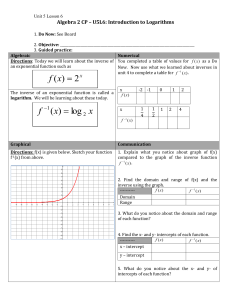
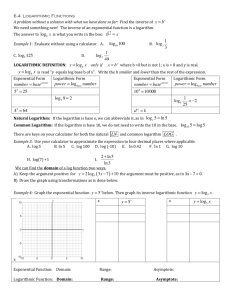
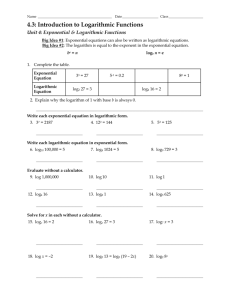
Logarithmic Functions: Lesson on Exponential Inverses
advertisement
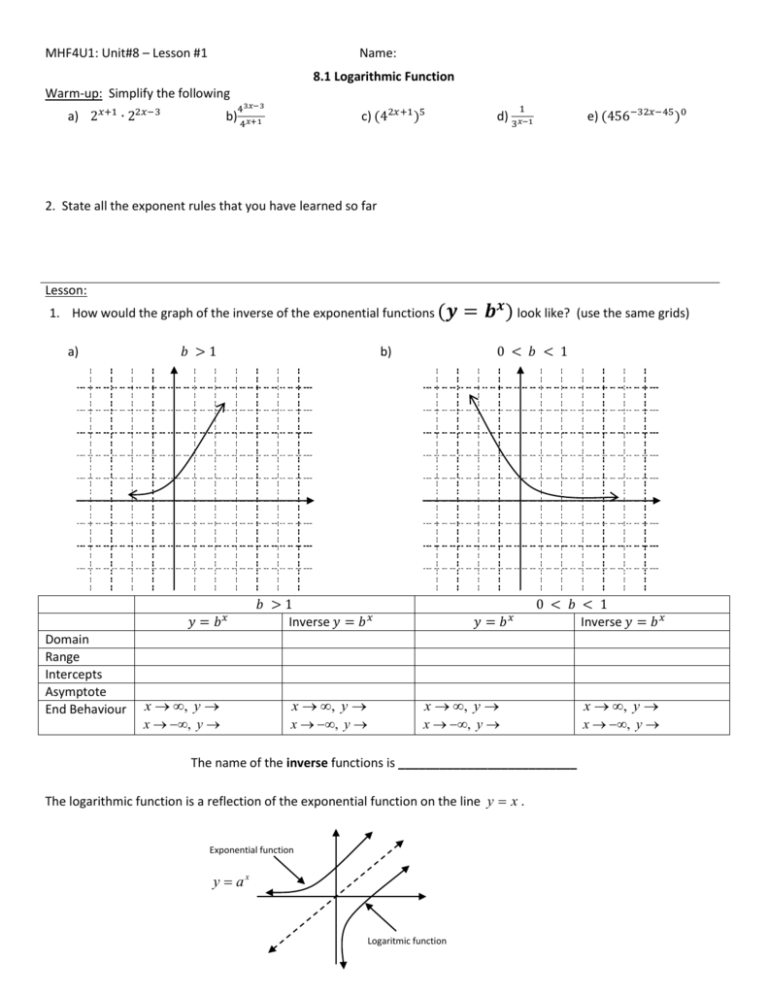
MHF4U1: Unit#8 – Lesson #1 Name: 8.1 Logarithmic Function Warm-up: Simplify the following a) 2𝑥+1 ∙ 22𝑥−3 b) 43𝑥−3 4 𝑥+1 c) (42𝑥+1 )5 d) 1 3𝑥−1 e) (456−32𝑥−45 )0 2. State all the exponent rules that you have learned so far Lesson: 1. How would the graph of the inverse of the exponential functions (𝒚 a) 𝑏 >1 𝑦 = 𝑏𝑥 Domain Range Intercepts Asymptote End Behaviour x , y x , y (use the same grids) 0 < 𝑏 < 1 b) 𝑏 >1 Inverse 𝑦 = 𝑏 𝑥 x , y x , y = 𝒃𝒙 ) look like? 𝑦 = 𝑏𝑥 0 < 𝑏 < 1 Inverse 𝑦 = 𝑏 𝑥 x , y x , y The name of the inverse functions is __________________________ The logarithmic function is a reflection of the exponential function on the line y x . Exponential function y ax Logaritmic function x , y x , y MHF4U1: Unit#8 – Lesson #1 Name: 2. To get the equation of the logarithmic function, you need to find the inverse function of y b x . Determine the inverse function of y 2 x . So Exponential form x2 and Logarithmic form y log 2 x y Definition The exponential function x b y can be written as the logarithmic function y log b x , where 𝑏 > 0 and b 1(same restrictions like the exponential function). The logarithm function x b y is the inverse of the exponential function y b . Hence, x x a y y log a x Example: y log2 8 since the exponent required on 2 (the base) to give 8 (the value of x) is 3. y 3 3. Write each exponential equation in Logarithmic form. 1 c) 2 3 b) 9 2 3 a) 5 3 125 1 8 4. Write each logarithmic equation in exponential form. a) log 4 64 3 b) log 6 1 1 6 c) log 3 1 0 5. Evaluate a) log 3 81 b) log 1 2 Homework: Pg. 451 #1ab, 2-3, 5-10 2 c) log5 5 d) log 3 1 e) log 6 0