Curriculum Development Unit Overview DRAFT Planning For Each
advertisement

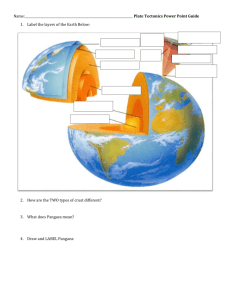
Curriculum Development Unit Overview DRAFT Planning For Each Unit DRAFT P Unit Title The Dynamic Earth Standards and Grade Level Expectations CAS Priority Standard Length of Unit 4 weeks (18-21 days) ES 3: The theory of plate tectonics helps explain geological, physical, and geographical features of Earth. a) develop, communicate, and justify an evidence-based scientific explanation about the theory of plate tectonics and how it can be used to understand geological, physical, and geographical features of the Earth(DOK 1-3) b) analyze and interpret data on plate tectonics and the geological, physical, and geographical features of Earth(DOK 1-2) c) understand the role plate tectonics has had with respect to long-term global changes in Earth’s systems such as continental build-up, glaciations, sea-level fluctuations, and climate change(DOK 1-2) d) Investigate and explain how new conceptual interpretations of data and innovative geophysical technologies led to the current theory of plate tectonics (DOK 2-3) CAS Supporting Standard ES 7: Natural hazards have local, national, and global impacts such as volcanoes, tsunamis, hurricanes, and thunderstorms. Connections to other CAS Standards include ES 1, ES 6, PS 6 Next Generation Science Standards HS-ESS1-5. Evaluate evidence of the past and current movements of continental and oceanic crust and the theory of plate tectonics to explain the ages of crustal rocks. HS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to illustrate how Earth’s internal and surface processes operate at different spatial and temporal scales to form continental and ocean-floor features. HS-ESS2-3. Develop a model based on evidence of Earth’s interior to describe the cycling of matter by thermal convection. Essential Unit Question(s) (Engaging-Debatable): How does the theory of plate tectonics explain how the Earth changes? How does the changing earth cause natural hazards that impact humans (locally and globally) and how can we predict and prepare for natural hazards? Science Concepts Plate Tectonics as a Builder of Landforms; Earth’s Interior; Earth Systems focus; Natural Hazards focusing on Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Tsunamis [This unit does not address weather related natural hazards such as tornadoes, hurricanes, and thunderstorms. ] Nature of Science A student in ESPS can demonstrate the following scientific skills: a) generate and justify evidence-based explanations using a variety of literature and scientific laws Curriculum Development Unit Overview DRAFT Planning For Each Unit DRAFT b) c) d) e) analyze, interpret, and share data (addressing both direct and indirect evidence) compare and evaluate the evolution of a scientific theory over time make evidence-based predictions and draw conclusions design an experiment and communicate findings Academic Vocabulary: Core: justify, analyze, compare, contrast, model, evidence (direct and indirect), predict Science-specific academic terms: theory Content Vocabulary: Core: DIVERGENT BOUNDARY, MID-OCEAN RIDGE, SEA FLOOR SPREADING RIFT VALLEY, CONVERGENT BOUNDARY, SUBDUCTION, OCEAN TRENCH, HOT SPOT, TRANSFORM BOUNDARY, ASTHENOSPHERE, LITHOSPHERE, OCEANIC CRUST, CONTINENTAL CRUST, seismic waves, GPS, paleomagnetism, Convection currents Review: continental drift, plate tectonics, PANGEA, density, tectonic plate, earthquake, volcano, tsunami, fault, constructive forces; destructive forces; crust, mantle, outer core, inner core, Additional: subduction zone, VOLCANIC ARC, continental arc, CONTINENTAL ACCRETION theory, seismic waves (p/s/surface) supercontinent cycle, magnitude, Richter scale, epicenter, focus Vertical Alignment 6th Grade – ES1 – Complex interactions exist between Earth’s structure and natural processes that over time are both constructive and destructive. 5th Grade – ES2 – Earth’s surface changes constantly through a variety of processes and forces. Curriculum Development Unit Overview DRAFT Planning For Each Unit DRAFT KEY SUMMATIVE(S) ( includes links to related rubrics) Summative: Impact of Plate Boundaries on Earth’s Surface TTThere are two parts to this summative: 1) Part 1 Students create a poster on the geologically hazards of a region / perform a gallery walk to gather evidence 2) AND 2) Part 2 a RAFT that has the students produce a written product that has them choose the least and most hazardous location. Critical Content / Key Skills: What students will know and be able to do Learning Activities (LA) / Formative Assessments (FA)/ Key Resources (KR) / Extensions (EXT) How does the theory of plate tectonics explain how the Earth changes? How does the changing earth cause