The Unit Organizer
advertisement
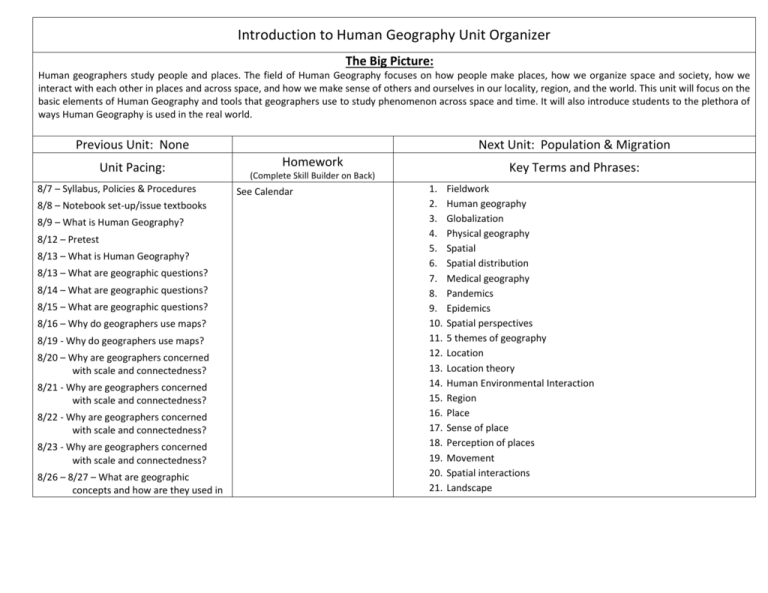
Introduction to Human Geography Unit Organizer The Big Picture: Human geographers study people and places. The field of Human Geography focuses on how people make places, how we organize space and society, how we interact with each other in places and across space, and how we make sense of others and ourselves in our locality, region, and the world. This unit will focus on the basic elements of Human Geography and tools that geographers use to study phenomenon across space and time. It will also introduce students to the plethora of ways Human Geography is used in the real world. Previous Unit: None Unit Pacing: 8/7 – Syllabus, Policies & Procedures 8/8 – Notebook set-up/issue textbooks 8/9 – What is Human Geography? 8/12 – Pretest 8/13 – What is Human Geography? 8/13 – What are geographic questions? 8/14 – What are geographic questions? 8/15 – What are geographic questions? 8/16 – Why do geographers use maps? 8/19 - Why do geographers use maps? 8/20 – Why are geographers concerned with scale and connectedness? 8/21 - Why are geographers concerned with scale and connectedness? 8/22 - Why are geographers concerned with scale and connectedness? 8/23 - Why are geographers concerned with scale and connectedness? 8/26 – 8/27 – What are geographic concepts and how are they used in Next Unit: Population & Migration Homework Key Terms and Phrases: (Complete Skill Builder on Back) See Calendar 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Fieldwork Human geography Globalization Physical geography Spatial Spatial distribution Medical geography Pandemics Epidemics Spatial perspectives 5 themes of geography Location Location theory Human Environmental Interaction Region Place Sense of place Perception of places Movement Spatial interactions Landscape answering geographic questions? 8/28 – Review 8/29 – FRQ Exam 8/30 – MC Exam 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. Cultural landscape Sequent occupance Cartography Reference maps Thematic maps Absolute location GPS Relative location Mental maps Activity spaces Generalized maps Remote sensing Geographic Information System (GIS) Scale Region Functional region Formal region Perceptual region Culture Cultural trait Cultural complex Cultural hearth Cultural diffusion Independent invention Time-distance decay Cultural barriers Expansion diffusion Contagious diffusion Hierarchical diffusion Stimulus diffusion Relocation diffusion Environmental determinism 54. 55. 56. 57. Isotherms Possibilism Cultural ecology Political ecology Unit Objectives/AKS Content Areas: A. Geography as a field of inquiry B. Evolution of Key Geographical concepts & models associated with notable geographers C. Key concepts underlying the geographical perspective; location, space, place, scale, pattern, regionalization, & globalization D. Key geographical skills: a. How to use & think about maps & spatial data b. How to understand & interpret the implications of associations among phenomena in places c. How to define regions & evaluate the regionalization process d. How to characterize& analyze changing interconnections among places E. New sources of technologies, such as GIS & GPS F. Sources of geographical ideas & data: the field











