Theories of Motivation Assignment DUE: Wednesday/Thursday
advertisement
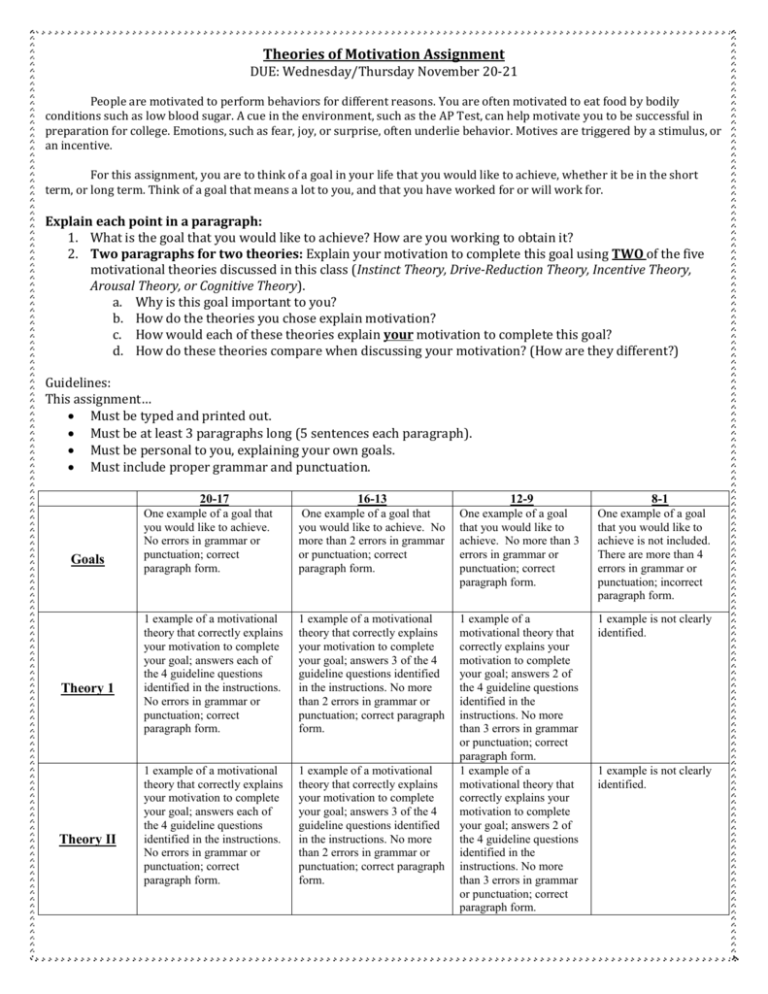
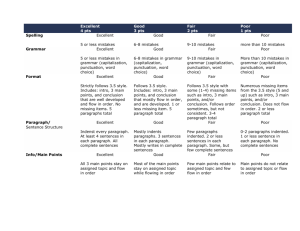
Theories of Motivation Assignment DUE: Wednesday/Thursday November 20-21 People are motivated to perform behaviors for different reasons. You are often motivated to eat food by bodily conditions such as low blood sugar. A cue in the environment, such as the AP Test, can help motivate you to be successful in preparation for college. Emotions, such as fear, joy, or surprise, often underlie behavior. Motives are triggered by a stimulus, or an incentive. For this assignment, you are to think of a goal in your life that you would like to achieve, whether it be in the short term, or long term. Think of a goal that means a lot to you, and that you have worked for or will work for. Explain each point in a paragraph: 1. What is the goal that you would like to achieve? How are you working to obtain it? 2. Two paragraphs for two theories: Explain your motivation to complete this goal using TWO of the five motivational theories discussed in this class (Instinct Theory, Drive-Reduction Theory, Incentive Theory, Arousal Theory, or Cognitive Theory). a. Why is this goal important to you? b. How do the theories you chose explain motivation? c. How would each of these theories explain your motivation to complete this goal? d. How do these theories compare when discussing your motivation? (How are they different?) Guidelines: This assignment… Must be typed and printed out. Must be at least 3 paragraphs long (5 sentences each paragraph). Must be personal to you, explaining your own goals. Must include proper grammar and punctuation. 20-17 Goals Theory 1 Theory II 16-13 12-9 One example of a goal that you would like to achieve. No errors in grammar or punctuation; correct paragraph form. One example of a goal that you would like to achieve. No more than 2 errors in grammar or punctuation; correct paragraph form. One example of a goal that you would like to achieve. No more than 3 errors in grammar or punctuation; correct paragraph form. One example of a goal that you would like to achieve is not included. There are more than 4 errors in grammar or punctuation; incorrect paragraph form. 8-1 1 example of a motivational theory that correctly explains your motivation to complete your goal; answers each of the 4 guideline questions identified in the instructions. No errors in grammar or punctuation; correct paragraph form. 1 example of a motivational theory that correctly explains your motivation to complete your goal; answers 3 of the 4 guideline questions identified in the instructions. No more than 2 errors in grammar or punctuation; correct paragraph form. 1 example is not clearly identified. 1 example of a motivational theory that correctly explains your motivation to complete your goal; answers each of the 4 guideline questions identified in the instructions. No errors in grammar or punctuation; correct paragraph form. 1 example of a motivational theory that correctly explains your motivation to complete your goal; answers 3 of the 4 guideline questions identified in the instructions. No more than 2 errors in grammar or punctuation; correct paragraph form. 1 example of a motivational theory that correctly explains your motivation to complete your goal; answers 2 of the 4 guideline questions identified in the instructions. No more than 3 errors in grammar or punctuation; correct paragraph form. 1 example of a motivational theory that correctly explains your motivation to complete your goal; answers 2 of the 4 guideline questions identified in the instructions. No more than 3 errors in grammar or punctuation; correct paragraph form. 1 example is not clearly identified.