Horizontal Curriculum Map by 3-Week Block COURSE: LOC 9 Block
advertisement
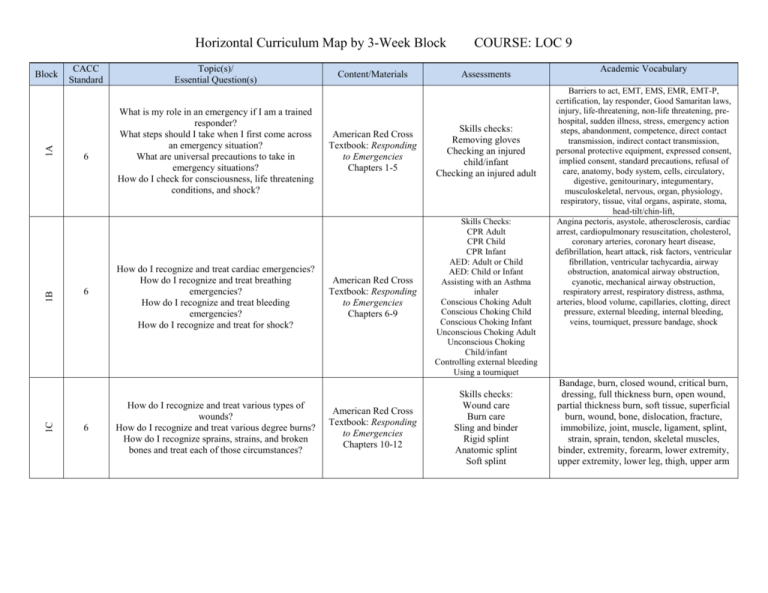
Horizontal Curriculum Map by 3-Week Block 1C 1B 1A Block CACC Standard 6 6 6 Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) What is my role in an emergency if I am a trained responder? What steps should I take when I first come across an emergency situation? What are universal precautions to take in emergency situations? How do I check for consciousness, life threatening conditions, and shock? How do I recognize and treat cardiac emergencies? How do I recognize and treat breathing emergencies? How do I recognize and treat bleeding emergencies? How do I recognize and treat for shock? How do I recognize and treat various types of wounds? How do I recognize and treat various degree burns? How do I recognize sprains, strains, and broken bones and treat each of those circumstances? Content/Materials COURSE: LOC 9 Assessments American Red Cross Textbook: Responding to Emergencies Chapters 1-5 Skills checks: Removing gloves Checking an injured child/infant Checking an injured adult American Red Cross Textbook: Responding to Emergencies Chapters 6-9 Skills Checks: CPR Adult CPR Child CPR Infant AED: Adult or Child AED: Child or Infant Assisting with an Asthma inhaler Conscious Choking Adult Conscious Choking Child Conscious Choking Infant Unconscious Choking Adult Unconscious Choking Child/infant Controlling external bleeding Using a tourniquet American Red Cross Textbook: Responding to Emergencies Chapters 10-12 Skills checks: Wound care Burn care Sling and binder Rigid splint Anatomic splint Soft splint Academic Vocabulary Barriers to act, EMT, EMS, EMR, EMT-P, certification, lay responder, Good Samaritan laws, injury, life-threatening, non-life threatening, prehospital, sudden illness, stress, emergency action steps, abandonment, competence, direct contact transmission, indirect contact transmission, personal protective equipment, expressed consent, implied consent, standard precautions, refusal of care, anatomy, body system, cells, circulatory, digestive, genitourinary, integumentary, musculoskeletal, nervous, organ, physiology, respiratory, tissue, vital organs, aspirate, stoma, head-tilt/chin-lift, Angina pectoris, asystole, atherosclerosis, cardiac arrest, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, cholesterol, coronary arteries, coronary heart disease, defibrillation, heart attack, risk factors, ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, airway obstruction, anatomical airway obstruction, cyanotic, mechanical airway obstruction, respiratory arrest, respiratory distress, asthma, arteries, blood volume, capillaries, clotting, direct pressure, external bleeding, internal bleeding, veins, tourniquet, pressure bandage, shock Bandage, burn, closed wound, critical burn, dressing, full thickness burn, open wound, partial thickness burn, soft tissue, superficial burn, wound, bone, dislocation, fracture, immobilize, joint, muscle, ligament, splint, strain, sprain, tendon, skeletal muscles, binder, extremity, forearm, lower extremity, upper extremity, lower leg, thigh, upper arm 2C 2B 2A Block CACC Standard 6 6 Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) Content/Materials Assessments How do I treat injuries of the head, neck, and spine? How do I treat injuries to the chest, abdomen, and pelvis? American Red Cross Textbook: Responding to Emergencies Chapters 13-16 Skills: Responding to Head, neck spine injury Responding to chest, abdomen, pelvis injury Assisting with an Epinephrine Autoinjector How do I treat insect bites and stings? What are the signs and symptoms of substance abuse and misuse and how would I treat someone suspected of substance abuse or misuse? How do I treat heat related illnesses and cold related injuries? American Red Cross Textbook: Responding to Emergencies Chapters 17-19 Skills: Treating bites and stings Responding to heat illness Responding to cold injuries How do I respond to water-related emergencies? How do I respond to pediatric, older adult, and special first aid situations? How would I respond to an emergency childbirth situation? How do I respond in unique wilderness situations? American Red Cross Textbook: Responding to Emergencies Chapters 20-23 Skills: Water related emergencies Pediatric emergencies Older adult emergencies Wilderness emergencies Academic Vocabulary Concussion, manual stabilization, spine, vertebrae, abdomen, chest, pelvis, genitals, rib cage, sternum, absence seizure, aura phase, clonic phase, complex partial seizure, diabetes, diabetic emergency, epilepsy, fainting, febrile seizure, generalized tonic-clonic seizure, glucose, grand mal seizure, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, insulin, partial seizure, post-ictal phase, simple partial seizure, stroke, tonic phase, transient ischemic attack, absorbed poison, anaphylaxis, ingested poison, inhaled poison, injected poison, poison, poison control center Antivenin, Lyme disease, rabies, Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, addiction, cannabis products, dependency, depressant, drug, hallucinogen, inhalant, medication, overdose, stimulant, substance