Mechanisms of Inheritance Test Review
advertisement

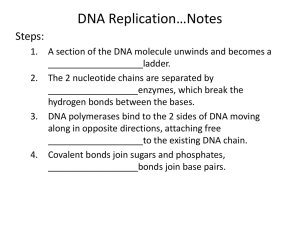
Mechanisms of Inheritance Test Review Outline significant scientific contributions/discoveries that led to the current understanding of the structure and function of the DNA molecule. (Secret of Life Video: Watson & Crick, Wilkins & Franklin, Pauling) Describe the structure of a DNA nucleotide. (deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogen bases) Describe and draw the structure of a DNA molecule. (double helix, nucleotides, base pairing, bonds) Describe the process of DNA replication. (template, semi-conservative replication, enzymes (helicase, DNA polymerase, ligase), leading strand, lagging string, 5’ to 3’, Okazaki fragments) Compare and contrast DNA and RNA in terms of their structure, use, and location in the cell. Outline the steps involved in protein synthesis. (coding DNA, template DNA, mRNA, codon, anticodon, introns, exons, amino acid, transcription, tRNA, anticodon, ribosome, translation) Understand genetic mutations. (cause, types (chromosomal, point, frameshift, insertion, deletion), consequences ___________________________________________________________________ Vocabulary central dogma of molecular biology: doctrine that genetic instructions in DNA are copied by RNA, which carries them to a ribosome where they are used to synthesize a protein (DNA → RNA → protein) Chargaff's rules: observations by Erwin Chargaff that concentrations of the four nucleotide bases differ among species; and that, within a species, the concentrations of adenine and thymine are always about the same and the concentrations of cytosine and guanine are always about the same messenger RNA (mRNA): type of RNA that copies genetic instructions from DNA in the nucleus and carries them to the cytoplasm ribosomal RNA (rRNA): type of RNA that helps form ribosomes and assemble proteins transfer RNA (tRNA): type of RNA that brings anticodons and amino acids to ribosomes where they are joined together to form proteins codon: group of three nitrogen bases in nucleic acids that makes up a code “word” of the genetic code and stands for an amino acid, start, or stop genetic code: universal code of three-base codons that encodes the genetic instructions for the amino acid sequence of proteins promoter: region of a gene where a RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription of the gene protein synthesis: process in which cells make proteins that includes transcription of DNA and translation of mRNA transcription: process in which genetic instructions in DNA are copied to form a complementary strand of mRNA translation: process in which genetic instructions in mRNA are “read” to synthesize a protein chromosomal alteration: mutation that changes chromosome structure frameshift mutation: deletion or insertion of one or more nucleotides that changes the reading frame of the genetic material genetic disorder: disease caused by a mutation in one or a few genes germline mutation: mutation that occur in gametes mutagen: environmental factor that causes mutations mutation: change in the sequence of bases in DNA or RNA point mutation: change in a single nucleotide base in the genetic material somatic mutation: mutation that occurs in cells of the body other than gametes Practice Questions: 1. What are the base pairs? Why do they arrange themselves in this way? 2. What are the differences between DNA and RNA? 3. What is the purpose of DNA? 4. What is the purpose of mRNA? 5. What is the purpose of tRNA? 6. What is the purpose of amino acids? 7. Transcription: a) What is the purpose? b) Where does it happen? c) What molecules are involved? d) What are the steps involved? e) What processes occur after mRNA is transcribed, and before it is translated? 8. Translation: a) What is the purpose? b) Where does it happen? c) What molecules are involved? d) What are the steps involved? 9. Complete the following table: DNA Coding Strand DNA Template Strand codon anticodon amino acid GCG GTA AAC tryptophan AGC 10. The following is a strand of coding DNA. 5’-ATGCGGATAAAAATATCC-3 a) List the template DNA b) List the mRNA c) How many codon are there? d) List the anticodons e) List the amino acid sequence 11. Mutations: a) What are the sources of mutations? b) What type of mutations are there? c) Why aren’t all mutations harmful? ***These are samples of concepts that are important to understand. Make sure you are also studying your notes, assignments, and labs. The test will be a combination of multiple choice and written response.