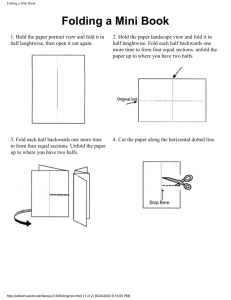
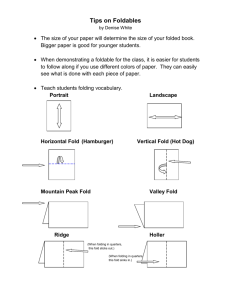
Folding notes - Ramsgrange Community School
advertisement

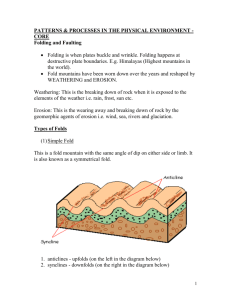
FOLDING Parts of a fold (see p.47) A. Anticline (upfolds) B. Syncline (downfolds) Types of folds (see p.47) A. Simple/Symmetric B. Asymmetric C. Overfold D. Overthrust fold E. Chevron fold Case Study The Munster ridge and valley region -350-400 million years ago huge amounts of sand were deposited in the south and southwest of Ireland -This formed a rock that we call Old Red Sandstone -Later a muddy sea covered the area and limestone formed on top of the sandstone -300 million years ago the plates collided and fold mountains (amorican folding) were formed -These mountains stretch from Waterford to Kerry e.g. Comeraghs, Silvermines and the Galtees. -The top of the mountains are made of resistant (tough) sandstone rock because the limestone that once covered them was eroded. -The limestone in the valleys (synclines) was not eroded and still remains e.g. in Blackwater valley and Golden Vale -This has led to the region being called the Munster Ridge and Valley Region Fold Mountain Building (Orogeny) in Ireland A. Caledonian Folding -400 million years ago -E.g. Leinster Mountains B. Amorican Folding -300 million years ago -Munster Ridge and Valley Region C. Alpine Folding -50 million years ago -Too young to be found in Ireland -E.g. Alps and Himalayas