b - Gurukul Home Tutor
advertisement
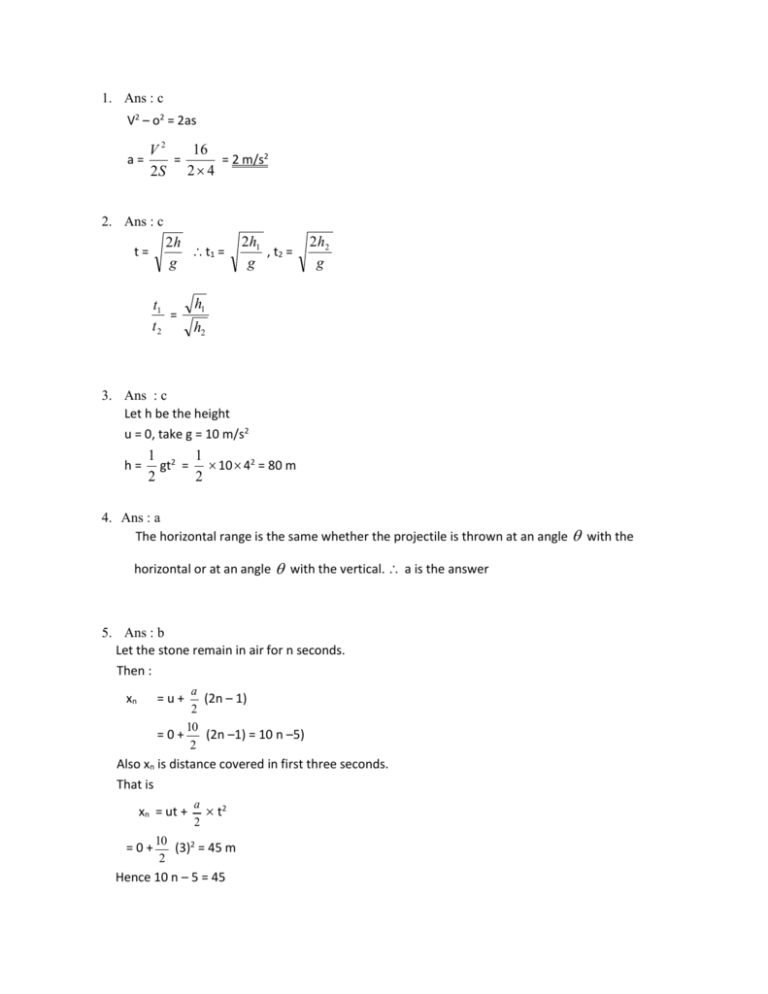
1. Ans : c V2 – o2 = 2as 16 V2 = = 2 m/s2 2S 2 4 a= 2. Ans : c 2h t1 = g t= t1 = t2 2h1 , t2 = g 2 h2 g h1 h2 3. Ans : c Let h be the height u = 0, take g = 10 m/s2 h= 1 2 1 gt = 10 42 = 80 m 2 2 4. Ans : a The horizontal range is the same whether the projectile is thrown at an angle with the horizontal or at an angle with the vertical. a is the answer 5. Ans : b Let the stone remain in air for n seconds. Then : a (2n – 1) 2 10 =0+ (2n –1) = 10 n –5) 2 xn =u+ Also xn is distance covered in first three seconds. That is xn = ut + =0+ a 2 t2 10 (3)2 = 45 m 2 Hence 10 n – 5 = 45 Which gives n = 5 seconds 6. Ans : c Potential energies at the highest point are equal to the loss in kinetic energies. In the first case KE = 1 mu2 2 = PE at the highest point In the second case KE = 1 m (u cos 60)2 2 = 1 1 m u 2 2 = 1 1 mu2 4 2 2 1 mu 2 2 The ratio is =4:1 1 1 mu 2 4 2 Note : If the projectile makes an angle 60o with vertical, it will make an angle 30o with the horizontal initial vertical velocity is u sin = u sin 30 = u cos 60. 7. a Exp.: Action is directed opposite to the reaction 8. b Exp.: The tension between P and Q acceleration double the mass as compared to that between Q and R 9. d Exp.: Here mg sin 𝑎 = 8. To make it move up with the same acceleration, we need to apply force F such that F – mg sin 𝑎. Because acceleration down the inclined plane is g sin 𝑎. 10. c Exp.: Let the acceleration if system be 𝑎. Then 𝑎 = 5 N/( 6 + 4) kg = 0.5 ms –2 Force on the block of mass 4 kg = 4× 0.5 N = 2 N 11. a 43 – 18 = 25 (Mn) 12. c Bond orders : H2+ : 21 , H2 : 1, H2 − : H2 − has an anti bonding electron 13. 1 2 d Look for sp carbon. As p orbital participation decreases, bonded pair of electrons is closer to carbon. 14. c Ti2+ : 3d2 and Ni2+ : 3d 8 15. b By removal of electron B.O. changes as NO : 1 21 to 2 O2 : 2 to 2 21 F2 : 1 to 1 21 16. d KO2 : K + and O2− NO : . N̈ = O 17. N2 : 3, N2+ and N2− : 2 12 , N22− 18. ∶ 2 a Bond order and related properties of diatomic molecules may be remembered thus. Molecule B2 C2 N2 O2 F2 B. O 1 2 3 2 1 Count the total number of electrons in the diatomic molecule Molecule B2 C2 N2 O2 F2 – No of e 10 12 14 16 18 B. O 1 2 3 2 1 19. e In tetro compounds (complexes in which O2– is the ligand ) the