WEATHERING WORKSHEET NAME Read chapter 3 pages 68
advertisement

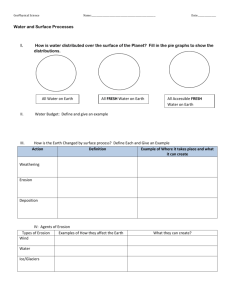
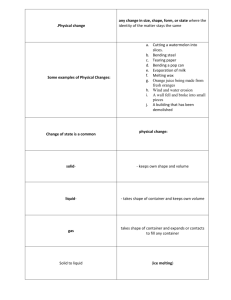
WEATHERING WORKSHEET Read chapter 3 pages 68-74 to answer the following: NAME _________________ DATE _______ HOUR ____ 1. Determine if the following are an example of physical (mechanical) weathering, chemical weathering or erosion. (use the abbreviations PW, CW and E to fill in the blanks) A. waves was ashore _________________ B. ice cracking driveway cement ____________ C. rusting __________________________ D. boulders splitting due to tree roots ________ E. limestone dissolving to make caves _________ F. an avalanche __________________________ G. pebbles bouncing along a stream bed __________ H. expansion of outer granite layer due to pressure release _______________ 2. How does mechanical weathering help with chemical weathering? 3. Describe an exfoliation dome. Give an example. 4. What type of acid is mainly in acid rain? Explain how it forms. 5. What does the K-feldspar in granite turn into when it weathers? This is an example of which type of weathering? 6. In your own words, describe how granite can turn into sandstone. 7. Heat speeds up a chemical reaction. Why then does chemical weathering proceed so slowly in a desert? 8. Read the section on “Climate” on page 74. Which type of weathering would be most dominate in a climate like Grosse Pointe? Explain why. 9. Use the term differential weathering to describe how the sculpted rock in Bryce National Park (photo on page 75) formed. Use your own words! 10. Explain why a marble tombstone weathers faster than a granite tombstone.