Angles and Radian Measure 6.3
advertisement

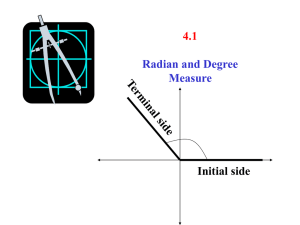
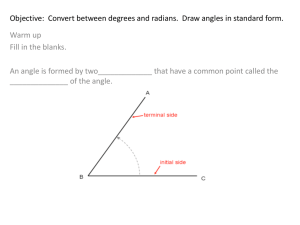
6.3 Angles and Radian Measure Section 6.3 includes three parts. Once all sets of notes and assignments are completed, a graded assignment will be given. Here is the checklist with a pacing guide to ensure you are staying on track to finish the section when needed. Part 1 (Days 1-2) o o Extending Angle Measure (example 1) Arc Length and Radian Measure (example 2) o Converting Between Degrees and Radians (examples 3 and 4) Assignment: pg. 441 # 1-33 odds Part 2 (Day 3) o o Arc Length and Angular Speed Arc Length (example 5) Central Angle Measure (example 6) Assignment: pg. 441 # 47- 63 odds Part 3 (Days 4-5) o o Linear and Angular Speed (Example 7) Assignment: pg. 442 # 69-83 odds Days 6-7 will be a graded assignment of the section. You will turn in your completed notes and assignments for a grade equal in size to the graded assignment. Extending Angle Measure (pg. 433- 434) In an angle, the starting position of the ray is called the _______________________ and its final position after the rotation is called the__________________________. An angle is said to be in standard position is its vertex is at the _____________ and its initial side is on the _____________________________________. Angles formed by different rotations that have the same initial and terminal sides are called _____________________________. Follow Example 1: Find three angles coterminal with an angle of 600 in standard position. Practice 1: Find three angles coterminal with an angle of300 in standard position. Arc Length (pg. 434- 435) The length of an arc depends on the _____________________ of the circle and the measure of the ____________________________ that it intercepts. The length l of an arc is l= Example 2: Finding an Angle Given an Arc Length An arc in a circle has an arc length l which is equal to the radius r. Find the measure of the central angle that the arc intercepts. Practice 2: An arc in a circle has an arc length l which is equal to one- half of its radius r. Find the measure of the central angle that the arc intercepts. Radian Measure (pg. 435- 437) Because it simplifies many formulas in calculus and physics, radians are used as a unit of ___________________________________ in mathematical and scientific applications. Angle measurement in radians can be described in terms of the ____________________ which is the circle of radius 1 centered at the ___________________. The Unit Circle Converting Between Degrees and Radians (pg. 437- 438) П radians = ____________0 Dividing both sides by П shows that 1 radian = ______________ ≈ _______________ Similarly, both sides of the original equation can be divided by 180. To convert radians to degrees, multiply by To convert degrees to radians, multiply by Example 3: Converting from Radians to Degrees Convert the following radian measurements to degrees. Practice 3: Convert the following radian measurements to degrees. D. 𝜋 9 E. 3𝜋 5 F. 5𝜋 Example 4: Convert from Degrees to Radians Convert the following degree measurements to radians. a. 750 b. 2200 c. 4000 Practice 4: Convert the following degree measurements to radians. d. 1500 e. 3300 Assignment: pg. 441 # 1-33 odds f. 5400 Arc Length and Angular Speed The formula for arc length can also be written in terms of radians. An arc with central angle measure θ radians has length In other words, the arc length is the radius time the radian measure of the central angle of the arc. Example 5: Arc Length The second hand on a clock is 6 inches long. How far does the tip of the second hand move in 15 seconds? solution: Every 60 seconds, the second hand makes a full revolution, or ________ radians. During a 15 second interval it will make ___________ of a revolution, moving through an angle of _______________________ radians, so the tip of the second hand travels along an arc with a central angle measurement of ______. therefore, the distance that the tip moves in 15 seconds is the arc length l = rθ = ______________ = ____________ ≈__________ inches Practice 5: The second hand on a clock is 5 inches long. How far does the tip of the second hand move in 45 seconds? Example 6: Central Angle Measure Find the central angle measure (in radians) of an arc of length 5 cm on a circle with a radius of 3 cm. solution: Solve the arc length formula l = rθ for θ. Practice 6: Find the central angle measure (in radians) of an arc of length 11 cm on a circle with a radius of 4 cm. Assignment: pg. 441 # 47 – 63 odds Linear and Angular Speed (pg. 439- 440) Suppose that a wheel is rotating at a constant speed around its center. There are two ways to measure the speed of a point on the outer edge of the wheel, __________________________ speed and ______________________ speed. linear speed = ___________ = _________ angular speed = __________ = _________ where θ is the ___________________________ of the angle through which the object travels in time t. Notice that linear speed = _____________________________ Example 7: Linear and Angular Speed A merry-go-round makes 8 revolutions per minute. a. What is the angular speed of the merry-go-round in radians per minute? b. How fast is a horse 12 feet from the center traveling? c. How fast is a horse 4 feet from the center traveling? Practice 7: A circular mobile above a baby’s crib makes 5 revolutions per minute. a. What is the angular speed of the mobile in radians per minute? b. How fast is a toy 9 inches from the center traveling in feet per minute? c. How fast is a toy 6 inches from the center traveling in feet per minute? Assignment: pg. 442 # 69- 83 odds