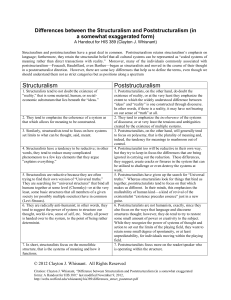
Structuralism vs. Post-Structuralism: Key Concepts
advertisement

Post-structuralism is a modern philosophical school of thought. It grew out of, and in response to, the philosophy of structuralism. Structuralism as a school of thought hit its stride during the radical movements of the 1950s and 1960s, particularly in France, although it had its roots back at the beginning of the 20th century. Structuralists look at the foundational structures implicit in all productions of a culture, and undertake an analysis of the many parts that create something, to get a better understanding of the creation. The basic premise of structuralism is that all things have a structure below the level of meaning, and that this structure constitutes the reality of that thing. Post-structuralists hold that in fact even in an examination of underlying structures, a slew of biases introduce themselves, based on the conditioning of the examiner. At the root of post-structuralism is the rejection of the idea that there is any truly essential form to a cultural product, as all cultural products are by their very nature formed, and therefore artificial. Structuralism Intellectual movement in France in the 1950s and 1960s. Structuralism posits that discrete cultural elements are not explanatory in and of themselves, but rather form part of a meaningful system and are best understood with respect to their location within the structure as a whole. Post-Structuralism Post-structuralism emerged in France during the 1960s as an antinomian movement critiquing structuralism. Post-structuralism is the rejection of the idea that there is any truly essential form to a cultural product, as all cultural products are by their very nature formed, and therefore artificial. Post-Structuralism was created as a counter thought movement to counter act the growing structuralism movement. There is no specific definition to give Post-Structuralism but to easiest way to describe it is that it is the rejection of the idea that there is any truly essential form to a cultural product, as all cultural products are by their very nature formed, and therefore artificial.