central atom transfers its electrons in its outer shell to each O atoms and receives back O2 – in sp3 vacant orbitals 20. e Anhydrous AlCl3 covalent with Al in sp2 - vacant orbital on Al is the reason for hydrolysis. AlCl3 + 3 H2O ⟶ Al (OH)3 + 3 HCl 21. e 1s, 2p , 3d and 4f have no node : Number of nodes = n −(ℓ + 1) 22. b 1 1 1 𝑛22 1 𝜈 = 𝑅𝐻 ( 2 − 𝑛 ) ; 𝑛1 = 1 and 𝑛2 = ∞ 𝑐 Then 𝜈 = 𝑅𝐻 ; 𝜈 = 𝜆 and 𝜈 = 𝜆 = 𝑐 𝜈 E = h𝑣 = hc 𝜈 = hc RH 23. a E = 12 mv2 3 −19 E = 10× 10 × 1.6 × 10 2𝐸 1 2 J 2×10×103 ×1.6×10−19 ν = (𝑚) = ( 9.1×10−31 1 2 7 ) = 5.9× 10 24. c 1 1 1 𝑛22 RH (𝑛 2 − 𝜈= ) ; n2 = ∞ n1 = 1, 2 and 3 respectively 𝑐 𝜈=𝜆=𝑐𝜈 1. 2. 3. 25. a 109677 ×102 ×3×108 12 109677 ×102 ×3×108 22 109677 ×102 ×3×108 32 1 eV = 1.6× 10−19 J 𝜆𝑂 = ℎ𝑐 𝐸𝑂 = 6.63 ×10−36 ×3×108 2.3×1.6×10−19 = 5.4 × 10−7 m (5.4 × 10−7 × 109 = 540 𝑛𝑚 26. a The pyrenoids are small spherical protein bodies surrounded by starch deposition. They are found singly or in numbers embedded in the chloroplast of many algae and bryophytes. 27. b The chief source of carragenin is red algae, Chondrus crispus. 28. a Life cycle in Spirogyra is haplontic as dominant phase in life is haploid and diploid phase is represented only by zygote or zygospore 29. c Bryophytes are simple chlorophyll containing non vascular plants. They show heteromorphic alternation of generation in which the gametophyte is the dominant phase. 30. C In funaria, antheridium represents male sex organ and archegonium shows female sex organ. It is situated on the apex of stem. 31. a In Dahlia, roots do not originate from radicles and are therefore,adventitious. Roots of radish, carrot and beet originate from radicle are the examples of modified tap root. 32. b The main purpose of sub-aerial modification of stem is vegetative propagation, as found in runner, offset, stolon and sucker. The examples of sucker are Chrysanthemum, Mint etc 33. d Bulbil is a structure rich in food materials and serves the function of vegetative propogation. 34. a The mustard (Brassica campestris) belongs to cruciferae (Brassicaeae). The stamens of this family is characteristically tetradynamous. 35. B When the stamens are united to petals the stamens are called epipetalous. Such condition is found in solaaceae, malvaceae, compositae etc. 36. b 37. a 38. b 39. d 40. b 41. b 42. b 43. b 44. c 45. a