natural hazards that impact humans (locally and globally) and how can we predict and prepare for natural hazards? CORE: (~5 pd) 1b Current Model of Earth’s Interior (~1 pd) 1c Density of Earth Materials 1dba Earth’s Layers – Analyzing Data 1eb Evidence of Earth’s Interior Earth’s Interior – Layers 1. How do we know the composition and arrangement of the Earth’s interior? I can… a) b) c) d) e) distinguish between indirect and direct evidence and relate this to the evidence that supports our current model of the Earth’s interior. (DOK 1-2) Identify and describe our current model of the layers of the Earth (DOK1) [density, state of matter, major mineral content, pressure, temperature, inner core, outer core, asthenosphere, lithosphere, mantle, crust – oceanic, continental] collect and analyze data about the density of Earth materials (DOK2) analyze data about characteristics of the layers of the Earth (DOK2) Compare and contrast various pieces of evidence that support specific aspects of our current model of the Earth’s interior (DOK 2-3) [Earthquake waves (p and s and surface), ophiolites, digging holes, exposed rock layers, density meters, magnetic field lines] Additional: 1a Direct versus Indirect Evidence – Brown Bag Earth Curriculum Development Unit Overview DRAFT Planning For Each Unit DRAFT Continental Drift and the Evolution of Plate Tectonics 2. How and why have our ideas of plate movement changed through time (past and present) and what evidence do we have for it? I can 2ab Continental Drift and Story of Pangaea PowerPoint and Reading 2abc Development of Plate Tectonic Theory – EarthComm 2c Developing the Theory Reading and Foldable a) Describe Wegener’s evidence for continental drift (DOK1) b) Identify weaknesses in Wegener’s ideas and why continental drift was not accepted by the scientific community (DOK1) c) Describe how new evidence (often based on new technology) (sonar, drilling samples, magnetic fields) changed our ideas about plate movement. (DOK 1-2) i. ii. iii. iv. Pre-Wegener – 1596’s – 1620’s (Bacon’s maps) – 1858 (Sneider) - explorers – observational evidence Wegener – 1912’s – climate evidence/paleoclimate, fossil evidence, landforms, coal fields, mountain ranges 1950’s 1960’s - Sonar; Sea floor spreading; drilling of ocean floor; bathymetric maps, 1970’s -1980’s ??? Satellite altimetry - GPS Mechanism of Plate Tectonics 3. What causes the movements of the plates? I can a) Compare and contrast the different types of Earth materials (oceanic vs continental) in terms of their density. (DOK2) b) Describe the impact of temperature and pressure on the density of Earth materials. (DOK1-2) c) Describe how density and convection work together to move the lithospheric plates. (DOK1) 3abc Convection Current Demo Stations 3ac EarthComm Guided Reading-Measuring the Motion of Lithospheric Plates 3ac Convection Currents Worksheet If time find a Shared reading short-on convection currents and include You tube video Convection Currents Video Clip-You Tube http://youtu.be/p0dWF_3PYh4 Curriculum Development Unit Overview DRAFT Planning For Each Unit DRAFT Types of Plate Boundaries and their impact on Earth 4. What are the different types of plate boundaries and how do they impact us and the Earth? (landforms, catastrophic events, etc.) a) b) c) d) e) f) I can Describe the distribution and composition (oceanic, continental) of plates on Earth (DOK1) Compare and contrast (movement, location, landforms, specific examples) the three major types of plate boundaries. (DOK2) Identify which boundaries are ‘building’ and which are ‘destroying’ crust and use this information to predict future plate movement and resulting changes in the Earth’s surface. (DOK2-3) Identify and explain the relationship between plate boundaries and the distribution of volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis on the Earth. (DOK1-2) Assess relative risks/benefits of different plate boundaries and relate these to the local and global hazards found at specific locations on Earth. (DOK 2-3) Use my understanding of plate tectonics to assess risks and benefits of living / vacationing in certain locations (DOK 2-3) Possible Extension(s) Surface Phenomena (Weathering, Erosion, Deposition) 4ab Plotting Plate Movement Activity 4b Plate Boundaries Graphic Organizer 4b Plate Tectonics Web-quest 4ac Earth-Past, Present, Future Activity 4bdef Investigating Plate Boundaries Activity 4abc SeaFloor Spreading Lab 4abc SeaFloor Spreading 3D Model 1. *** Curriculum Development Unit Overview DRAFT Planning For Each Unit DRAFT Curriculum Development Unit Overview DRAFT Planning For Each Unit DRAFT Colorado Academic Standards for Science 1. P = priority S = supporting Connections also to… P: ES1 S: ES2 PS 3 Still need to look more at this