abuse, substance misuse, synergistic effect, tolerance, withdrawal, frostbite, heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heat stroke, hypothermia, hypothalamus Distressed swimmer, drowning, reaching assist, throwing assist, wading assist, Alzheimer’s Disease, child abuse, child neglect, disability, hearing loss, impairment, mental function, motor function, motor impairment, sensory function, sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), vision loss, disaster, remote, wilderness 3C 3B 3A Block CACC Standard Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) Content/Materials 6O How can I apply the skills I have learned in Basic First Aid and CPR to a variety of field scenarios? Students will spend six days having field tests of all major skills taught in the basic first aid/CPR course 6O What can I do to personally prepare myself and my family for likely emergencies? What can I do to mitigate negative consequences of emergencies for me and my family? What is the Chemistry of fire? How can I mitigate fire risk? How can I suppress small fires and decide how big is too big a fire to attempt to suppress? 6O How do I triage multiply victims in a disaster situation? What is the I-D-M-DEAD triage system? How do I maintain sanitary conditions in a disaster situation and ensure water purification? How do I conduct a search and rescue sizeup? When and how should I go about conducting search and rescue operations as a teen CERT member? FEMA Community Emergency Response Team Participant Manual Unit 1 Unit 2 IS100a on FEMA independent study FEMA Community Emergency Response Team Participant Manual Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Assessments Academic Vocabulary No new academic vocabulary Students will spend six days having field tests of all major skills taught in the basic first aid/CPR course Family Emergency Plan Roles in School Emerg Plan Hazard Mitigation Activity Fire Suppression activity IS100A Triage scenario using flowchart on page 133 of CERT participant manual Unit 5 scenario Hazard mitigation, preparedness, infrastructure, emergency operations plan, suppression, emergency, sheltering, structural, impact, operations, logistics, personal protective equipment, preparedness, intentional, technological, natural, sizeup, precautions, utility, extinguishing, evacuation, fire triangle, exothermic chemical reaction, Class A/B/C/D/K fires, placards, hazardous materials, I-D-M-DEAD triage system, sanitation, purification, triage, morgue, centralized, decentralized, immediate, delayed, minor, accessible, expandable, head-to-toe assessment (DCAP-BTLS) acronym, inhalation, amputation, impaled, dislocation, displaced, structures, terrain, stable, priorities, resources, masonry, reinforcing, construction, utilities, recessed, disorientation, collapses, void, search markings, evaluate, triangulation, grid search, leveraging, crib, extrication, carry 4C 4B 4A Block CACC Standard Topic(s)/ Essential Question(s) 6O What is the structure of CERT teams within the larger Incident Command System? What is the Incident Command System? How does the ICS link to how NVMI will respond to emergencies? What documentation is required when I am activated as part of CERT? What are the protocols I should follow when reporting as part of CERT to an incident? What is the psychology associated with disaster situations? How should my knowledge of disaster psychology shape my response to disasters? 6O 6O How do I respond to Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear, or Explosive device terrorist situations? How can I recognize the signs of possible terrorism? What is sheltering in place? How can I prepare my home and community/school for possible terrorist attacks? How can I apply and demonstrate the skills I have learned this year to school emergency situations? Content/Materials FEMA Community Emergency Response Team Participant Manual Unit 6 Unit 7 IS 317: FEMA CERT Assessments Tabeltops on NVMIlikely scenarios for CERT deployment IS 317 completion Academic Vocabulary Tabletop, disaster psychology, documentation, Incident Command System, structure, disaster psychology, trauma, physiological symptoms, stress, Critical Incident Stress Debriefing (CISD), impact phase, inventory phase, rescue phase, recovery phase, cognitive functions, mediating factors, traumatic. trauma NVMI Emergency Plan FEMA Community Emergency Response Team Participant Manual Unit 8 Unit 9 FEMA Terrorism Course Cadets will have six different scenarios based in the NVMI emergency plan and do both tabletop and field exercises on their response to those situations CERT Manual Unit 8 scenarios CERT Written Final Exam Chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, explosive, terrorism, shelter in place, contamination, decontamination, hot zone, warm zone, cold zone, simulation CERT Final Simulation Cadets will have six different scenarios based in the NVMI emergency plan and do both tabletop and field exercises on their response to those situations: Earthquake, Chemical Spill, Active Shooter on Campus, Fire, Flood, Bomb Threat No new Academic Vocabulary








