High School Model C - Workshops+SJCOE Workshop Management
advertisement
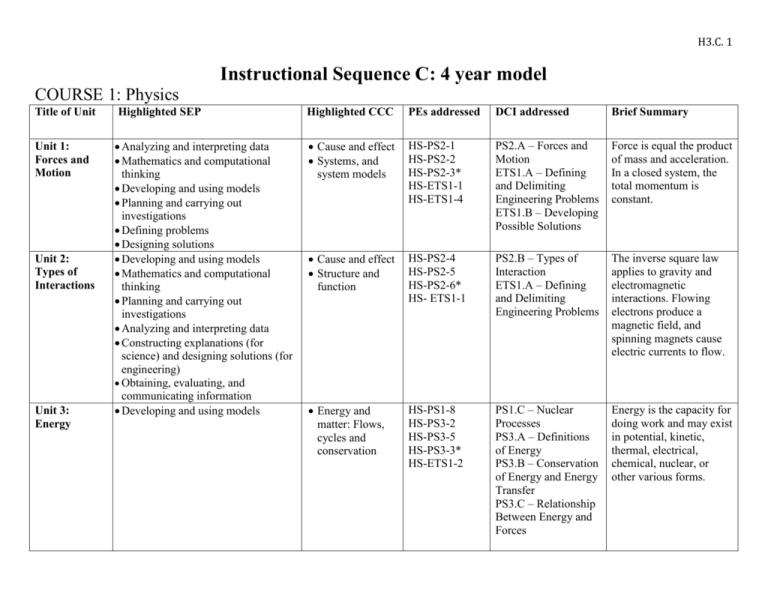
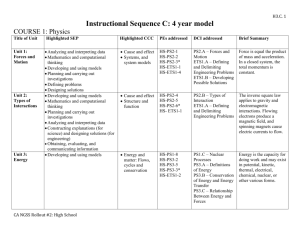
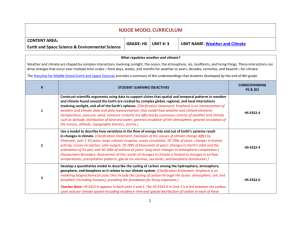
H3.C. 1 Instructional Sequence C: 4 year model COURSE 1: Physics Title of Unit Highlighted SEP Highlighted CCC PEs addressed DCI addressed Brief Summary Unit 1: Forces and Motion Analyzing and interpreting data Mathematics and computational thinking Developing and using models Planning and carrying out investigations Defining problems Designing solutions Developing and using models Mathematics and computational thinking Planning and carrying out investigations Analyzing and interpreting data Constructing explanations (for science) and designing solutions (for engineering) Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information Developing and using models Cause and effect Systems, and system models HS-PS2-1 HS-PS2-2 HS-PS2-3* HS-ETS1-1 HS-ETS1-4 PS2.A – Forces and Motion ETS1.A – Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems ETS1.B – Developing Possible Solutions Force is equal the product of mass and acceleration. In a closed system, the total momentum is constant. Cause and effect Structure and function HS-PS2-4 HS-PS2-5 HS-PS2-6* HS- ETS1-1 PS2.B – Types of Interaction ETS1.A – Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems The inverse square law applies to gravity and electromagnetic interactions. Flowing electrons produce a magnetic field, and spinning magnets cause electric currents to flow. Energy and matter: Flows, cycles and conservation HS-PS1-8 HS-PS3-2 HS-PS3-5 HS-PS3-3* HS-ETS1-2 PS1.C – Nuclear Processes PS3.A – Definitions of Energy PS3.B – Conservation of Energy and Energy Transfer PS3.C – Relationship Between Energy and Forces Energy is the capacity for doing work and may exist in potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, or other various forms. Unit 2: Types of Interactions Unit 3: Energy H3.C. 2 Unit 4: Asking questions Waves and Using mathematics and Electromagne computational thinking tic Radiation Engaging in argument from evidence Obtaining, evaluating and communicating information Energy & matter Cause & effect Systems & system models Stability and change HS-PS4-1 HS-PS4-3 HS-PS4-4 HS-PS4-5* HS-PS4-2 HS- ETS1-1 PS4.A – Wave Properties PS4.B – Electromagnetic Radiation PS4.C – Information Technologies and Instrumentation PS3.D – Energy in ETS1.A – Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems Electromagnetic radiation has many applications, and can be modeled as a wave of changing electric and magnetic fields or as particles called photons. H3.C. 3 Course 2: Chemistry Unit Key SEP Unit 1: Structures and Properties of Matter Developing & using models Planning and carrying out investigations Engaging in argument from evidence Developing and using models Using mathematics and computational thinking Constructing explanations and designing solutions Unit 3: Using mathematics and Conservation of computational thinking Energy and Energy Developing and using models Transfer Planning and carrying out investigations Analyzing and interpreting data Asking questions and defining problems Constructing explanations and designing solutions Unit 2: Chemical Reactions Key CCC Patterns Cause and effect Energy and matter Structure and function PEs addressed DCI addressed HS-PS1-1 HS-PS1-2 HS-PS1-3 HS-PS1-4 PS1.A – Structure and Properties of Matter Patterns Energy and matter Stability and change Cause and effect HS-PS1-5 HS-PS1-6* HS-PS1-7 HS-ETS1-2 Energy and matter Scale, proportion, and quantity HS-PS3-1 HS-PS3-4 HS-PS3-3 Brief Summary The properties of matter are a function of atomic and molecular structure. Atomic and molecular structure can be inferred from the properties of bulk matter. PS1.B – Chemical Chemical processes can reactions be predicted and ETS1.C – explained knowing the Optimizing the properties of the Design Solution reactants, conditions, and the Law of the conservation of mass PS3.B – Energy cannot be created Conservation of nor destroyed, but may Energy and Energy change form. The Transfer entropy of an isolated system increases over PS3.D – Energy in time. Chemical Processes and Everyday Life H3.C. 4 Course 3: Biology Title of Unit Highlighted SEP Unit 1: DNA to cells to systems Developing & using models Planning and carrying out investigations Constructing explanations and designing solutions. Unit 2: Cell reproduction linked to growth. Developing & using models Unit 3: Light energy to chemical energy to life. Developing & using models Constructing explanations and designing solutions Highlighte d CCC Systems and System Models Structure and Function Stability and Change Systems and System Models PEs addressed HS-LS1-1 HS-LS1-2 HS-LS1-3 Energy and Matter HS-LS1-5 HS-LS1-6 HS-LS1-7 HS-LS1-4 HS-LS2-1 