View
advertisement

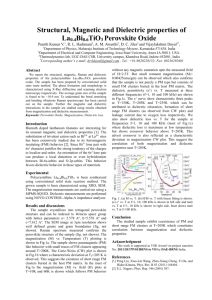
Dielectric, Ferroelectric and Magnetic Studies of Sm/Ni Modified Bi4Ti3O12 Ceramics Sumit Bhardwaj1, Joginder Paul1*, Kuldeep Kumar Sharma2, Ravi Kumar1, 3 1 Centre for Material Science and Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Hamirpur (H.P.)-177005, India 2 Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology, Hamirpur (H.P.)-177005, India 3 Beant college of Engineering and Technology, Gurdaspur (PB.)-143521, India * Corresponding author’s e-mail: jp_phy@yahoo.in, Tel.: +91-9418179401; Fax: +91-1972-223834 Abstract: Lead free Bi4-xSmxTi3-xNixO12 (x=0.0, 0.03) ceramics have been synthesized by solid state route. X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern confirms the formation of single phase orthorhombic structure. Frequency dependent dielectric constant and loss tangent was found to decrease with substitution, due to reduction in interfacial polarization. The remanant polarization (2P r) value was found to increase with substitution. The M-H curve shows the presence of weak ferromagnetism in the system. These materials can be used for future multiferroic applications. Keywords: Ceramics, microstructure, dielectric constant, ferroelectricity, ferromagnetism. Introduction Materials with two or more ferroic orders such as ferroelectric, ferromagnetic or ferroelastic are known as multiferroic materials. These materials can be used in multiple state memories, data storage devices, sensors and transducers [1]. The mechanism for ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism are mutually exclusive to each other, hence existence of single phase multiferroic materials are very rare. Among the lead free materials bismuth titanate (BIT) is one of the ferroelectric materials with high Tc (675 ºC). Some reports are available in literature related to multiferroic nature of BIT [2]. In this paper, we have presented the dielectric, ferroelectric and magnetic studies of Sm/Ni substituted BIT ceramics. Results and Discussion Fig. 1(a) shows the X-ray diffraction pattern of the prepared samples. All the diffraction peaks are indexed to pure bismuth titanate having orthorhombic unit cell (JCPDS card No. 89-7500). Lattice parameters were calculated and it is found that orthorhombic distortion increases with substitution. Fig. 1(b) and (c) shows the FE-SEM images for x=0.0 and x=0.03 respectively. Plate like grain growth is observed for both the samples and grain size is found to increase with substitution. Fig. 2(a) shows the frequency dependent dielectric constant and loss tangent (shown in inset) and is found to decrease with substitution. This decrease is attributed to the increase in grain size as observed in FE-SEM images, which results in decrease in interfacial polarization. Fig. 2(b) shows the room temperature P-E loops for both the samples. The 2Pr and 2Ec values were found to increase with substitution. This can be due to the increased orthorhombic distortions and reduction in domain wall pinning. Fig. 2(c) demonstrates the M-H curve of both the samples. Pure BIT shows the diamagnetic nature of the material. Upon Ni2+ substitution, observation of S-type non-saturated curve shows the magnetic nature of the material with weak ferromagnetism. This can be ascribed to the existence of F-centre exchange mechanism in the system. Fig. 1 (a) XRD, SEM images (b) x=0.0(c) x=0.03. Fig. 2 (a) Dielectric constant and loss tangent, (b) P-E hysteresis loop, (c) M-H curve. References [1] H. Schmid, “Multi-ferroic magnetoelectrics”, Ferroelectrics, 162, (1994), 317-338. [2] X. Q. Chen, F. J. Yang, W. Q. Cao, D. Y. Wang, and K. Chen, “Room-temperature magnetoelectric coupling in Bi4(Ti1Fe2)O12−δ system” J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 43, (2010), 065001.