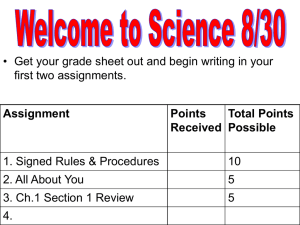
Neutralization Reaction Lab
advertisement
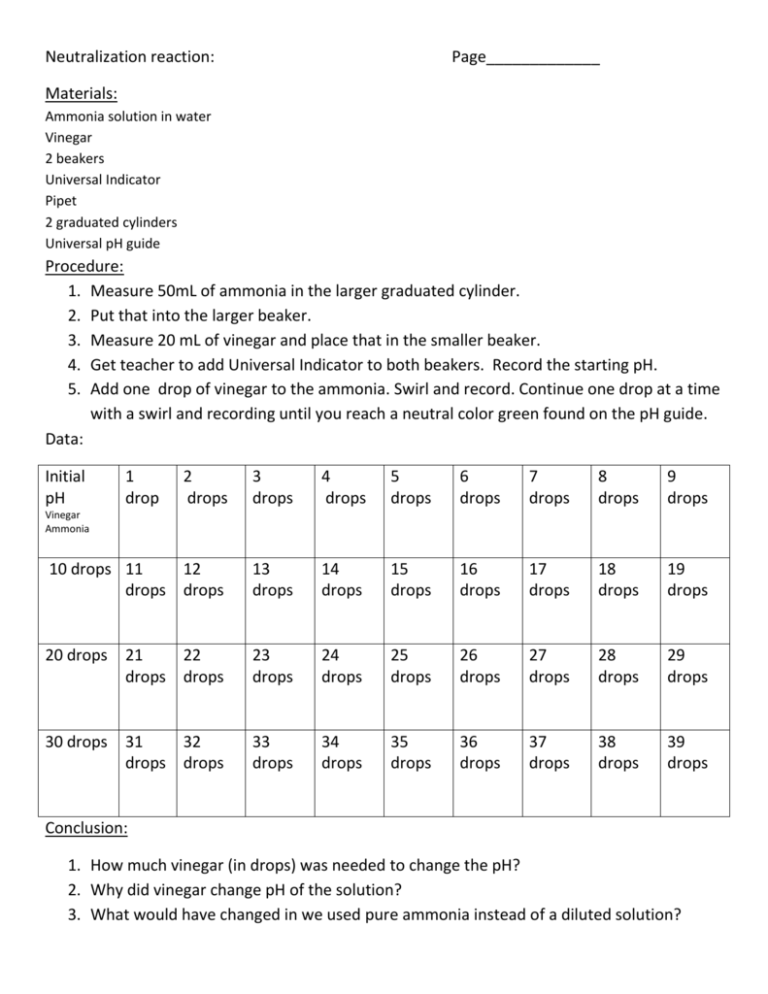
Neutralization reaction: Page_____________ Materials: Ammonia solution in water Vinegar 2 beakers Universal Indicator Pipet 2 graduated cylinders Universal pH guide Procedure: 1. Measure 50mL of ammonia in the larger graduated cylinder. 2. Put that into the larger beaker. 3. Measure 20 mL of vinegar and place that in the smaller beaker. 4. Get teacher to add Universal Indicator to both beakers. Record the starting pH. 5. Add one drop of vinegar to the ammonia. Swirl and record. Continue one drop at a time with a swirl and recording until you reach a neutral color green found on the pH guide. Data: Initial pH 1 drop 2 drops 3 drops 4 drops 5 drops 6 drops 7 drops 8 drops 9 drops 10 drops 11 12 drops drops 13 drops 14 drops 15 drops 16 drops 17 drops 18 drops 19 drops 20 drops 21 22 drops drops 23 drops 24 drops 25 drops 26 drops 27 drops 28 drops 29 drops 30 drops 31 32 drops drops 33 drops 34 drops 35 drops 36 drops 37 drops 38 drops 39 drops Vinegar Ammonia Conclusion: 1. How much vinegar (in drops) was needed to change the pH? 2. Why did vinegar change pH of the solution? 3. What would have changed in we used pure ammonia instead of a diluted solution?