Unit 4: Using Mathematical and Scale, Influences Computational Thinking proportio HS-LS2-2 on n and population quantity growth. Unit 5: Developing & using models Systems HS-LS2-3 Interconnect Using Mathematical and HS-LS2-4 and edness of HS-LS2-5 System Computational Thinking matter and Models Constructing Explanations energy Energy and Designing Solutions cycling. and Matter DCI addressed Brief Summary LS1.A-Structure and Function How do we know that DNA codes for proteins that actually do things in cells? How do systems work in a multi-celled organism and what happens if there is a change in the system? How do organisms survive even when there are changes in their environment? Understanding the relationship between DNA and proteins and how these relate to how a cell functions. Building on concepts of cells as living organisms that can carry on life and how cells work together to become organs and organ systems. Homeostasis is defined and examples given. LS1.B- Growth How do organisms grow and still maintain fidelity in how their cells and development perform? of organisms What happens after a cell divides? In order for organisms to grow there has to be some fidelity between parent cells and daughter cells this happens during cell division. LS1.CHow do living things acquire energy for life? Organization for How do organisms store energy? matter and How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration connected? energy flow in What components are necessary to build more complex molecules? organisms Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are linked to the movement of energy through plants and animals. Understanding how they interact together to provide energy for living systems is discussed in this unit. LS2.AHow and why do populations change over time? Interdependent Density dependent and independent factors, what determines relationships in whether a population grows or not. ecosystems LS2.B- Cycles of matter and energy transfer in ecosystems Why is the cycling of matter and energy important? How is matter and energy linked in ecosystems? 10% law of energy, models of cycling of matter (carbon and nitrogen) and how linked to energy. H3.C. 5 Unit 6: Changes in ecosystems natural and human. Unit 7: Who helps who survive? Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions Stability and Change HS-LS2-6 HS-LS2-7* HS-ETS1-3 Engaging in argument from Evidence Cause and Effect HS-LS2-8 Unit 8: Why do we look like our parents? Unit 9: Variation, necessary for life. Asking Questions and defining Problems Cause and Effect HS-LS3-1 Analyzing and Interpreting Data Engaging in Argument from Evidence Scale, Proporti on and Quantity HS-LS3-2 HS-LS3-3 Unit 10: How we are all related. Obtaining, Evaluating and Communicating Information Patterns HS-LS4-1 Unit 11: Evidence of Natural Selection Analyzing and Interpreting Data Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions Analyzing and Interpreting Data Using Mathematics and Computational Thinking Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions Engaging in Argument from Evidence Patterns Cause and Effect HS-LS4-2 HS-LS4-3 Patterns Cause and Effect HS-LS4-4 HS-LS4-5 HS-LS4-6 Unit 12: Why adapt? LS2.CEcosystem dynamics, functioning, and resilience LS2.D- Social interactions and group behavior What types of interactions cause changes in ecosystems that ultimately effect populations? To what extent can humans “undo” their negative impact on the environment? Conservation biology, unintended consequences, human impacts. How do organisms ensure that their gene pool gets passed on? What affects a population’s chance of survival? Individuals raising young rather than having young, colonies, and herds used for protecting young so traits passed on and other modes of kin selection. LS3.AHow are characteristics of one generation passed to the next? Inheritance of What allows traits to be transmitted from parents to offspring? traits How DNA carries the code for traits and how this gets passed from generation to generation. LS3.B- Variation What is the chance of a trait being passed from one generation to of traits another? What happens if there is a mutation in that gene? What combinations of alleles are possible? What contributes to phenotypes? Punnett squares, prediction models, how do we get variation? LS4.A- Evidence What evidence shows that different species are related? of common How did modern day humans evolve? ancestry and Common ancestor and branches of change. Explanation of how diversity humans evolved. LS4.B-Natural What processes influence natural selection? Selection What do changes in patterns of phenotypes mean? What Darwin observed and the conclusions he drew from his observations. LS4.CAdaptation and human effects on biodiversity How does natural selection lead to adaptation in populations? How