟 𝑟 1 ℎ𝑟 12 𝑖𝑛 60 𝑚𝑖𝑛 1 𝑚𝑖 1 𝑓𝑡 2𝜋 𝜋 𝑚𝑖𝑛 Reciprocal Identities 1 csc 𝑥 = sin 𝑥 1 sin 𝑥 = sec 𝑥 = cos 𝑥 = cot 𝑥 = csc 𝑥 1 cos 𝑥 1 sec 𝑥 1 tan 𝑥 1 tan 𝑥 = cot 𝑥 Ratio Identities tan x = cot 𝑥 = sinx cos x cos 𝑥 Odd-Even Identities cos(−𝑥) = cos 𝑥 , sin(−𝑥) = − sin 𝑥 , tan(−𝑥) = − tan 𝑥 sec(−𝑥) = sec 𝑥 , csc(−𝑥) = − csc 𝑥 , cot(−𝑥) = − cot 𝑥 Sum and Difference Identities sin(𝑎 + 𝑏) = sin 𝑎 cos 𝑏 + cos 𝑎 sin 𝑏 sin(𝑎 − 𝑏) = sin 𝑎 cos 𝑏 − cos 𝑎 sin 𝑏 cos(𝑎 + 𝑏) = cos 𝑎 cos 𝑏 − sin 𝑎 sin 𝑏 cos(𝑎 − 𝑏) = cos 𝑎 cos 𝑏 + sin 𝑎 sin 𝑏 tan(𝑎 + 𝑏) = sin 𝑥 Pythagorean Identities sin2 𝑥 + cos2 𝑥 = 1 , 1 + cot 2 𝑥 = csc 2 𝑥 , tan2 𝑥 + 1 = sec 2 𝑥 tan(𝑎 − 𝑏) = tan 𝑎+tan 𝑏 1−tan 𝑎 tan 𝑏 tan 𝑎−tan 𝑏 1+tan 𝑎 tan 𝑏 Cofunction Identities 𝜋 sin ( − 𝑥) = cos 𝑥 2 𝜋 Half-Angle Identities , cos ( − 𝑥) = sin 𝑥 2 𝜋 tan ( − 𝑥) = cot 𝑥 2 𝜋 , 2 csc ( − 𝑥) = sec 𝑥 2 𝜋 , sec ( − 𝑥) = csc 𝑥 2 Double-Angle Identities sin 2𝑥 = 2 sin 𝑥 cos 𝑥 cos 2𝑥 = cos2 𝑥 − sin2 𝑥 cos 2𝑥 = 2 cos2 𝑥 − 1 cos 2𝑥 = 1 − 2 sin2 𝑥 tan 2𝑥 = 2 tan 𝑥 1−tan2 𝑥 1−cos 𝑥 2 2 𝑥 1+cos 𝑥 cos = ±√ 2 2 𝑥 1−cos 𝑥 2 𝑥 1+cos 𝑥 sin 𝑥 tan = ±√ cot ( − 𝑥) = tan 𝑥 𝜋 𝑥 sin = ±√ tan = 2 𝑥 1+cos 𝑥 1−cos 𝑥 2 sin 𝑥 tan = Solving Triangles Law of Sines sin 𝐴 𝑎 = sin 𝐵 𝑏 = sin 𝐶 𝑐 or 𝑎 sin 𝐴 = 𝑏 sin 𝐵 = 𝑐 sin 𝐶 Law of Cosines 𝑐 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 − 2𝑎𝑏 cos 𝐶 𝑏 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑐 2 − 2𝑎𝑐 cos 𝐵 𝑎2 = 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 − 2𝑏𝑐 cos 𝐴 Area of a Triangle 1 1 1 𝐾 = 𝑏𝑐 sin 𝐴 = 𝑎𝑐 sin 𝐵 = 𝑎𝑏 sin 𝐶 2 2 2 Vectors ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ with 𝐴 = (𝑥1 , 𝑦1 ) and 𝐶 = (𝑥2 , 𝑦2 ) is 𝐴𝐶 ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ = ⟨𝑥2 − 𝑥1 , 𝑦2 − 𝑦1 ⟩ The component form of 𝐴𝐶 ⃗⃗| = √𝒂𝟐 + 𝒃𝟐 The magnitude of a vector 𝑣⃗ with component form ⟨𝑎, 𝑏⟩ is |𝒗 𝑏 The reference angle 𝛼 for the direction angle 𝜃 of the vector ⟨𝑎, 𝑏⟩ is given by 𝛼 = |tan−1 |. Figure out 𝑎 which quadrant this angle should be in and measure the angle counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. The horizontal component of the vector ⟨𝑎, 𝑏⟩ is 𝑎 = |𝑣⃗| cos 𝜃 The vertical component of the vector ⟨𝑎, 𝑏⟩ is 𝑏 = |𝑣⃗| sin 𝜃 For a real number 𝑘 and a vector 𝑣⃗ = ⟨𝑣1 , 𝑣2 ⟩, the scalar product of 𝑘 and 𝑣⃗ is 𝑘𝑣⃗ = 𝑘⟨𝑣1 , 𝑣2 ⟩ = ⟨𝑘𝑣1 , 𝑘𝑣2 ⟩. The vector 𝑘𝑣⃗ is a scalar multiple of the vector 𝑣⃗. ⃗⃗ ± 𝒗 ⃗⃗ = ⟨𝒖𝟏 ± 𝒗𝟏 , 𝒖𝟐 ± 𝒗𝟐 ⟩ . Vector Addition/Subtraction: If 𝑢 ⃗⃗ = ⟨𝑢1 , 𝑢2 ⟩ and 𝑣⃗ = ⟨𝑣1 , 𝑣2 ⟩, then 𝒖 ⃗⃗ 𝒗 If 𝑣⃗ is a vector and 𝑣⃗ ≠ ⃗0⃗, then |𝒗⃗⃗| is a unit vector (vector with magnitude 1) in the direction of 𝑣⃗. ⃗⃗ ∙ 𝒗 ⃗⃗ = 𝒖𝟏 𝒗𝟏 + 𝒖𝟐 𝒗𝟐 . The dot product of two vectors 𝑢 ⃗⃗ = ⟨𝑢1 , 𝑢2 ⟩ and 𝑣⃗ = ⟨𝑣1 , 𝑣2 ⟩ is 𝒖 ⃗⃗⃗∙𝒗 ⃗⃗ 𝒖 If 𝜃 is the angle between two nonzero vectors 𝑢 ⃗⃗ and 𝑣⃗, then 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝜽 = |𝒖⃗⃗⃗||𝒗⃗⃗| . Trigonometric Form of Complex Numbers A complex number 𝑧 = 𝑎 + 𝑏𝑖, where 𝑖 = √−1 can be written in trigonometric form as 𝑧 = 𝑟(cos 𝜃 + 𝑖 sin 𝜃) or 𝑧 = 𝑟 cis 𝜃, where 𝑟 = √𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 is the modulus of 𝑧 and direction angle 𝜃 is referred to as the argument. 𝑧1 𝑧2 = 𝑟1 𝑟2 [cos(𝜃1 + 𝜃2 ) + 𝑖 sin(𝜃1 + 𝜃2 )] = 𝑟1 𝑟2 cis 𝜃 𝑧1 𝑟1 𝑟1 = [cos(𝜃1 − 𝜃2 ) + 𝑖 sin(𝜃1 − 𝜃2 )] = cis 𝜃 𝑧2 𝑟2 𝑟2 𝑧 𝑛 = 𝑟 𝑛 [cos(𝑛𝜃) + 𝑖 sin(𝑛𝜃)] = 𝑟 𝑛 cis(𝑛𝜃)