5.7Notes
advertisement
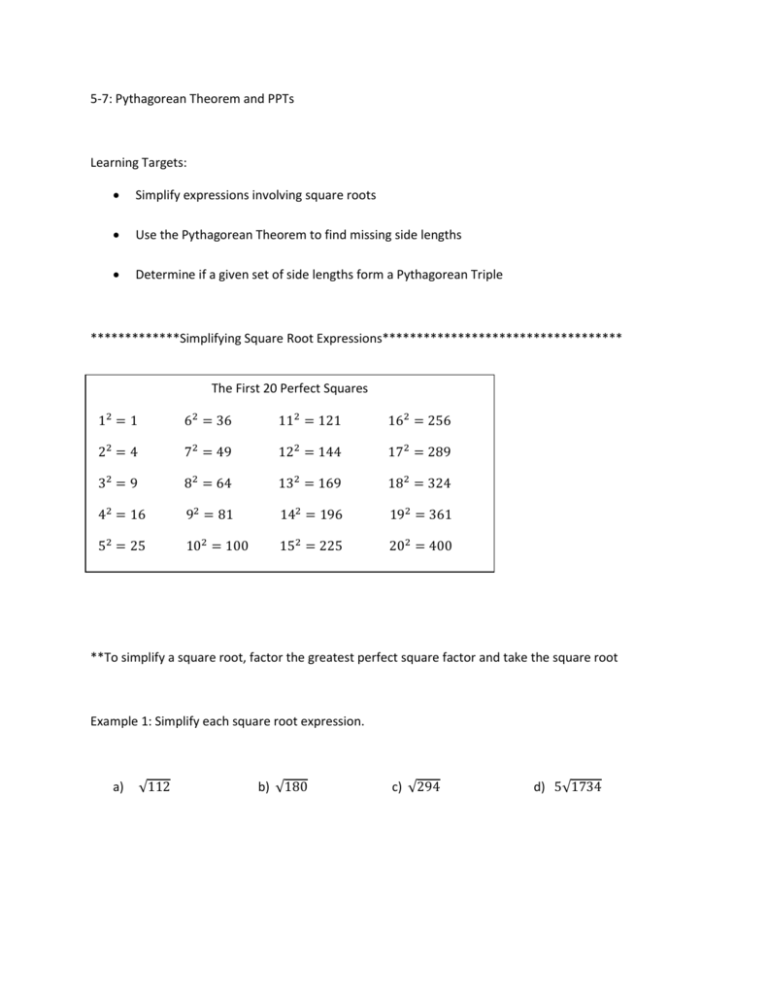
5-7: Pythagorean Theorem and PPTs Learning Targets: Simplify expressions involving square roots Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing side lengths Determine if a given set of side lengths form a Pythagorean Triple *************Simplifying Square Root Expressions*********************************** The First 20 Perfect Squares 12 = 1 62 = 36 112 = 121 162 = 256 22 = 4 72 = 49 122 = 144 172 = 289 32 = 9 82 = 64 132 = 169 182 = 324 42 = 16 92 = 81 142 = 196 192 = 361 52 = 25 102 = 100 152 = 225 202 = 400 **To simplify a square root, factor the greatest perfect square factor and take the square root Example 1: Simplify each square root expression. a) √112 b) √180 c) √294 d) 5√1734 ***************************The Pythagorean Theorem**************************** ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 shown below is a right ∆ ↔ 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 = 𝑐 2 . A a, b are the lengths of the legs opposite the acute ∠𝑠 c is the length of the hypotenuse c b C B a Example 2: Find the missing side lengths. Give answers in simplest radical form. a) 12 15 15 b) 8 10 F Example 3: Wes drives 19 miles east, 2 miles north, 5 miles east, and then travels 5 more miles north before arriving at his destination. How far did he travel from his starting point “as the crow flies”? ******************************Pythagorean Triples****************************** A Pythagorean Triple is a set of 3 nonzero whole numbers a, b, and c such that 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 = 𝑐 2 . ** (3, 4, 5) form a Pythagorean Triple since 32 + 42 = 52 ** 12 + 2.42 = 2.62 , but (1, 2.4, 2.6) do not form a Pythagorean triple. Why? 16 Example 3: Find the missing side lengths. Then tell if the lengths form a Pythagorean Triple. a) b) 9 30 16 F 7 5-7: Pythagorean Theorem and PPTs Learning Targets: Simplify expressions involving square roots Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing side lengths Determine if a given set of side lengths form a Pythagorean Triple *************Simplifying Square Root Expressions*********************************** The First 20 Perfect Squares 12 = 1 62 = 36 112 = 121 162 = 22 = 4 72 = 49 122 = 144 172 = 32 = 9 82 = 64 132 = 182 = 42 = 16 92 = 81 142 = 192 = 52 = 25 102 = 100 152 = 202 = **To simplify a square root, factor the greatest perfect square factor and take the square root Example 1: Simplify each square root expression. a) √112 b) √180 c) √294 d) 5√1734 ***************************The Pythagorean Theorem**************************** ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 shown below is a right ∆ ↔ 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 = 𝑐 2 . A a, b are the lengths of the legs the acute ∠𝑠 c is the length of the hypotenuse c b C B a Example 2: Find the missing side lengths. Give answers in simplest radical form. a) 12 15 15 b) 8 10 F opposite Example 3: Wes drives 19 miles east, 2 miles north, 5 miles east, and then travels 5 more miles north before arriving at his destination. How far did he travel from his starting point “as the crow flies”? ******************************Pythagorean Triples****************************** a, b, and c such that 𝑎2 + A Pythagorean Triple is a set of 3 nonzero whole numbers 𝑏2 = 𝑐 2. ** (3, 4, 5) form a Pythagorean Triple since 32 + 42 = 52 and 3, 4, and 5 are all whole numbers. ** 12 + 2.42 = 2.62 , but (1, 2.4, 2.6) do not form a Pythagorean triple. Why? 16 Example 3: Find the missing side lengths. Then tell if the lengths form a Pythagorean Triple. a) b) 9 30 16 F 7 ( 3 , 4 , 5 ) ( 5, 12, 13) ( 7, 24, 25) ( 8, 15, 17) ( 9, 40, 41) (11, 60, 61) (12, 35, 37) (13, 84, 85) (16, 63, 65) (20, 21, 29)


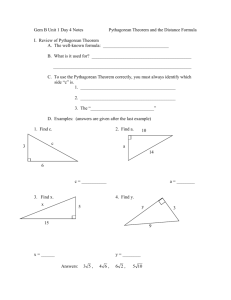

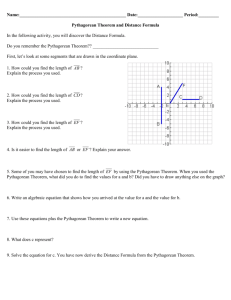

![Pythagorean Theorem Choice Menu]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006637104_1-ef489d42c5b94dc2216093dd08d2b47e-300x300.png)
