Maths - A Curriculum That Counts
advertisement

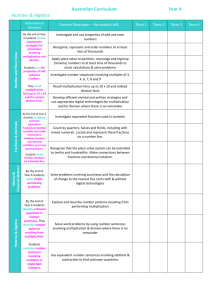
A* A* A B B/C C D New Number Grade Old KS2/3 Level Old GCSE Grade MATHS ASSESSMENT and PROGRESSION CRITERIA FRAMEWORK 10 + 9 - 10 + 8 - 9 8a8b 8c7a 7b7c 6a6c + 7 - + 6 - + 5 - + 4 - + 3 - Assessment and Progression Criteria: Calculate or estimate gradients of graphs and areas under graphs (including quadratic and other non-linear graphs), and interpret results in cases such as distance-time graphs, velocitytime graphs and graphs in financial contexts GPs with rational base & integer index Simplify surds, rationalise denominator Calculate exactly with surds. Apply and interpret limits of accuracy, including upper and lower bounds Calculate with roots, & fractional indices. Convert between recurring decimals and fractions Compound measures Eg density & pressure. Standard index form including conversions & calculations Understand & use roots. Set up, solve and interpret the answers in growth & decay problems, including compound interest Interpret direct and inverse proportion equations and graphs Work with % greater than 100% Use fractions, percentages (including reverse percentage and simple) and ratio as operators and to describe proportion. Round numbers & measures to an appropriate degree of accuracy & to specified sig figures. Use rounding to check answers and determine, in the context of a problem, an appropriate degree of accuracy. Estimate answers; use estimates to check calculations. Round numbers and measures to an appropriate degree of accuracy or to a specified number of decimal places. Apply and interpret limits of accuracy. Order of operations. F/G U 4b3c 2c-1c &P levels + 2 - + 1 Foundation E/F 5a4a Add and subtract negative numbers Solve number & practical problems including those involving measure [Eg length, mass, volume, money] using decimal notation up to 3dp, using formal written methods for four operations: Long multiplication up to 4 digit by 2 digit. Divide by 1 and 2 digit integers and interpret remainders as whole number remainders, fractions, or by rounding, as appropriate for the context. Use the symbols =, ≠, <, >, ≤, ≥. Read Roman numerals to 1000 (M) & recognise years written in Roman numerals Solve quadratics using the formula. Solve simultaneous equations with a line & a quadratic. Construct direct & inverse proportion equations Change freely between compound units (e.g. density, pressure) in numerical & algebraic contexts Use standard measures of mass, time, length and money as well as compound measures including decimal quantities. Convert between compound measures. Work with general iterative processes; find approximate solutions to equations numerically using iteration Inequalities as regions on graphs and in set notation, solve quadratic inequalities Recognise and use simple geometric progressions (r^n where n is an integer, and r is a rational number > 0 or a surd) and other sequences Trig & exponential graphs. Apply the concepts of average & instantaneous rate of change (gradients of chords and tangents) in numerical, algebraic and graphical contexts Transforming graphs; translation & reflection of given functions Know the exact values of sinθ and cosθ for θ = 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°; know the exact value of tanθ for θ = 0°, 30°, 45° and 60° 3-D Trig & Pythag Arc lengths, angles and areas of sectors of circles, surface area and volume of composite solids Use vectors to construct geometric arguments and proofs (Vectors) Real life graphs including Construct and Vectors: Conditional dist/time, speed/time Volume and surface area interpret column vectors probability, and acceleration of spheres, cones and diagrams for and related expected (including harder fuctions pyramids. Congruence grouped diagramatic frequencies Eg reciprocal). Interpret and similarity for length, discrete data representation; with two-way the gradient at a point area and volume. and continuous add, subtract tables, tree on a curve as the Sine and cosine rules & data, including and use scalar diagrams and instantaneous rate of Area = ½ab sinC unequal width multiples Venn diagrams. change histograms Solve linear simultaneous equations Set up algebraic Apply & prove Use gradient & intercept of y = Compare Calculate Use the basic algebraically. expressions & standard circle mx + c lines. distributions probabilities congruence Solve quadratic equations through eq’ns from theorems Find eq'n of straight line from 2 of using using tree criteria for factorising where rearranging is needed situations. concerning point or gradient and a point. mean, diagrams and triangles first. Factorise quadratics of the form ax² + Change the angles, radii, Interpret straight line gradient as median, other (SSS, SAS, bx + c. subject of tangents and a rate of change. mode, range, representations ASA, RHS). Simplify and manipulate algebraic formulae. chords, and use Deduce roots of quadratic quartiles and of dependent & Apply Basic expressions (including those involving surds Solve linear them to prove functions algebraically inter-quartile independent 2-D Trig and algebraic fractions) by expanding inequalities in related results Reciprocal graphs. range events. products of two or more binomials 2 variables Expand and factorise Sketch and interpret Use mathematical argument Infer properties of populations or Basic 2-D Trig. quadratics (a = 1). linear and quadratic to show equivalency of distributions from a sample, whilst graphs. Compare lengths, algebraic expressions. knowing the limitations of sampling. The difference of 2 