Emergency Information - Kirkwood Community College
advertisement

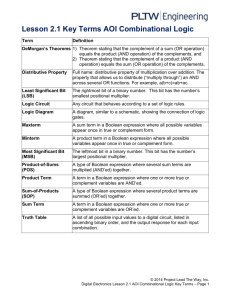
Digital Circuits ELT-309-CRF01 Summer 2014 Instructor: Jim Trepka Other Instructor Information: Office: 140 Jones Hall Telephone: 398-7146 Email: jim.trepka@kirkwood.edu Home Page: http://faculty.kirkwood.edu/jtrepka/ Section Number: 0219731 Monday 8:00-10:00 Tuesday 8:00-10:00 Wednesday 8:00-10:00 Thursday 8:00-10:00 Friday 8:00-10:00 Credit hours: 3 Course description: Presents the analysis and design of digital circuits. Boolean algebra is introduced as a tool in working with basic gates, flip-flops, counters, shift registers, adders, timers and busses. Laboratory and computersimulation exercises provide enhanced understanding. Prerequisites: ELT-517 Course Materials Needed: 1. Digital Fundamentals 10th Edition, Thomas L. Floyd, ISBN: 0-13235923-5 (Prentice Hall). 2. 35 in 1 Deluxe Digital Lab Exploration Kit, Chaney Electronics, Inc. 3. RF Clicker Books and course materials for this course are available at the Kirkwood Bookstore. Learning Outcomes and Course Competencies: 1. Construct digital circuits from schematics. 2. Display professional conduct including teamwork, punctuality, and proper language. 3. Troubleshoot digital circuits using a logic probe. 4. Define switch debouncing and build a circuit to debounce a switch. Chapter 1 Competencies Explain the basic difference between digital and analog quantities Show how voltage levels are used to represent digital quantities Describe various parameters of pulse waveform such as rise time, fall time, pulse width, frequency, period, and duty cycle Identify fixed-function digital integrated circuits according to their complexity and the type of circuit packaging Identify pin numbers on integrated circuit packages Chapter 2 Competencies Review the decimal number system Count in the binary number system Convert from decimal to binary and binary to decimal Apply arithmetic operations to binary numbers Determine the 1’s and 2’s complements of a binary number Express signed binary numbers in sign-magnitude, 1’s complement, 2’s complement, and floating- point format Carry out arithmetic operations with signed binary numbers Convert between the binary and hexadecimal number systems Add numbers in hexadecimal form Convert between the binary and octal number system Express decimal numbers in binary coded decimal (BCD) form Add BCD numbers Convert between the binary system and the Gray code Interpret the American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) Chapter 3 Competencies Describe the operation of the inverter, the AND gate, and the OR gate Describe the operation of the NAND gate and the NOR gate Express the operation of NOT, AND, OR, NAND, and NOR gates with Boolean algebra Describe the operation of the exclusive- OR and exclusive NOR gates Recognize and use both the distinctive shape logic gate symbols and the rectangular outline logic gate symbols of ANSI/IEEE Standard 91-1984 Construct timing diagrams showing the proper time relationships of inputs and outputs for the various logic gates Discuss the basic concepts of programmable logic Make basic comparisons between the major IC technologiesCMOS and TTL Explain how the different series within the CMOS and TTL families differ from each other Define propagation, delay time, power dissipation, speed-power, product, and fan-out in relation to logic gates List specific fixed-function integrated circuit devices that contain the various logic gates Used each logic gate in simple applications Troubleshoot logic gates for opens and shorts by using the oscilloscope Chapter 4 Competencies Apply the basic laws and rules of Boolean algebra Apply DeMorgan’s theorems to Boolean expressions Describe gate networks with Boolean expressions Evaluate Boolean expressions Simplify expressions by using the laws and rules of Boolean algebra Convert any Boolean expression into sum-of-products (SOP) form Convert any Boolean expression into a product of-sums (POS) form Use a Karnaugh map to simplify Boolean expressions Use a Karnaugh map to simplify truth table functions Utilize “don’t care” conditions to simplify logic functions Write VHDL program for simple logic Apply Boolean algebra, the Karnaugh map method, and VHDL to a system application Chapter 5 Competencies Analyze basic combinational logic circuits, such as AND-OR, ANDOR-Invert, exclusive-OR, and exclusive-NOR Use AND-OR and AND-OR-Invert circuits to implement sum-ofproducts (SOP) and product-of-sums (POS) expressions Write the Boolean output expression for any combinational logic circuit Develop a truth table from the output expression for a combinational logic circuit Used the Karnaugh map to expand an output expression containing terms with missing variables into full SOP form Design a combinational logic circuit for a given Boolean output expression Simplify a combinational logic circuit to its minimum form Use NAND gate to implement any combinational logic function Use NOR gates to implement any combinational logic function Write VHDL programs for simple logic circuits Troubleshoot faulty logic circuits Troubleshoot logic circuits by using signal tracing and waveform analysis Apply combinational logic to a system application Chapter 6 Competencies Distinguish between half-address and full-address Use full-address to implement multibit