DNA Replication Notes - TangHua2012-2013
advertisement
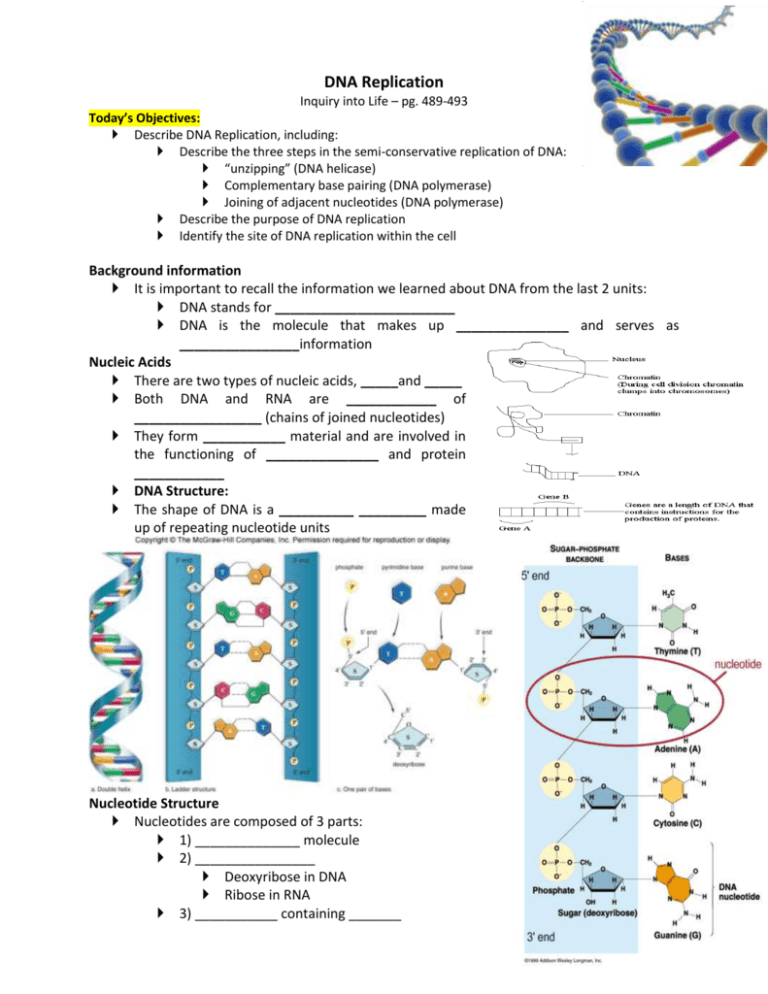
DNA Replication Inquiry into Life – pg. 489-493 Today’s Objectives: Describe DNA Replication, including: Describe the three steps in the semi-conservative replication of DNA: “unzipping” (DNA helicase) Complementary base pairing (DNA polymerase) Joining of adjacent nucleotides (DNA polymerase) Describe the purpose of DNA replication Identify the site of DNA replication within the cell Background information It is important to recall the information we learned about DNA from the last 2 units: DNA stands for ________________________ DNA is the molecule that makes up _______________ and serves as ________________information Nucleic Acids There are two types of nucleic acids, _____and _____ Both DNA and RNA are ____________ of _________________ (chains of joined nucleotides) They form ___________ material and are involved in the functioning of _______________ and protein ____________ DNA Structure: The shape of DNA is a __________ _________ made up of repeating nucleotide units Nucleotide Structure Nucleotides are composed of 3 parts: 1) ______________ molecule 2) ________________ Deoxyribose in DNA Ribose in RNA 3) ___________ containing _______ Nitrogen containing bases Two types: ___________ – adenine (A) and guanine (G) _______________ – thymine (T), uracil (U) and cytosine (C) DNA has A,G,T,C, RNA has A,G,U,C Purines are __________ than pyrimidines and have a __________ ring structure Pyrimidines are __________ than purines and have a ________ ring structure When the bases bond together to form the “rungs of the DNA _________” they do so in a set pattern. The alternating sugar and phosphates make up the _______ (_____________). The bases make up the _________. Complementary Base Pairing ____________ always bonds to ___________ ______ hydrogen bonds _________ always bonds to _________ ________ hydrogen bonds This bonding of bases is called ___________________ base pairing They cannot bond any other way because 2 purines would __________ and 2 pyrimidines would be too _________ to form the rungs of the ladder The double strand is held in place by hydrogen bonds between the bases. It is the ____________ and ________ as well as the ________ of the bases that determine what kind of ____________ will develop. Order of Bases Example: ATCCGATT means something entirely different than ACCGTTAT, just as the words hate and heat mean different things even though they contain the same letters As a DNA strand lengthens, it twists into a double spiral called a __________ ________ Candy DNA Model Next class you will build a DNA molecule using CANDY! (you can eat it after you are finished) Functions of DNA 1) _____________ (duplicates) itself so each new cell has a complete, ____________ copy 2) ____________ the activities of a cell by producing ____________ The combination of proteins determines the characteristics of each living organism 3) Undergoes occasional _____________ (mistakes in replication) which accounts for the _________ of living things on earth DNA Replication Steps in DNA Replication: 1. The DNA molecule becomes untwisted by the enzyme _______ ___________ breaking the H-bonds. The 2 strands that make up DNA become _____________. Each side acts as a _____________. (ie. The weak hydrogen bonds between the paired bases are broken by an enzyme) 2. New complementary ________________, always present in the nucleus, move into place and pair with complementary bases on the ___________ __________. ___ joins to ___ ___ joins to ___ 3. The ____________ nucleotides, through their sugar-phosphate components become ___________ together along the newly forming chain. The enzyme _______ _______________ helps this. (Adds nucleotides to template). 4. When the process is finished, 2 ______________ DNA molecules are present, ____________to each other and to the ___________ molecule. 5. Both DNA will now wind back up into their _________ shape. DNA replication is called __________________________ because each new double helix is composed of an old (___________) strand and a new (____________) strand. Each strand conserves a length of the old strand ___________ assist the ___________ process, _______ together the nucleotides, and assist the ______________ process and many others. When errors are made in replication. A ___________ can arise.