squares. Enlargement areas and y = mx + c with parallel Know the difference including Compare distributions using mean, Solve quadratic equations volumes using lines. between equation and negative median, mode and range and consider graphically and by factorising ratio notation. identity. scale factors outliers. (a=1) Solve simultaneous Area of circles & equations graphically. Understand and use Cumulative frequency graphs, Understand and use algebraic compound shapes composite functions box plots, equal width histograms. factors. Cubic Graphs. Fibbonacci & quadratic sequence, nth term of quadratic sequence Use y = mx + c to identify perpendicular lines. Identify and interpret roots, intercepts, turning points of quadratic functions graphically. Eq’ns & graphs: Circles (centre origin), Exponential (+ &- base) Manipulate algebraic expressions (including laws of indices). Use angle facts up to parallel lines including obtaining simple proofs. Find the nth term and understand a reverse process as an inverse function. Draw, interpret and use bearings, scale drawings and maps. Solve addition & subtraction multi-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations & methods to use & why. Recognise and use relationships between operations, including inverse operations (e.g. cancellation to simplify calculations and expressions. Formal written division with answers up to 2dp Round whole numbers to a required degree of accuracy (nearest 10, 100 1000 etc). Round decimals with two decimal places to the nearest whole number & to one dp. Interpret and use negative numbers in context, count forwards and backwards with positive and negative whole numbers, including through zero Understand and use place value: Read, write, order and compare numbers (up to 3dp and up to 10 000 000) and determine the value of each digit Count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number up to 1 000 000 Add, subtract, multiply and divide fractions (mixed, proper or improper) and simplify answers. Understand 3/8 means 3 divided by 8 and evaluate it as a decimal. Read and write decimal numbers as fractions [for example, 0.71 = 71/100]. Recognise &use thousandths and relate them to tenths, hundredths and decimal equivalents Add, subtract multiply & divide whole numbers mentally & using formal written methods. Multiply and divide by 10, 100 and 1000 (including decimals) Recall and use equivalences between simple fractions, decimals and percentages, including in different contexts. Compare two quantities using percentages. Interpret % and % changes as a fraction or a decimal, & interpret these multiplicatively Solve problems involving % change, including % increase/decrease Use and describe congruence and similarity (including finding lengths). Translation (with vector notation), rotation, reflection and enlargement. Solve loci problems including the use of standard ruler and compass constructions Use the mean, mode, median & range to compare and analyse sets of data. Use charts, tables and diagrams (inc pie charts) to interpret, analyse and compare data. Use scatter diagrams and lines of best fit to find correlation and make predictions. Enumerate sets and combinations of sets systematically using tables, grids and Venn diagrams. Perimeter of 2-D Probabilities of mutually shapes. exclusive events sum to Area of parallelograms, Enumerate one. triangles and trapezia. possibilities Construct sample space Volume and surface of diagrams to calculate area of cubes and combinations theoretical probabilities. cuboids (cm², cm³, m² of two Record describe and & m³, extending to variables. analyse the frequency of mm³ and km³) Apply outcomes of probability Change freely between systematic experiments using tables related standard units listing and frequency trees. (e.g. time, length, area, strategies Understand that volume/capacity, including use empirical unbiased mass) in numerical of the samples tend towards contexts. product rule theoretical probability Construct and interpret for counting distributions, with plans and elevations of increasing sample size 3-D shapes. Perimeter of composite Solve problems involving similar Use & interpret algebraic Use standard conventions & Complete, read & Define percentage as rectilinear shapes (measure shapes or related quantities or Describe notation, for example: ab, 3y, a², notations for labelling & referring interpret ‘number of parts per & calculate in cm & m). sizes using integer scale factors. linear a³, a²b , a/b, brackets & to sides, angles, points, lines, information in hundred’. Area of squares & Solve problems involving unequal number coefficients written as fractions vertices, edges, planes, parallel tables, inc Solve problems which rectangles using standard sharing & grouping using sequences, rather than as decimals. lines, perpendicular lines, right timetables. require knowing units (cm² & m²) & estimate knowledge of fractions and generate Express missing number angles, polygons, regular Interpret & percentage and decimal areas of irregular shapes. multiples. terms from problems algebraically. polygons and polygons with construct pie charts equivalents of 1/2, 1/4, 1/5, Recognise that shapes with either a Understand & use standard reflection and/or rotation & line graphs & use 2/ , 4/ and those fractions Solve problems involving same areas can have 5 5 term-to-term mathematical formulae. symmetries. these to solve multiplication & division, with a denominator of a different perimeters & viceor a positionSubstitute numerical values into Use angle properties; round a problems. Calculate including scaling by