parallel binary address Explain the differences between ripple carry and look-ahead carry parallel adders Use the magnitude comparator to determine the relationship between two binary numbers and use cascaded comparators to handle the comparison or larger numbers Implement a basic binary decoder Use BCD-to-7-segment decoders in display systems Apply a decimal-to-BCD priority encoders in a simple keyboard application Convert from binary to Gray code, and Gray code to binary by using logic devices Apply multiplexers in data selection, multiplexed displays, logic function generation, and simple communications systems Use decoders as demultiplexers Explain the meaning of parity Use parity generators and checkers to detect bit errors in digital systems Implement a simple data communications system Identify glitches, common bugs in digital systems Chapter 7 Competencies Use logic gates to construct basic latches Explain the difference between S-R latch and a D latch Recognize the difference between a latch and a flip-flop Explain how S-R, D, and J-K flip-flops differ Understand the significance of propagation delays, set-up time, hold time, maximum operating frequency, minimum clock pulse widths, and power dissipation in the application of flip-flops Apply flip-flops in basic application Explain how retriggerable and nonretriggerable one-shots differ Connect a 555 timer to operate as either an astable multivibrator or a one-shot Troubleshoot basic flip-flop circuits Assessment of Student Learning: Student learning will be assessed via exams, homework, and class room participation. Late Work/Make-up Test Policy: Missed exams must be made up on or before the next class period. In a rare situation where the exam can not be made up in that time period, the student will be given an exam different than that taken by the rest of the class. Class Attendance Policy and College Sponsored Activities: As stated in the Student handbook: In compliance with Public Law 105244, Kirkwood Community College makes a wide variety of general institutional information available to students. For additional information, go to http://www.kirkwood.edu/pdf/uploaded/630/student_handbook.pdf Productive Classroom See student handbook Learning http://www.kirkwood.edu/pdf/uploaded/630/student_handbook.pdf Environment: Plagiarism Policy: See student handbook http://www.kirkwood.edu/pdf/uploaded/630/student_handbook.pdf Campus Closings: See student handbook http://www.kirkwood.edu/pdf/uploaded/630/student_handbook.pdf Learning Environment The classroom and laboratory conditions will be conducive to teaching and student learning. To promote and maintain that environment, all Expectations: pagers, cellular phones, and other autonomous means of communication shall be deactivated during instructional periods. RINGING OF CELL PHONES DURING CLASS WILL RESULT IN POINTS DEDUCTED FROM YOUR CLASS ROOM PARTICPATION AND PROFESSIONAL CONDUCT GRADE. Participants are expected to come to class prepared to actively participate in class. Americans with Disabilities Act: Students with disabilities who need accommodations to achieve course Competencies should file an accommodation application with Learning Services, Cedar Hall 2063 and provide a written plan of accommodation to your instructor prior to the accommodation being provided. Student Evaluation: Exams - 3 exams will be given during the session – 40% of final grade. These exams will be comprehensive. Exam 1 will be worth 10%, Exam 2 will be work 10%, and Exam 3 will be worth 20% of final grade. Build Exam – A circuit build exam will be worth 5% of your final grade. Homework Homework will be assigned according to the schedule on my course web page. Homework will be worth 20% of your final grade. Labs - Labs from the 35 in 1 Deluxe Digital Lab Exploration Kit and any other lab activities will be worth 25% of your final grade. Class Room Participation and Professional Conduct - 10% of your final grade Points will be added to classroom participation and professional conduct grade based on the following: 1. Arrival at class by 8 am which will be measured by clicker’s questions 2. Participation in debugging exercises and Multisim exercises Points will be deducted from the classroom participation and professional conduct grade for the following: 1. Inappropriate language or jokes. 2. Ringing of cell phones in class. 3. Disrupting the class. 4. Leaving class early or not arriving back to class by 9:00, after the 8:50 break. How final grades are determined: As described above. Grading Scale: B+ A 94 - 100 B 87 – 89.99 C+ 83 – 86.99 C 77 – 79.99 D+ 73 – 76.99 D 67 – 69.99 63 – 66.99 F 59.99 and less A- 90 – 93.99 B- 80 – 82.99 C- 70 – 72.99 D- 60 – 62.99 Drop Date: Students dropping a class during the first two weeks of a term may receive a full or partial tuition refund for 16 week terms, for shorter courses check with Enrollment Services for total withdraw information. Details of the refund schedule are available from Enrollment Services in 216 Kirkwood Hall. For detailed discussion of drop dates and policies, please read the student handbook. Final Exam Information: The final exam for this class is scheduled on Thursday June 26, 2014 at 8 am for those with perfect attendance. Emergency Information: See student handbook http://www.kirkwood.edu/pdf/uploaded/630/student_handbook.pdf Other Information: none