Vaccination - Garden International School

Vaccination Information
The following is some information to help you keep a track of what vaccinations your children should have and when to have them. As each country’s immunisation schedule is slightly different, please do follow your own country’s advice. The first 3 vaccinations are highly recommended additional vaccinations due to our locale.
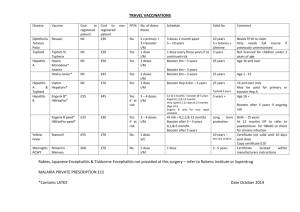
Immunisation
Hepatitis B*
Hepatitis A*
Typhoid*
Infant
(Birth – 2 years)
Three doses
Two doses (after age 1)
School Entry
(4-6 years old)
Adolescent
(11-12 years old)
Oral or Injection
Triple Antigen
Diphtheria,
Pertussis(whooping cough), Tetanus
Poliomyelitis
Haemophilus influenzae type b
Measles, Mumps,
Rubella (MMR)
Four doses
Three doses
Three doses
First booster Second booster
First booster Second booster
Booster
1st dose (12-15mths) Booster
Varicella (chicken pox) One dose (after age 1) Second dose
Meningococcal One dose (and booster 13-
Human Papilloma
Virus
18 yrs old)
Three doses (girls)
*Hep B In Malaysia 3 doses are given commencing at birth. Given the higher risk of exposure to the virus in Malaysia it is highly recommended for all visitors to have this vaccination. The course can be completed over a period of 6 months.
*Hep A Given the risk of exposure to the virus in Malaysia it is highly recommended to have this vaccination. Two doses are given at least 6 months apart AND after age 1 year.
*Typhoid Given the risk of exposure to the bacterium in Malaysia it is highly recommended to have this vaccination. There are 2 methods of vaccinating for Typhoid.
ORAL -4 capsules on alternate days INJECTABLE -single injection
-minimum age is 6 years
-booster required every 5 years
-minimum age is 2 years
-booster required every 2 years
Varicella –chicken pox. Two doses are required unless immunity obtained by having the illness.
Rotavirus vaccine This is recommended for babies in the first year. Older children and adults need not have this vaccination.
Pneumococcal vaccine This is recommended for children under the age of 5 years. Older children and adults need not have this vaccination unless they have immunocompromising conditions.
Meningococcal There is variation on recommendations. In most of Europe and Australia young children routinely receive this vaccine. In the USA it is recommended to have 2 doses – the first dose at 11 or 12 years of age, with a booster dose at age 16. If the first dose (or series) is given after the
16th birthday, a booster is not needed.
As most of GIS students go on to university after school, and therefore are very likely to be living in shared accommodation, the risk of contracting meningitis is increased. As such, it is recommended to have a dose before finishing school/moving to college.
Human Papilloma Virus Currently given to girls only but research and discussion is underway on including boys in the programme. Three doses are given, the second dose 1 to 2 months after the first dose and the third dose 6 months after the first dose. The course is given at age 13 years.
Japanese Encephalitis (JE) This is not a recommended vaccination in Malaysia or the western world.
In Asia there have been, and continue to be, outbreaks of JE. The recommendation is for vaccination of those travelling to rural areas for periods of more than a month.
JE is transmitted to a human through the bite of mosquitoes infected with the Japanese encephalitis virus. Mosquitoes become infected by feeding on domestic pigs and wild birds infected with the
Japanese encephalitis virus. Human-to-human transmission does NOT occur.
In Japan, vaccination against JE is part of the routine vaccinations and in our professional opinion
Japanese students who are likely to be returning home either to visit or stay permanently should follow the routine schedule for JE in Japan. The routine is for the 1 st dose of JE vaccine at 3 years of age followed by a booster at 9 years of age.
The following has been quoted from the Infectious Disease Surveillance Center which was last updated on April 1, 2011. http://idsc.nih.go.jp/vaccine/dschedule/Imm11EN.pdf
A new Japanese Encephalitis vaccine, made with dry cell culture, was approved in accordance with the provisions of the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law on February 23 rd , 2009. It was allowed to be used in the routine immunization on June 2, 2009. Active recommendation for its use had been suspended since May 30, 2005. However, the active recommendation policy was reactivated in 2010 for the first inoculation dose at three years of age.
From August 27, 2010, the use in stage 2 routine immunization has become possible. Also, those who missed the stage 1 vaccination are now able to receive the remaining doses as part of routine immunization in the age range for this stage, 9-13 years old.
Tuberculosis (TB) Vaccination and disease management of tuberculosis is very complex. As such, we can only give very brief information here. If you require further information, please refer to your
Health Care Provider.
In Malaysia the BCG vaccination is given at birth before any exposure to the tuberculin bacteria.
However, in the USA and other Western Countries it is not routinely given.
In countries where tuberculosis is more common, infants are vaccinated with bacillus Calmette-
Guerin (BCG) vaccine because it can prevent severe tuberculosis in children. The BCG vaccine isn't recommended for general use in the United States because it isn't very effective in adults and it causes a false-positive result on a TB skin test. Researchers are working on developing a more effective TB vaccine. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/tuberculosis/ds00372/dsection=prevention
Tuberculosis is still quite prevalent in Malaysia. This is why spitting in public should be discouraged.
Cough etiquette should be practiced (coughing into shoulder or elbow crook). If anyone has a persistent cough lasting several months, they should see a doctor and be investigated for TB.
The prognosis if you contract TB is very good but it is essential, absolutely essential, that you complete the course of antibiotics which you need to take for several months.