Era Readings
advertisement

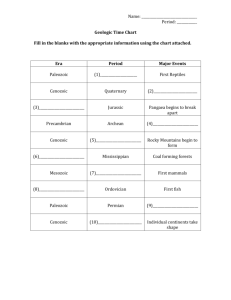
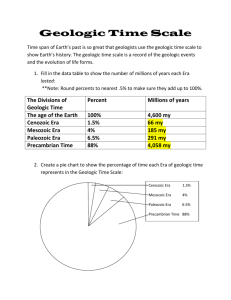
Precambrian Era Means: “Earliest Eon” Description: 85% of earth’s age has happened in this period! The oldest rocks of the continents formed during this time. During this time, the majority of life on earth was in the form of algae and small marine life. The multi-celled organisms of this time fell into three categories; 1) sponges, 2) cnidarians (jellyfish and coral) and 3) annelids (flatworms) Precambrian in Utah: Precambrian rock can be found on Antelope Island in the Great Salt Lake. Pictures: A Precambrian flatworm fossil Precambrian Jellyfish (replica) Precambrian Sponge (these sponges can still be found alive today!) Precambrian flatworm fossil Paleozoic Era Means: “Ancient Life” Description: This era produced the beginnings of the fossil fuels we know as coal, oil and natural gas. These fuels were formed from the remains of decaying animals and plants; plants and animals that were alive during the Paleozoic Era! Much of the earth was still covered by ocean and areas that are not under water today (such as Utah) were under oceans back then. That means that we find marine (ocean) fossils in places where there is no longer an ocean. Some of Utah’s oldest fossil remains are trilobites and ammonites, which are sea animal. Paleozoic in Utah: In Utah, we have many deposits of the fossil fuels that began in the Paleozoic Era. They are located in Carbon County, the Uinta Basin and other places. Pictures: Trilobite fossil Opabinia sea animal (notice the five eyes and “arm/mouth”!) Ammonite fossil Mesozoic Era Means: “Middle Life” Description: This era is associated with dinosaurs and early mammals! The Rocky Mountains, and other mountain ranges, began to take shape during this era. Big earthquakes and volcanoes began to change the geography of the earth. The climate of earth was much warmer, sea levels were higher and life began to dominate the earth rather than the sea. We begin to see flowering plants, insects, early birds and of course…dinosaurs! Mesozoic in Utah: Many dinosaurs roamed all over North America, but a lot of their bones have been found in Utah! Large deposits of dinosaur bones have been found near the cities of Jensen, Vernal and Price. Pictures: Utahraptor Cycad plant (still around today!) Crusafontia (a predecessor to the squirrel) Brontosaurus Cenozoic Era Means: “Recent Life” Description: The earth’s surface began to look like how it does today during this era. Giant mammals, like wholly mammoths and saber tooth tigers, began to replace the dinosaurs. It became colder too. Ice caps and glaciers covered many mountains and surfaces. When they melted, they caused the sea and lake levels to rise, which flooded a lot of land and changed coast lines. Humans showed up at the end of this era. Cenozoic in Utah: Utah was not covered with ice, but many glaciers formed in the top of our mountains. When the ice melted, it filled in low lands such as the area that became the Great Basin Region. Utah’s ancient Lake Bonneville was a remnant of an ice age. Pictures: Wholly Mammoth Brontotherium (relative to the rhino) Saber Toothed tiger