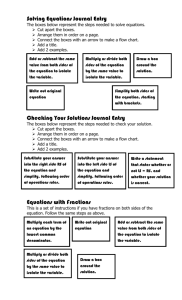
Steps for solving 1 step equations
advertisement

Steps for solving 1 step equations
*Steps for solving 1 step Equations*
You MUST have these steps for ALL equation problems
1. Copy the problem
2. Show the inverse operation on both sides
3. Simplify both sides
{The solution should be the last step of the
equation problem
The CHECK STEP MUST INCLUDE THE FOLLOWING
4. Copy the problem with the solution substituted for the variable
5. Simplify both sides
Final step must show both sides as equal values
Do not assume your solution is correct
Do the arithmetic for the check step
The check step will stop mistakes if done correctly
(Ex. 1)
a + 5 = 11
Here 5 is being added so….
-5 -5
we subtract 5 from both sides to isolate a
a = 6
(solution step)
Check
a + 5 = 11
6 + 5 = 11
11 = 11
substitute 6 for a
(final step) 6 is a solution
________________________________________________________________________
(Ex. 2)
240 = 4z
4
4
60 = z
Check
240 = 4z
Here z is multiplied by 4 so….
we divide both sides by 4 to isolate z
(solution step)
240 = 4 (60)
Substitute 60 for z
240 = 240
*inverse operations are operations that undo each other
Solving Equations
To solve an equation means to find the solution. The solution is the
_______value__ of the variable that makes the sentence true____.
To solve an equation you isolate the ___variable___ on one side. This is
done by using inverse operations. An inverse operation_cancels_another
operation.
Addition and _subtraction_ are inverses of each other.
__Multiplication__ and division are inverses of each other.
There are certain properties of equality that allow us to subtract, add,
multiply and divide from each side of an equation. You will hear me say
over and over, “Whatever you do to one side, you have to do to the other
side.” When solving equations, we have to “keep the balance.” These
properties are listed in the book and will be pointed out as we cover that
property. You must become very familiar with them and know them.
PAY ATTENTION -- BE DILIGENT---YOU WILL SUCCEED!
Solving 2 step operations:
A two- step equation has two operations
The process is made easier if you add or subtract before you multiply
or divide.
Ex. 1.
2 y + 3 = 11
-3 -3
2y = 8
2 2
subtract 3 from both sides
Y=4
Check:
2(4) + 3 = 11
8 + 3 = 11
11 = 11
Ex. 2
x–5=2
3
+5 +5
Add 5 to both sides
x= 7
3
3 x=7 3
3
X = 21
Check:
21 – 5 = 2
2=2
Multiply each side by 3