COCS 304 DATA STRUCTURE
advertisement

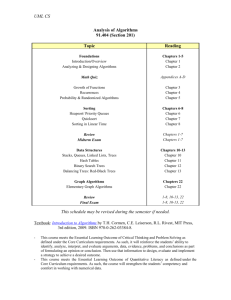
3 2 0 4 Prerequisite COCS 304 Credit Units Data Structures Training Code/No Lab Course name Lecture Units COCS 203 Course Objectives: To introduce students to the notion of programming complexities and performance tradeoffs To expose the students to the implementation of classical data structures such as stacks, queues, lists, sets and maps To teach the students the concepts of recursion, searching and sorting techniques in programming Course Description: This course is a continuation of COCS 202 and COCS 203. While COCS 202 focused on procedural programming issues, COCS 203 on object oriented programming method and COCS 204 focuses on data issues. The course also introduces the notion of complexity and performance tradeoffs in examining classic algorithms such as sorting and searching and classic data structures such as lists, sets and maps. The course will include a mixture of data structure implementation as well as using off-the-shelf components from the Java Collections Framework. Course Outlines: Representation of Numeric Data: range, precision, and rounding errors, arrays, Representation of Character Data: strings and string processing Introduction To Algorithms And Data Structures: Notion of algorithm, time complexity and space complexity, linear and non linear data structures Linked Lists: representation of single, two and multi dimensional arrays, sparse matrices and their representation Recursion in Java Stacks Queues: array based implementation in push & Pop operations, infix to postfix conversion, postfix evaluation, Queues: array based implementation, circular queues, De-queue, Priority Queues Trees: Terminology and basic properties, binary tree, representing binary trees threaded binary trees, Binary search trees. Searching And Sorting: Linear search, binary search, different types of sorting techniques, comparison of searching and sorting methods Course outcomes: Upon finishing this course, the students should have: The knowledge of linear and non-linear data structures The ability to find complexity of algorithms The knowledge of recursion The knowledge of sorting, searching algorithms and techniques Textbook: Nell Date, Daniel T. Joyce, Chip Weems, Object – Oriented Data Structures Using Java, Jones & Batlett Publiher, 2002, ISBN 0763710792 Other Reference: William H. Ford, William R. Topp, Data Structures with Java, Prentice Hall, 2005, ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp, Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach, 2nd edition, Addison Wesley ,March 2010 , ISBN 0136091814 Micheal T Goodrich and Roberto Tamasia, Data Structure & Algorithms in JAVA, Fourth Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2004 Time table for distributing theoretical course contents Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Theoretical course contents Reviews of Java Programming Representation of Numeric Data: range, precision, and rounding errors, arrays, Representation of Character Data: strings and string processing Introduction To Algorithms And Data Structures: Notion of algorithm Time complexity and space complexity, Big O Notation Linear and non linear data structures Linked Lists: representation of single, two and multi dimensional arrays Sparse matrices and their representation Recursion Stacks Queues: array based implementation in push & Pop operations, infix to postfix conversion, postfix evaluation, Queues: array based implementation, circular queues, De-queue, Priority Queues Trees: Terminology and basic properties, binary tree, representing binary trees threaded binary trees, Binary search trees. Searching And Sorting: Linear search, binary search, Sorting techniques, comparison of searching and sorting methods Reviews Final exam. Remarks Exam 1 Exam 2 Grading: Quiz 1 Quiz 1 Homework 1 Homework 2 Homework 3 Homework 4 Labs Exercises Lab Exam Exam 1 Exam 2 Final Exam TOTAL 5 5 4 4 4 4 7 7 10 10 40 100