Social Studies Western Hemisphere Learning Targets
advertisement

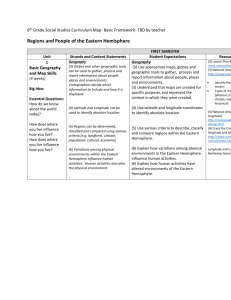
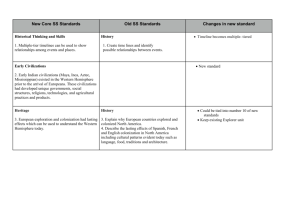
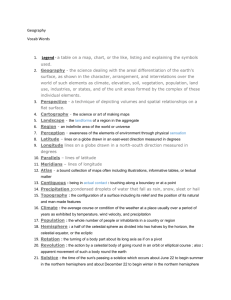
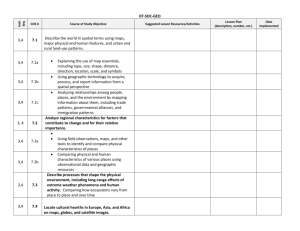
Geography of the Western Hemisphere Learning Targets and Success Criteria GEO4: Globes and other geographic tools can be used to gather, process and report information about people, places and environments. Cartographers decide which information to include in maps. We are learning to use appropriate maps, globes and geographic tools to find information about people, places and environments. We are looking for the parts of a map, globe or geographic tool (i.e., legend/key, title, compass rose) that help us to understand the information presented. GEO5: Latitude and longitude can be used to make observations about location and generalizations about climate. We are learning to use latitude and longitude to locate places in the Western Hemisphere. We are looking for a line of latitude and a line of longitude that intersect at a specific place in the Western Hemisphere. We are learning to use latitude to form a general idea about the climate of a location. We are looking for locations that are closer to the Equator to have warmer climates than locations farther from the Equator. GEO6: Regions can be determined using various criteria (e.g. landform, climate, population, cultural or economic). We are learning to identify and describe regions within the Western Hemisphere. We are looking for a common characteristic (landform, climate, population, culture, economics) that can be used to identify a region. GEO7: Variations among physical environments within the Western Hemisphere influence human activities. Human activities also alter the physical environment. We are learning to explain how characteristics of different physical environments affect how people live and work in the Western Hemisphere. We are looking for the relationship between the physical environment and the job and outdoor recreational opportunities specific to an area. We are learning to explain how humans alter the physical environment. We are looking for examples of how humans have changed the physical environment to meet their needs. Unit 1: Geography of the Western Hemisphere Learning Targets Last revised: August 7, 2013 ECON13: Information displayed in circle graphs can be used to show relative proportions of segments of data to an entire body of data. We are learning to read, interpret and construct circle (pie) graphs. We are looking for the relationship between the size of each section (part) in the circle graph (whole) and the value it represents. ECON15: The availability of productive resources (i.e., human resources, capital resources and natural resources) promotes specialization that leads to trade. We are learning to explain how the availability of productive resources in a region promotes specialization and results in trade. We are looking for how regions use their resources to determine what to produce and trade. ECON16: The availability of productive resources and the division of labor impact productive capacity. We are learning to explain how the division of labor affects productive capacity. We are looking for how dividing a job into separate tasks increases productivity (how many items are made). ECON17: Regions and countries become interdependent when they specialize in what they produce best and then trade with other regions to increase the amount and variety of goods and services available. We are learning to explain how regions and countries are interdependent, or depend on each other, for goods and services. We are looking for examples of how regions and countries specialize in what they produce best, and trade for items they cannot produce easily. Unit 1: Geography of the Western Hemisphere Learning Targets Last revised: August 7, 2013