Convection, Conduction, Radiation Evidence of Close Reading and
advertisement

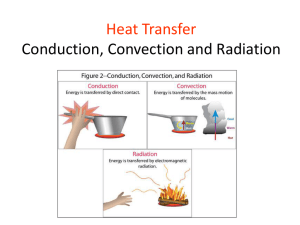
CLOSE READING STRATEGY NONFICTION TEXT First Read: Highlight all bold, italics, and graphics Second Read: Annotate next to your highlighting that you did during the first read the meaning behind the bold, italics, and graphics Third Read: Circle all important vocabulary words and underline the meaning of the words. CLOSE READING STRATEGY QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS First Read: Highlight key words in questions and circle the word or words that tell you what you have to do. Second Read: Search for the answer in the text and annotate where you found it by indicating in the margin of the text the question number. Third Read: Next to the question explain why you chose that answer and use the process of elimination. Convection, Conduction, and Radiation There are three ways that heat can be transferred. These are convection, conduction, and radiation. Convection. Convection is heat transfer that occurs when warm particles move in currents. For example, when a pot of water is boiled, the water molecules closest to the bottom of the pot are heated the most. As they heat, they become less dense. This causes them to rise to the top of the pot.As the hot molecules rise to the top, they take the heat with them. The cooler particles then drop to the bottom. The heat transfer is occurring because of the movement of the warm particles. The same movement of heated particles happens in air, where warm air rises and cooler air takes its place. Conduction. Conduction is heat transfer that occurs when particles are in contact with each other. For example, if a hot saucepan is placed on a bench, heat will flow from the hot surface of the saucepan to the colder bench. This heat flow from a hot object to a cold object will continue until the objects reach the same temperature. Radiation. Like convection and conduction, radiation can transfer heat through matter. However, radiation is different in that it can also transfer heat through empty space. Through the process of radiation, heat flows in the form of waves. The radiation waves flow from hot objects and are absorbed by cooler objects. The cooler objects heat up as they absorb the waves. The heat that is transferred from the Sun to the Earth is an example of radiation. All three types of heat transfer involve a flow of heat from a warm object to a cold object. As the cold object absorbs the heat, it becomes hotter. The warm object is losing the heat that the cold object is absorbing, and so it is becoming cooler. This flow from warm object to cool object continues until both objects reach equilibrium. This is the point where both objects are the same temperature. 1. Which of the following is the correct definition of convection? A. the transfer of heat by currents B. the electromagnetic radiation from the surface of an object which is due to the object's temperature C. the transmission of heat across empty space D. the transmission of heat across matter 2. Radiation, conduction, and convection are methods of energy transfer. Of these methods, radiation is the only one in which energy can be transferred through _______. A. matter. B. solids. C. liquids. D. space. 3. In which of the following methods of heat transfer is it necessary for the objects to be directly touching one another? A. conductio n B. convection C. radiation D. All of these 4. Which of the following is an example of convection? A. a hot object transferring heat to a cooler one B. the rays of the Sun warming the earth C. a hot oven warming the air around it D. hot air rising and cooler air falling 5. When hot and cold air meet, the hot air rises to the top. Which process causes the hot air to rise? A. conduction n B. induction C. radiation D. convection n 6. Convection currents form when warm air rises and cold air sinks.What causes the warm air to rise and the cold air to sink? A. a difference in weather B. a difference in substance C. a difference in climate D. a difference in density 7. A transfer of heat within a liquid or gas that involves warm particles moving in currents is A. radiation n B. correction. C. convection. D. conduction n 8. The light from the Sun heats a metal surface. This is an example of A. radiation. B. reflection. C. conduction. D. convection. 9. Heat can be transferred through conduction, convection, and radiation. What is necessary in order for heat to be transferred by conduction? A. Heat must be transferred through space. B. The objects must be in direct contact with one another. C. Heat must be transferred in the form of currents. D. The substances must be liquids or gases. 10. Which of the following is an example of only the process of conduction? A. Leftovers become warm when reheated in the microwave. B. A dog's bowl of water warms up out in the Sun. C. A metal spoon becomes warm when placed in a cup of hot tea. D. Campers warm up while sitting by a campfire.