How do you know when to add –s or -es?
advertisement

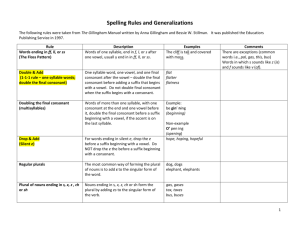
Intermediate Book Word Patterns Cheat Sheet Evolving Reader Year 1 Cycle 1 Week 1: How do you know when to add –s or -es? o A plural noun is more than one person, place or thing. Usually, you add –s to the end of a word to make it plural, or more than one. o BUT - if a word ends in CH, SH, S, X (and sometimes O) you add es to make the word mean “more than one”. How do you know when to change the y to i and add es, or when to just add s? o If 'y' is preceded by a consonant, change it to i and add 'es'. If it is preceded by a vowel, just add s. Week 2: How do you know when to add s, ‘s, or s’ to make a word possessive? o Plural forms The plural form of a noun indicates simply that there are more than one of the person or thing in question. For most nouns, the plural form includes the letter "s" at the end of the word: dogs, trees, turtles o Nouns ending in s, z, ch, sh, and x Nouns with these letters at the end call for an "es" in the plural form. This added syllable makes pronunciation easier. Beaches, foxes, wishes o Nouns ending in o Some nouns ending in o are pluralized with an “s,” while others call for “es.” These words must be memorized, because there is no simple rule to explain the differences. Echoes, autos, heroes, memos, potatoes, pimentos, vetoes, pros Source: Hodges' Harbrace Handbook, 13th edition Week 3: When adding –ed, how do you know if you double the last letter, drop the “e”, or do nothing? o When a word ends with a "silent e" or "sneaky e", drop the “e” before adding a vowel suffix. Ex: trade + ed = traded glide + ed = glided o When a vowel suffix is added to a root word that ends with one vowel and one consonant, the final consonant is doubled before adding the suffix. Vowel suffixes are ed, ing and y. Ex: stop + ed = stopped Stop ends with a vowel followed by one consonant. Suffix -ed is a vowel suffix. The ending consonant, "p" is doubled before adding the suffix. Week 4: How do you know how to pronounce “ed” at the end of a word? (It can make three sounds: /ed/ (treated), /d/ (loved), or /t/ baked) *If you are not sure if a sound is voiced or unvoiced, put your hand on your throat when you say the sound. If it is voiced, you will feel a vibration, or movement, in your throat. If it is unvoiced, you will feel nothing in your throat. o If the last sound of the word is unvoiced* (uses no only air to make the sound) except t, the -ed will sound like /t/. o Look at the words kiss and hope. The last sound of kiss is /s/. It doesn't use the voice to make the sound. So the -ed will not use a voice to make a sound either. The word sounds like /kist/. The word hope ends with /p/. It doesn't use the voice so /t/ is at the end. It sounds like /hopt/. o If the last sound of the word is voiced* (uses some noise to make the sound) except d, the -ed will sound like /d/. o Look at the words learned and played. The last sound of learn is /n/. It uses the voice. The -ed will also have a voice sound like /d/. So learned sounds like /lernd/. Play also has a voiced sound at the end. Played is pronounced /pleid/. o If the last sound to the word is /d/ or /t/, the -ed will sound like /id/. o Look at the words wanted and mended. They end with a /t/ or /d/. Wanted sounds like /wantid/ and mended sounds like /mendid/. o Note: Don't think about the spelling, only think about the final sound. For example, cough sounds like /kaf/. /f/ is unvoiced. Coughed is /kaft/. Week 5: What words does the apostrophe replace in contractions made with have, not, and will? o ‘ve = have o n‘t = not o ‘ll = will Week 6: What do the prefixes dis-, mis-, and un- mean? o dis- not, away from, reversal, or apart (“not” is the most commonly used) For Example: disagree means to not agree. o mis- bad, badly, wrong, wrongly (“wrong and wrongly” are the most commonly used) For example: misprint means wrongly printed o un- The Prefix "un" means "not". For example, the word, "unable" means "not able". Week 7: What are some compound words that contain the words down, over, under, and up? (go to http://www.enchantedlearning.com/grammar/compoundwords/ for an extensive list) o down- downstairs, downstream, downtown o over- overboard, overburden, overcast o up- upstate, upstream, upswing Week 8: When adding –ing, how do you know if you double the last letter, drop the “e”, or do nothing? o When a word ends with a "silent e" or "sneaky e", drop the “e” before adding a vowel suffix. Ex: trade + ing = trading glide + ing = gliding o When a vowel suffix is added to a root word that ends with one vowel and one consonant, the final consonant is doubled before adding the suffix. Vowel suffixes are ed, ing and y. Ex: stop + ing = stopping Stop ends with a vowel followed by one consonant. Suffix -ing is a vowel suffix. The ending consonant, "p" is doubled before adding -ing.