2013 Protocol for Administration of Influenza Vaccine in Egg
advertisement

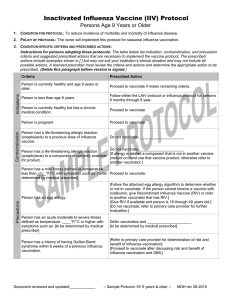
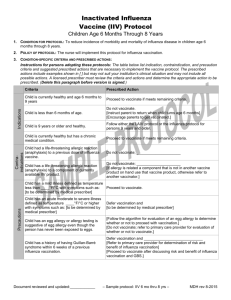
2013 Protocol for Administration of Influenza Vaccine in Egg-Allergic Patients 1. Patients with a history of suspected egg allergy should be evaluated by an allergist to determine the status of their egg allergy, but this should not delay their influenza vaccination. 2. Patients with confirmed egg allergy can still receive influenza vaccine, but it is important to determine the current status of the patient’s egg allergy, irrespective of their vaccination status 3. All patients with egg allergy of any severity, including anaphylaxis, should receive the influenza vaccine annually, using any age-approved brand of influenza vaccine in an age-appropriate dose. Such patients can receive the vaccine as a single dose without prior vaccine skin testing. 4. For patients age 18 and older, there are two influenza vaccines not grown in eggs: 1) Flucelvax, prepared from virus propagated in cell culture, and 2) Flublok, recombinant hemagglutinin proteins produced in an insect cell line. Either of these can be safely administered to egg-allergic patients. 5. All patients receiving any influenza vaccines should be observed for 30 minutes in a medical setting that has appropriate personnel and equipment to deal with any adverse reaction. Special precautions regarding medical setting and waiting periods after administration of influenza vaccine to egg-allergic recipients beyond those recommended for any vaccine are not warranted. References: Adverse Reactions to Vaccines Practice Parameter 2012 Update (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;130:25-43) 2013 Update to be published in JACI as a “Letter to the Editor” that incorporates this information.