New Jersey Special Education Classifications
advertisement

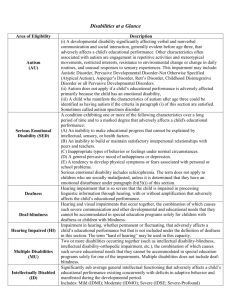
New Jersey Special Education Classifications Under New Jersey Administrative Code Title 6A, Chapter 14, students between the ages of 3 and 21 are eligible for special education and related services if they meet the criteria for one or more of fourteen recognized disabilities. Eligibility is determined collaboratively by the IEP team, who can recommend classification only if the student’s academic deficiencies are not the result of “a lack of instruction in reading, including the essential components of reading instruction, or math or due to limited English proficiency” (NJAC 6A:14-3.5(b)). What follows is a list of the fourteen NJ eligibility classifications, along with a “plain English” description of each one. If you want to read exactly what the law says about each one, click the link above to read the law online, or download the NJ Special Ed Code at the bottom of this page (PDF). You can also contact your or your child’s case manager to ask for a NJ Special Education Code booklet. It is important to note that the following descriptions are for special services eligibility ONLY, and do not necessarily reflect medical diagnostic criteria. Auditorily Impaired: Corresponds to “auditorily handicapped” in federal eligibility legislation. Students with this disability can not hear within normal limits due to: Physical impairment One of the two following conditions o Deafness – complete inability to hear o Hearing impairment – Can be a permanent or fluctuating inability to hear Regardless of the cause, the impairment adversely affects academic performance. Autistic: Students with the “Autistic” classification have a pervasive developmental disability that may impact their ability to interact socially and communicate, both verbally and nonverbally. These students are often resistant to changes in environment and routine, and find comfort in repetition. Cognitively Impaired: Students with this classification have significantly below average levels of cognitive functioning along with deficits in adaptive functioning (basic life skills). According to NJ law, there are three levels of cognitive impairment: Mild – These students are considered comparatively high functioning. Moderate – These students require life skill training, but should be able to function with minimal supervision after training. Severe – These students are unable to care for themselves, and require caregiver supervision for even their most basic needs Communication Impaired: These students have language disorders that are not a result of an auditory impairment. Testing for this impairment involves the addition of a speech-language therapist to the evaluation team. Students with CI may also be eligible for additional speech & language services. Emotionally Disturbed: These students’ educational performance is adversely affected by one or more of the following: An inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers/teachers Inappropriate behaviors or feelings under normal circumstances A general pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression A tendency to develop physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems Multiply Disabled: Students have two or more disabling conditions, the combination of which cannot be accommodated for in a program designed solely to address one of the impairments. Deaf/blindness: Simultaneous hearing and visual impairments which cause such severe communication, developmental, and/or educational problems that programs strictly for the deaf or for the blind cannot accommodate the student’s needs. Orthopedically Impaired: Student has a severe malformation, malfunction, or loss of bone, muscle, or tissue that adversely affects educational performance (medical documentation is required). Other Health Impaired: A medical assessment is required for this classification. Students with the OHI classification are characterized by having limited strength, vitality or alertness due to chronic or acute health problems. This/these condition/s adversely affect the student’s educational performance. Preschool Child with a Disability: For children between the ages of three and five who experience developmental delay (33% delay in one area or 25% delay in two or more areas) in one or more of the following areas: Physical (gross/fine motor; sensory) Cognitive Communication Social/emotional Adaptive Social Maladjustment: Students exhibit a consistent inability to conform school behavior standards. This behavior is seriously disruptive to the education of the student and/or other students, and is not due to the conditions described under Emotionally Disturbed. Specific Learning Disability (SLD): A disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes involved in language skills that manifests in an imperfect ability to listen, think, speak, read, write, spell, or perform mathematical calculations. Specific learning disabilities may be determined by finding a severe discrepancy between current achievement and intellectual ability in: basic reading skills reading comprehension oral expression listening comprehension mathematical calculation mathematical problem solving written expression reading fluency SLDs may also be identified by utilizing a response to scientifically based interventions. SLDs are not the results of visual, hearing, or motor disabilities, general cognitive deficits, emotional disturbance or environment, or cultural or economic disadvantage. Traumatic Brain Injury: An acquired injury to the brain caused by external force/insult to the brain, resulting in full or partial functional disability or psychosocial impairment. Visually Impaired: A visual impairment (partial or total) that adversely impacts a student’s educational performance. An assessment by a specialist is required. Download the New Jersey Administrative Code, Title 6A, Chapter 14