completing the square
advertisement

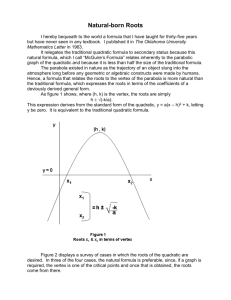
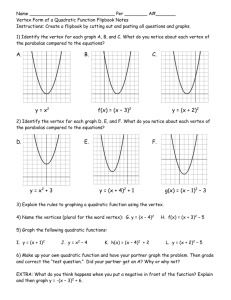
ALGEBRA 2 LECTURE Q – 3: Finding Roots of Quadratic Equations Reading Assignment: Chapter 5, Pages 299 – 313 COMPLETING THE SQUARE STEPS TO COMPLETING THE SQUARE: 1. Get the quadratic equation in standard form 2. Divide by a 3. Move c to right hand side of equation 4. Divide b by 2, square it, and add the result to both sides of equation 5. Compare Left hand side with a2 + 2ab + b2 6. Apply formula a2 + 2ab + b2 = (a + b)2 7. Solve for x EXAMPLE 1: Solve x2 + 6x – 16 = 0 by completing the square EXAMPLE 2: Solve 2x2 + 6x – 7 = 0 by completing the square TRY THIS PAGE 301: Solve x2 + 10x – 24 = 0 by completing the square Solve 2x2 + 10x – 6 = 0 by completing the square ALGEBRA 2 LECTURE Q – 3: Finding Roots of Quadratic Equations VERTEX FORM EXAMPLE 3: Given g(x) = 2x2 + 12x + 13, write the function in vertex form, and give the coordinate of the vertex and the equation of the axis of symmetry. TRY THIS PAGE 302: Given g(x) = 3x2 – 9x – 2, write the function in vertex form, and give the coordinate of the vertex and the equation of the axis of symmetry. ALGEBRA 2 LECTURE Q – 3: Finding Roots of Quadratic Equations QUADRATIC FORMULA EXAMPLE 4: Use the quadratic formula to find the roots of x2 + 5x – 14 = 0 EXAMPLE 4: Use the quadratic formula to find the roots of 4x2 = 8 – 3x TRY THIS PAGE 308 Use the quadratic formula to solve: x2 – 7x + 6 = 0 2x2 – 6x = – 3 HW Q – 3 Page 304 #17, 21, 25, 29, 33, 37, 39, 41, 43, 45; Page 311 # 11, 15, 19, 23, 27