do changes in ecosystems influence populations? What are the cause and effect criteria for changes in populations? Populations maintaining diversity. Selective pressures and what that means for survival. H3.C. 6 Course 4: Earth/Space Science Title of unit Key SEP Key CCC Unit 1: Oil & Gas Developing and using models Engaging in an argument from evidence Energy and matter: Flows, cycles, and conservation Unit 2: Climate Developing and using models Analyzing and interpreting data Systems and system models Energy and matter: Flows, cycles, and conservation Stability and Change Cause and effect Unit 3: Mountains, Valleys, and Coasts Plan and conduct investigation s Developing and using models Stability and change Unit 4: Water & Farming Planning and carrying out investigation s Analyzing & interpreting data Systems and systems models Cause and effect Stability and change PE’s addressed HS-ESS2-6 HS-ESS2-7 HS-ESS2-2 HS-ESS2-4 HS-ESS2-6 HS-ESS3-2 HS-ESS3-5 HS-ESS3-6 HS-ETS1-1 HS-ESS2-1 HS-ESS2-5 HS-ESS3-1 HS-ESS3-5 HS-ETS1-3 HS-ESS2-5 HS-ESS3-1 HS-ESS3-3 HS-ESS3-5 HS-ETS1-1 HS-ETS1-4 DCI’s addressed ESS2.A Earth Materials and Systems ESS2.E Bio geology ESS3.A Natural Resources Brief Summary Where do oil and gas come from? What is the impact of driving cars and using other fossil fuels on the Earth system? Oil and gas are crucial resources that allow us to harness energy from ancient life, but we also unleash ancient carbon into our atmosphere. ESS2.A Earth Materials and What regulates weather and climate? Systems What effects are humans having on the ESS3.C Human Impacts on climate? Earth Systems Data reveal that carbon in our atmosphere ESS3.D Global Climate Change has a big impact on global temperatures and ETS1.A Defining and Delimiting climate. Humans, in turn, have a big impact Engineering Problems on carbon in our atmosphere. ESS2.A Earth Materials and How did California’s landscape get to look Systems the way it does today? ESS2.C The Role of Water in What forces shape the Earth’s surface? Earth’s Surface Processes How do those processes affect humans? ESS3.B Natural Hazards Water shapes and sculpts our landscapes. ESS3.D Global Climate Change The process is sometimes thought of as ETS1.B Developing Possible slow and steady, but often occurs as Solutions catastrophic events when driving forces exceed resisting forces. ESS2.C: The Roles of Water in Why do droughts have such a strong impact Earth’s Surface Processes on California and other parts of the world? ESS3.A Natural Resources How will changes in climate affect our ESS3.D Global Climate Change water resources? ETS1.A Defining and Delimiting California depends on its precious water Engineering Problems resources to sustain its people and its farms. ETS1.C Developing Possible Solutions H3.C. 7 Developing Cause and Effect Unit 5: and using Causes and models effects of Earthquakes Constructing explanations HS-ESS1-5 HS-ESS2-1 HS-ESS2-3 HS-ESS3-1 ESS2.A Earth Materials and Systems ESS2.B Plate Tectonics and Large-Scale System Interactions What causes earthquakes? Earthquakes and motion at the surface give clues to what goes on deep inside the Earth. How do Earth’s natural systems influence our cities? How do cities affect Earth’s natural systems? The majority of California residents live in urban areas that were shaped by the natural environment. Our continued growth in these areas requires that we also think about how human activity in turn affects the natural environment. What are stars made of? How do stars glow, and what causes them to be different colors? We are made of star-stuff and we depend on our closest star, Sun for all our energy. The light from stars tells us more about what they are and how they shine. How did the Universe begin? And how do we know? What are the predictable patterns of movement in our solar system? The structure of objects in our Universe and the motions of all bodies within it are driven by the competition between the explosive force of the Big Bang and the attractive force of gravity. Unit 6: Urban geoscience Defining problems (for engineering) Obtaining, evaluating, and using information Structure and function Systems and system models HS-ESS3-1 HS-ESS3-4 HS-ETS1-2 HS-ETS1-4 ESS3.C Human Impacts on Earth Systems ETS1.B Developing Possible Solutions ETS1.C Optimizing Design Solutions Unit 7: Star Stuff Developing and using models Constructing explanations Energy and Matter, Patterns Cause and effect HS-ESS1-1 HS-ESS1-3 HS-ESS1-6 ESS1.A The Universe and Its Stars ESS1.C The History of Planet Earth Unit 8: Motion in the Universe Constructing explanations Using mathematics and computation al thinking Scale, proportion, & quantity Structure and function HS-ESS1-2 HS-ESS1-4 HS-ESS1-6 ESS1.A The Universe and Its Stars ESS1.B Earth and the Solar System ESS1.C The History of Planet Earth