chemistry strand – atoms, elements, and compounds
advertisement

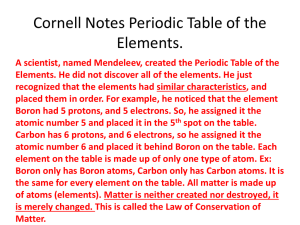
CHEMISTRY STRAND – ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND COMPOUNDS 1. Define each of the following terms and give examples of each: physical property, physical change, chemical property, chemical change. 1b. Define the following terms: Ductility, Conductivity, Malleability, Brittle, Lustre, Solubility 2. What do the following represent: atomic number, atomic mass, mass number 3. Locate the following on the periodic table and give an example of each: solids, liquids, gases, metals, metalloids, non-metals, hydrogen, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases. 3b. Is the periodic table organized according to atomic mass or atomic number? Explain. 4. What is the purpose for the staircase region on the periodic table? What type of elements occupy this region? 5. What does the group number indicate about the structure of the atoms of all the elements in that group? 6. What does the period number indicate about the structure of the atoms of all the elements in that period? 7. What are valence electrons? How many valence electrons do Alkali metals, Halogens, and Noble Gases have? 8. What are the maximum number of electrons in shells – 1,2,3 and 4. 9. Compare and contrast the physical properties of: metals, non-metals, and metalloids. Which are the only elements to be liquid at room temperature? 10. Write the Standard Atomic Notation and draw Bohr-Rutherford diagrams for the following elements: K, Be, O, Ne 11. Name the chemical families/groups learned about on the periodic table and provide their group number. 12. What dictates/determines the placement of an element into a specific family/group? 13. Which family/group on the periodic table contains the most reactive metals? 14. Which family/group contains the most reactive non-metals? 15. Which family/group contains inert (unreactive) elements? 16. Which family/group contains elements whose atoms have filled outer energy levels? 17. Compare Ionic compounds with Molecular compounds by explaining the options below a) Gains/Loses or Shares Electrons b) Metals must be present or only non-metals present c) Forms covalent bonds or ionic bonds d) Atoms will form a positive or negative charge or atoms will take on a slight positive or negative charge 18. Explain why ice floats on water even though they are both made of the same substance? Why is ice floating on water uniquely different than most solids in a liquid? 19. Identify the difference between elements and compounds. Organize the following as either compound or element: Water, Air, Gold, Sulfur, Carbon dioxide, oxygen, Methane, Silver, Bronze. 20. What is a molecular element? Name all of the diatomic elements which are also molecular elements (Hint: HOFBrINCl) Physics STRAND – Electricity 1. Define the following: static electricity, current electricity. Provide examples of each. 2. How can an object become positively charged? Negatively charged? 3. Define and give two (2) examples of insulators and conductors. 4. The movement of which subatomic particle is responsible for static charges on objects? 5. Draw a diagram of what happens to the charges on a neutral ebonite rod (or glass rod) when it is rubbed with neutral fur (or silk). Use information from the Electrostatic Series. What will happen if this rubbed ebonite rod is brought toward scraps of neutral paper? 6. Compare conduction, induction, and friction. 7. Which direction does electricity flow from and towards? 8. Compare the following: parallel circuit and series circuit. Draw a simple parallel and series circuit with 2 loads, a switch, and a two-cell battery. 9. Define electrical resistance and list the four (4) factors that affect resistance. For each factor, state the effect of each factor on resistance. 10. Complete the following chart that shows the symbols and units for each quantity. Quantity Symbol V I resistance 11. Define and draw the symbols fro each of the following parts of a circuit: a) cell e) conducting wire b) load f) motor c) bulb g) battery d) switch h) resistor Unit (unit symbol) 12. Define potential difference and current and describe two ways in which it can be calculated. 13. Rewrite the formulas used in calculating ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s laws. 14. Using the proper symbols, draw the following series circuit: a) A closed circuit with a battery, a closed switch, a light bulb, an ammeter measuring the current, and a voltmeter measuring the potential difference across the battery. b) An open circuit with 2 cells, an open switch, 3 light bulbs and a voltmeter measuring the potential difference across the 2nd light bulb. 15. Using the proper symbols, draw the following parallel circuits: a) A complete (closed) circuit with 1 cell, 3 motors, and a switch controlling each motor. b) An incomplete (open) circuit with 2 cells, 2 switches (one controlling each load), 1 bulb, 1 motor, and an ammeter measure the current through the motor. Use the GRASS method for the following questions: 16. A current of 0.50 A flows through a light bulb when a potential difference of 120 V is placed across the light bulb. What is the resistance of the light bulb? 17. The resistance of a conductor is 22 ohms when a current of 0.54 A runs through it. Calculate the potential difference between the ends of the conductor. 18. Familiarize yourself with rearranging the formulas learned in this unit. Biology STRAND 1. Distinguish between a biotic factor and an abiotic factor. Provide a definition and examples of each factor. 2. Which abiotic factors were altered in the pond study and how do effect ponds? 3. Describe the different modes of species interactions: competition, predation, mutualism, commensalism, parasitism. 4. What are invasive species? How can they be introduced into new ecosystems? 5. Describe primary and secondary succession. What causes each? 6. What is a food chain? What is a food web? What are trophic levels? Provide some examples for each. 7. What is a producer? What is a consumer? What is a decomposer? Define the four types of consumers: herbivores, omnivores, carnivores and scavengers. Which of these types of consumers are humans? 8. Refer to the following food chain: daffodil → butterfly → dragonfly → frog → snake (a) Label the organisms in this food chain by trophic level? (b) Which organism is the producer? The top carnivore? How do you know? 9. Which organisms do photosynthesis? What is needed to do photosynthesis and what is produced in photosynthesis? 10. What does sustainability in an ecosystem mean? 11. Distinguish between a population and a community? Space Explotation STRAND 1. Define the following terms: star, planet, universe, star, galaxy, supernova, black hole, natural satellite, artificial satellite, orbit, astronomical unit, and light year. 2. Use an acronym (or other memory aid) to help you remember the order of the planets from the Sun. Which planets take the shortest and longest time to revolve around the sun? 3. Name the different layers of the sun? Which layer is the hottest and where nuclear fusion occurs? Explain what is nuclear fusion? 4. Explain the difference between the heliocentric model and geocentric model 5. What is the relationship between size, colour, and absolute magnitude of a star? 6. Which stars live the longest? Explain. 7. What happens most of the time to meteorites that enter our atmosphere? 8. How are the temperatures and colours of stars related? Give examples. 9. Define luminous and nonluminous objects and give an example of each. 10. Label the diagram of the Sun on page 443. 11. Define and list the gas planets and rock/terrestrial planets. 12. What are the three characteristics of a planet? Why is Pluto not considered a planet? 13. What are the four seasons. What is a solstice? What is an equinox? What causes the seasons to occur? 14. Compare asteroids, meteors, comets. 15. Explain the difference between a meteoroid, meteor, and meteorite by using these terms in a sentence. 16. Compare and contrast a solar eclipse to a lunar eclipse. 17. How long is the lunar cycle? 18. Draw the lunar cycle? What is the difference between the waxing and waning phases of the moon? Label the waning and waxing phases on your drawing. 19. What is the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Explain how it works.