Unpacking Outcomes - North East School Division
advertisement

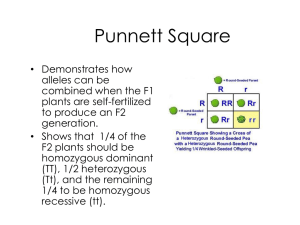
North East School Division Unpacking Outcomes Unpacking the Outcome Examine process of transfer of genetic information Examine influence on the transfer of genetic information Examine impact of transfer of genetic information on society past and present Outcome (circle the verb and underline the qualifiers) RE 9.1 Examine the process of and influence on the transfer of genetic information and the impact of that understanding on society past and present. KNOW Genetic conditions with unknown causes/ cures - some causes of male infertility, cystic fibrosis, Down’s syndrome, and muscular dystrophy Inherited traits - eye colour, chin shape, ear lobes, and tongue rolling Factors leading to cell changes - toxins, carcinogens, pesticides, smoking, overexposure to sunlight, and alcohol abuse Vocabulary – genetics, condition, technological, nucleus, cell, dominant, recessive, data, traits, inherit, environmental factors, reproductive biology, gene therapy, genetic engineering, population, disease, chromosome, gene, DNA, transmitting, impact, influence, process Parts of a cell related to the transfer of genetic information Examples of dominant and recessive traits How to observe properly, collect data, analyze data Family data of human traits Saskatchewan and Canadian contributions to the science and technology of genetics and reproductive biology How to research effectively from a variety of sources Related careers UNDERSTAND That genetics is an area still being vastly studied – many unanswered questions There is a cellular process in which genetic information is transferred Who we are and how we look is decided by our genes, which come from our parents There are dominant and recessive traits which impact things differently when combined in different ways There are factors that can change a cell’s genetic information Saskatchewan and Canada have contributed to the study of genetics and reproductive biology Genetics has had a tremendous impact on many aspects of our world We have to understand chromosomes, genes and DNA as well as reproduction in order to understand genetics BE ABLE TO DO Identify questions to investigate related to genetics. Provide examples of genetic conditions whose causes and cures are not understood according to current scientific and technological knowledge. Recognize that the nucleus of a cell contains genetic information and identify the relationship among chromosomes, genes, and DNA in transmitting genetic information. Identify examples of dominant and recessive traits in humans and other living things. Observe, collect, and analyze class and/or family data of human traits that may be inherited from parents Discuss environmental factors and personal choices that may lead to changes in a cell’s genetic information Provide examples of Saskatchewan and Canadian contributions to the science and technology of genetics and reproductive biology in plants and animals. Select and synthesize information from various sources to illustrate how developments in genetics, including gene therapy and genetic engineering, have had an impact on global and local food production, populations, the spread of disease, and the environment. Describe careers in Saskatchewan or Canada that require an understanding of genetics or reproductive biology. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why are we still so engaged in genetic research? Why is it so interesting? What questions do we still have? How is genetic information transferred and where does it happen? Why are we the way we are? How is it decided? What do genes have to do with it really? How do dominant and recessive traits work? How can the cell’s genetic information be changed? How has Saskatchewan and Canada contributed to this field? What jobs are available? How can I understand genetics? What do I need to know?