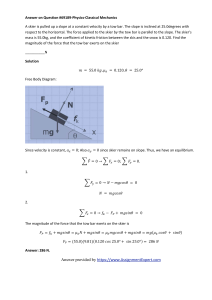
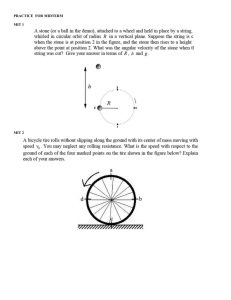
Forces & Motion test - The Eclecticon of Dr French
advertisement
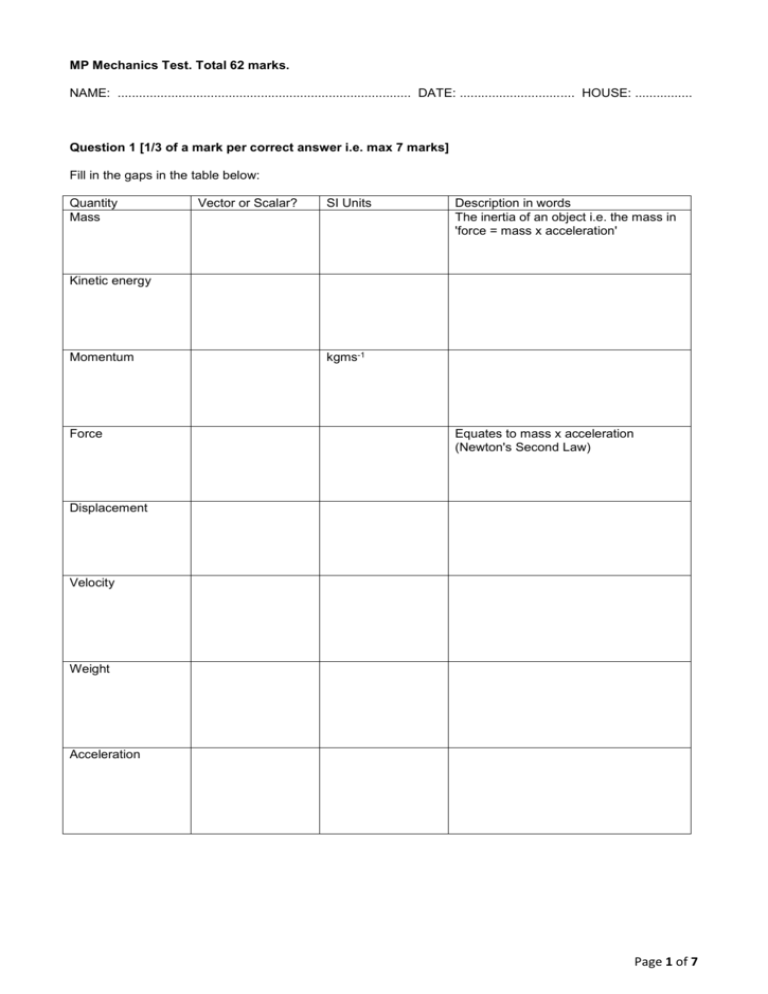
MP Mechanics Test. Total 62 marks. NAME: .................................................................................. DATE: ................................ HOUSE: ................ Question 1 [1/3 of a mark per correct answer i.e. max 7 marks] Fill in the gaps in the table below: Quantity Mass Vector or Scalar? SI Units Description in words The inertia of an object i.e. the mass in 'force = mass x acceleration' Kinetic energy Momentum Force kgms-1 Equates to mass x acceleration (Newton's Second Law) Displacement Velocity Weight Acceleration Page 1 of 7 Question 2 (19 marks) A skier of mass 80kg is being dragged by a tow rope. Initially the skier moves horizontally with an acceleration of a = 1ms-2. The forces acting on the skier are (i) gravity; (ii) normal contact with the slope; (iii) friction and (iv) the pull of the tow rope. (i) What is the normal contact force R (in Newtons) [1] R g 9.81ms-2 a (ii) What is the net horizontal force on the skier (use Newton's Second Law) [2] T F 0.05R (iii) Hence calculate the tension in the tow rope. [2] mg y x The skier now slides uphill at a constant velocity. The angle of the hill is 10o. (iv) What is the net force on the skier now? [1] (v) Using the diagram below, write down Newton's Second law, separately in the x and y directions [3] R T g 9.81ms-2 (vi) Hence work out the new normal contact force R and then the new tension in the tow rope T (which is still parallel to the slope). [3] F 0.05R 10o 10o mg y x Page 2 of 7 (v) The skier moves 100m up the slope. Calculate the work done by the tow rope. [2] (vi) The skier ascends the slope at a velocity of 2 ms -1. If only one skier is on the rope at a time, calculate the power at which the tow rope engine must work. [3] (v) State why a more powerful engine might be a good idea. [2] Page 3 of 7 Question 3 (14 marks) Dr French is playing the game of boule while on holiday in Brittany. He throws a metal ball at an angle of 30o to the horizontal at a speed of 8ms-1 The ball is launched from a height of 1m. y g 9.81ms-2 8ms-1 30o h a x R Calculate the following: (i) The initial upward velocity [1] (ii) The height gained when the upward velocity is zero. Hence work out h. [2] (iii) The time taken to reach the highest point (Hint use v u at , but think about what v, u and a are in this case) [2] (iv) The horizontal distance a travelled, which corresponds to the highest point on the trajectory. [2] Page 4 of 7 (v) Use energy or otherwise to work out the downward velocity at the point of impact [2] (vi) Work out the time taken for the boule to hit the floor from the maximum height. [2] (vii) Hence work out the range R of the boule. [3] Page 5 of 7 Question 4 (12 marks) England are playing Wales in a game of rugby. Ivor the giant Welsh prop (150kg) runs at 2 ms-1 towards Jim, the England winger, who is running at 8 ms-1 towards Ivor. Jim has a mass of 80kg. Ivor tackles Jim and they move together rather than bounce off each other. (i) What type of collision is this? What physical quantity is conserved, and what will be lost? [2] (ii) Draw BEFORE and AFTER diagrams to represent this situation. Use v to indicate the velocity of the Jim & Ivor mass after the collision. [3] (iii) Write down the total momentum BEFORE and AFTER the collision. [2] (iv) Work out the velocity of the combined mass of Ivor and Jim after the collision, and state which direction this is. [2] (v) Calculate the % of kinetic energy lost in the collision. [3] Page 6 of 7 Question 5 (3 marks) Boris makes a catapult using an elastic band of unstretched length 15cm. He uses it to launch a 10 gram strawberry 10m directly upwards from the point of release. Calculate the elastic modulus of the catapult, if the band doubles in length before being released. [ g = 9.81ms-2 ] Question 6 (3 marks) Sybil goes skydiving and deploys a parachute of area A = 95m2. It has a drag force acting upon it given by the equation F 12 cD Av2 where cD is the drag coefficient (which is 1.5), is the density of air (1.2kgm-3) and v is Sybil's downward velocity. If Sybil has a mass of 65kg, calculate her terminal velocity. [ g = 9.81ms-2 ] Question 7 (4 marks) Usain Bolt runs the bend of a 200m race in exactly 10s. He has unfortunately drawn lane one, which means his bend is exactly half a circle. (i) Calculate the radius of the bend which Usain runs. [2] (ii) Using the formula for centripetal acceleration a v2 , calculate the net radial force which must act r to cause Usain (mass 94kg) to run this bend. [2] Page 7 of 7