Topic 7 Assignment 2013 - PAC
advertisement
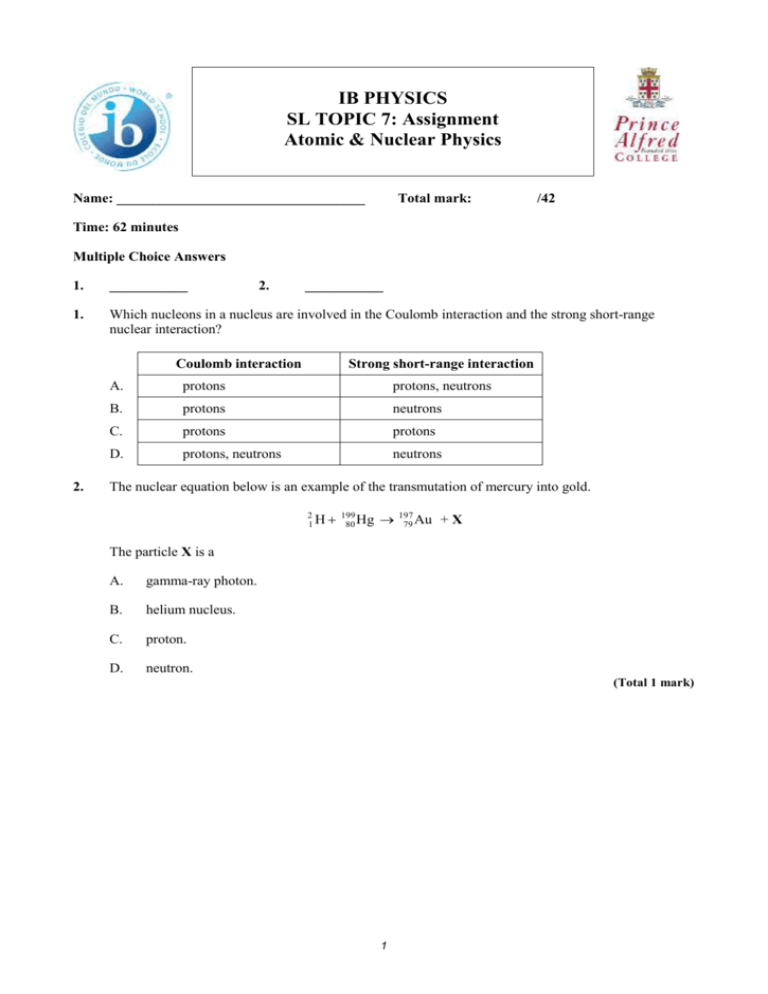
IB PHYSICS SL TOPIC 7: Assignment Atomic & Nuclear Physics Name: ___________________________________ Total mark: /42 Time: 62 minutes Multiple Choice Answers 1. ___________ 2. 1. Which nucleons in a nucleus are involved in the Coulomb interaction and the strong short-range nuclear interaction? Coulomb interaction 2. ___________ Strong short-range interaction A. protons protons, neutrons B. protons neutrons C. protons protons D. protons, neutrons neutrons The nuclear equation below is an example of the transmutation of mercury into gold. 2 199 1 H 80 Hg 197 79 Au +X The particle X is a A. gamma-ray photon. B. helium nucleus. C. proton. D. neutron. (Total 1 mark) 1 3. This question is about the Rutherford model of the atom. (a) Most alpha particles used to bombard a thin gold foil pass through the foil without a significant change in direction. A few alpha particles are deviated from their original direction through angles greater than 90°. Use these observations to describe the Rutherford atomic model. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (5) 2 199 (b) The isotope gold-197 ( 197 79 Au ) is stable but the isotope gold-199 ( 79 Au ) is not. (i) Outline, in terms of the forces acting between nucleons, why, for large stable nuclei such as gold-197, the number of neutrons exceeds the number of protons. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) 199 (ii) A nucleus of 199 79 Au decays to a nucleus of 80 Hg with the emission of an electron and another particle. State the name of this other particle. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 9 marks) 4. This question is about radioactive decay and binding energy. (a) Describe what is meant by radioactive decay. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) A nucleus of thallium-206 (Tl-206) undergoes radioactive decay to a nucleus of lead-206 (Pb-206). In the reaction equation below, identify the proton number Z of lead and the particle x. 206 206 82T Z Pb x Z: ................................................................................................................................. x: ................................................................................................................................. (2) 3 (c) The mass of a Tl-206 nucleus is 191 870 MeV c–2. Determine the binding energy per nucleon of Tl-206. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (4) (d) State why the binding energy of Pb-206 is greater than that of Tl-206. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 9 marks) 5. This question is about decay of radium-226. (a) A nucleus of the isotope radium-226 (Ra) undergoes α-decay with a half-life of 1.6 × 103 yr to form a nucleus of radon (Rn). Define the terms isotope and half-life. Isotope: ........................................................................................................................ ...................................................................................................................................... Half-life: ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) 4 (b) Using the grid below, sketch a graph to show how the activity A of a sample of radium-226 (Ra) would be expected to vary with time t over a period of about 5.0 × 103 yr. The activity of the sample at time t = 0 is A0. (3) (c) The nuclear reaction equation for the decay of radium-226 (Ra) may be written as 226 88 Ra (i) Rn α State the value of the proton number and neutron number of the isotope of radon (Rn). Proton number: ................................................................................................. Neutron number: ............................................................................................... (1) (ii) Outline why the binding energy of Ra is less than that of Rn. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 5 (d) The following data are available. mass of Ra mass of Rn mass of α = 226.0254 u = 222.0175 u = 4.0026 u Show that the energy released in the decay of a Ra nucleus is 4.94 MeV. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 10 marks) 6. This question is about α-particle scattering and nuclear processes. α-particle scattering Radium-226 decays with the emission of α-particles to radon (Rn). (a) Complete the nuclear reaction equation. 226 88 Ra Rn + (2) (b) Experimental evidence that supports a nuclear model of the atom was provided by α-particle scattering. The diagram represents the path of an α-particle as it approaches and then recedes from a stationary gold nucleus. (i) On the diagram, draw lines to show the angle of deviation of the α-particle. Label this angle D. (1) (ii) The gold nucleus is replaced by another gold nucleus that has a larger nucleon number. Suggest and explain the change, if any, in the angle D of an α-particle with the same energy and following the same initial path as in (b)(i). ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 6 (c) The diagram shows the initial path of an α-particle that approaches the gold nucleus along a line joining their centres. On the diagram draw the subsequent path of the α-particle. (1) Nuclear processes (d) The main nuclear process that gives rise to energy emission from the Sun may be simplified to 4H → He + energy. (i) State the name of this nuclear process. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) The total mass of four hydrogen (H) nuclei is 6.693 × 10–27 kg and the mass of a helium (He) nucleus is 6.645 × 10–27 kg. Show that the energy released in this reaction is 4.3 × 10–12 J. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (iii) The Sun has a radius R of 7.0 × 108 m and emits energy at a rate of 3.9 × 1026 W. The nuclear reactions take place in the spherical core of the Sun of radius 0.25R. Use these data and the answer in (d)(ii) to determine the number of nuclear reactions occurring per cubic metre per second in the core of the Sun. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 12 marks) 7