Magnifying Glass Investigation: Lenses & Magnification
advertisement

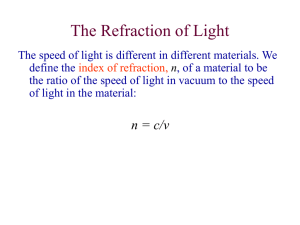
Magnifying Glass Investigation Group: _______________ Names: _________KEY________ Magnifying glasses are commonly used for examining objects that are small but not microscopic. In this simple investigation, you will get a “closer look” at how a magnifier works. 1) (2pts)Find a convex lens with a known focal length (most likely 75 mm or 150 mm). Confirm the advertised focal length by using a distant luminous object. Describe the procedure you used: Using the window across the room, we found f is approximately equal to the image distance=15.5 cm as expected. 2) (2 pts)Use this lens and a ruler to directly find the maximum magnification that can be obtained (this may require some creative thinking). Describe the procedure you used: By looking through the lens at a ruler, we found that the largest image that filled the 2.5 cm diameter lens was 1.3 cm, so m=2.5/1.3=1.9 times magnification 3) (2 pt)What is the distance between the lens and object (do) when this maximum magnification is obtained? Is this distance the same for different observers? How does this distance compare with the focal length? Is this what you would expect based on the theory presented in your textbook? d0=13 cm, which is slightly less than the focal length of 15 cm. This is consistent with the theory presented in our textbook (Figure 13-19). We found similar results for different observers. 4) (1pt) Compare the magnification you found with the equation for a simple magnifier: 𝑚 ≈ 25 𝑐𝑚 𝑓 m=25cm/15cm=1.7 x which is approximately equal to 1.9x 5) (2pt) How critical is the distance between your eye and the lens when using the magnifier? What happens to the image when this distance is increased beyond the focal length of the lens? The distance between eye and lens does not seem to matter much (same magnification with deye/lens plus or minus about 20 cm), but when the lens is held at arm’s length, the image viewed appears to be inverted and reduced. 6) (1 pt)Try experimenting with another convex lens that has a different focal length. Are your findings the same as before, or did you discover anything new? Similar findings with f=75 cm, but m=2.5/1.0=2.5x magnification, which is less than m=25/7.5=3x 7) (2pt)Find a concave lens that has a negative focal length. What do you observe when looking through this type of lens? How does the image change as you move the lens between your eye and the object you are viewing? When looking through the concave lens, the image viewed is reduced and upright no matter how close or far away the lens is to the object or eye. 8) (2pt) Find a convex/concave mirror. Examine your own image from different distances and describe what you observe: My image seen in the convex mirror is always reduced and upright, but in the concave mirror, my image is inverted and reduced for do less than f but enlarged and upright for do greater than f. 9) (1pt) What other interesting observations did you discover from this investigation? – participation grade