simple multiple of 10 or 25. versa. to-term rule expressions and formulae (inc point, straight line, vertically & interpret the fractions & problems involving Estimate volume & capacity Find % of an amount. scientific). opposite to find missing angles mean as an average simple rates. using cm cubes & water. Solve problems involving Identify multiples, Compare & order fractions, Work with coordinates in Use properties of rectangles to Identify and apply circle Apply ideas of converting between units of factors (divisors), all including fractions > 1. all four quadrants. deduce related facts & find definitions and randomness, fairness time. factor pairs, common Add and subtract fractions Understand and use lines missing lengths & angles. properties, including: and equally likely Convert between miles & km. factors, common with the same denominator parallel to the axes, y=x Derive & use the sum of angles in tangent, arc, sector and events to calculate Understand and use multiples and prime and denominators that are and y=-x. a triangle (e.g. to deduce & use segment. expected outcomes of approximate equivalences numbers (know primes multiples of the same Plot and interpret graphs the angle sum in any polygon, & Recognise, describe and multiple future between metric units and up to 19 and establish number. of non-standard (pieceto derive properties of regular build simple 3-D shapes, experiments. common imperial units such as whether others up to Convert between mixed wise linear) functions in polygons) & find unknown angles including making nets. Relate relative inches, pounds & pints. 100 are prime). Prime numbers and improper real contexts, to find in any triangles, quadrilaterals, & Identify properties of expected frequencies Solve problems involving the factors and fractions. approximate solutions to regular polygons. faces, surfaces, edges & to theoretical calculation and conversion of decomposition. Multiply proper fractions problems such as simple Distinguish between regular & vertices of: cubes, probability, using units of measure, using and mixed numbers by kinematic problems irregular polygons based on cuboids, prisms, appropriate language Recognise square and decimal notation up to three whole numbers, supported involving distance & reasoning about equal sides & cylinders, pyramids, & the 0 - 1 probability cube numbers and decimal places where by materials and diagrams speed. angles. cones and spheres scale. associated notation. appropriate. Use conventional notation for priority of operations, including brackets. Use positive integer powers and associated real roots (square, cube and higher), recognise powers of 2, 3, 4, 5 Estimate powers & roots of any given positive number Order positive and negative integers, decimals & fractions. Complete the square to solve quadratics & find vertex/turning point Transformations: Reflection, rotation, translation & enlargement (including fractional scale factors). Understand which properties of the shapes are preserved or changed after combined transformations Solve problems involving direct and inverse proportion, understand links between proportion, ratio and fractions. Convert between terminating decimals & fractions Use four operations on +ve & -ve integers, fractions and decimals. Construct and solve simultaneous eq’ns & interpret the solutions. Find the equation of a tangent to a circle at a given point Equivalent fractions including cancelling and writing over same denominator for comparison (including visual representations). Write % as a fraction with denominator 100, & as a decimal Understand and use place value: Read, write, order and compare whole numbers (up 1000) and determine the value of each digit Simplify & manipulate algebraic expressions by collecting like terms & multiplying a single term over a bracket. Find pairs of numbers that satisfy an eq’n with 2 unknowns. Solve linear equations in one unknown algebraically. Understand and use the concepts and vocabulary of expressions, eq’ns, formulae, terms & factors Estimate, draw and measure angles. Identify angles round a point or on a straight line totalling 360°or 180° & other multiples of 90° Add, subtract multiply and divide whole numbers mentally. Multiply and divide integers by 10 and 100 Sequences of triangular, square & cube numbers, simple APs. Interpret simple expressions as functions with inputs and outputs. Plot straight line graphs from given equation. Simple Reflection and Translation on co-ordinate axes Compare and classify geometric shapes based on their properties and sizes. Find and use properties of special triangles and quadrilaterals and other plane figures using appropriate language. Draw 2-D shapes using given dimensions & angles Understand visual representations of equivalent fractions including tenths and hundredths Identify 3-D shapes, including cubes and other cuboids, from 2-D representations Draw and measure line segments. Know angles are measured in degrees: estimate and compare acute, obtuse and reflex angles. Grade 1 includes all the elements of Foundation as well. For students operating below grade 1, they can be graded at F3, F2 or F1 (F3 the highest) Red text indicates fundamental concepts that should be thoroughly embedded. Repeated review until nailed! Circle definitions and properties: centre, radius, chord, diameter, circumference, know that the diameter is twice the radius Convert between different units of metric measure (for example, km & m; cm & m; cm & mm; g &kg; litre and millilitre) Solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information presented in a line graph