Note Guide Ohms, power, energy
Name ________________________________________ per _______
Note Guide Ohm’s Law, Power and Electrical Energy
Slide 1 – Voltage (Potential Difference)
1. Voltage measures __________________________. Measure of ____________ ___________
2. Unit for voltage is ________ (__)
3. “Potential difference” flows from ____________ energy to ______________ energy.
4. The potential difference of the battery is _______________.
5. The higher the energy, the greater the ____________ (________________ ___________).
Slide 2 – Current
6. Current is the ____________ of flow of an ____________ ______________.
7. The unit for current (__) is ________________ or ________ or (__).
8. How does the faucet help you understand the concept of electrical current?
Slide 3 –Resistance
9. Resistance-the ___________________ or _____________ the flow of current.
10. The unit for resistance is ________.
11. Draw the symbol:
Slide 4 – Review of Resistance, Current, and Voltage
12. Match the word on the left to the phrase on the right.
_______Resistance (R) How fast?
_______Current (I)
_______Voltage (V)
How much?
How much is it slowed down?
Slide 5 Electrical Measuring Instruments
13. __________________-used in parallel to measure voltage
14. __________________-used in series to measure current
15. ______________________-used to detect a current
16. _____________________-measures resistance
1
Slide 6-7 – Ohm’s Law
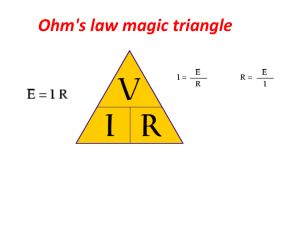
17. State Ohm’s law using symbols.
Georg Simon Ohm
18. If voltage goes _______, the charges move a little faster between atoms and we get ______ current.
19. A current vs. voltage graph shows us if resistance _____________.
20. Resistance of metals ______________ with temperature, because the particles ____________
______________ often causing more resistance.
Slide 8 Calculating Ohm’s Law
So, to find Current, we need to
DIVIDE voltage by resistance
And, to find Resistance, we need to
DIVIDE voltage by current.
Slide 9-10 – Calculate Ohm’s Law
21. Calculate the potential difference (voltage) across a 3 ohm resistor if a 0.5 amp current
flowing through it.
Formula Substitute Answer I =
V =
R =
2
22. A radio with a resistance of 240 ohms is plugged into a 120 V outlet. What is the current
flowing from the outlet?
Formula Substitute Answer I =
V =
R =
Slide 11- Practice
How many ohms of resistance must be present in a circuit that has 120 volts and a current flow equal to 10 amps?
Formula Substitute Answer I =
V =
R =
Slide 12 – Power
23. Is the rate at which ___________ _________.The unit for power ( ) is _____________.
24. State the formula for solving power problems:
So, to find Current, we need to
DIVIDE power by voltage
And, to find Voltage, we need to
Slide 13 where do power units come from:
Watts =
DIVIDE power by current.
____________ = ___________ X _______________
Joules second
Joules
Coulomb
Coulomb
second
3
Slide 14 Electrical Power Problem
If CD player uses 4.5 V with 0.2 amps of current, what is the power that it uses?
P =
I =
V =
Formula Substitute Answer
Slide 15 A toaster uses 950 W on a 120 volt circuit. What is the current?
Formula Substitute P =
I =
V =
Answer
Slide 16 – Electrical Energy
25. The unit for electrical energy is _________________________.
26. The formula for calculating electrical energy is
So, to find Power, we need to
DIVIDE energy by time.
And, to find time, we need to
DIVIDE energy by power.
4
Slide 17-18 Electrical Energy Problem
1. You use your hairdryer for 10 minutes every day. The hairdryer uses 1000 W. How many
kilowatt-hours does your hairdryer use in 12 days?
Formula Substitute Answer E =
P=
T =
2. A refrigerator operates at 3.5 kW of power. It runs for 18 hours per day. How many kilowatt-hours of energy are used per day?
E=
P =
T =
Formula Substitute Answer
3. You use your 60-W DVD player to watch your favorite movie. If the player uses 0.17 kWhr of energy while playing the film, what is the running time of the movie? (Watch your UNITS)
Formula Substitute Answer E =
P =
T =
5