reading check ch12
advertisement

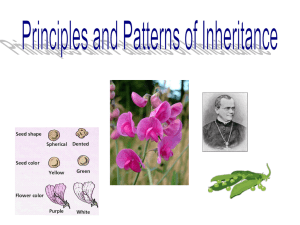
Reading Check 12.1 Complete this outline while you read section 12.1 of your textbook. You do not need to answer in complete sentences. Chapter 12, Section 1: Origins of Hereditary Science Mendel’s breeding experiments _____________________________ is the science of heredity and the mechanism by which traits are passed from parents to offspring. Modern genetics is based on Mendel’s explanations for the patterns of _____________________________ in garden _____________________________. To cross two plants, as Mendel did, means to ____________________________________________. When Mendel crossed a pea plant with purples flowers with a type that had white flowers, all the offspring had _____________________________ flowers. But when two of these offspring were crossed, some of their offspring had _____________________________ flowers and some had purple flowers. Features of pea plants List three reasons why pea plants are good subjects for heredity studies: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Physics features that are inherited are called _____________________________. A _____________________________ is one of several possible forms of a character. For example, purple is one of two possible _____________________________ for the flower color _____________________________ in pea plants. Since pea plant flowers contain both male and female reproductive parts, they can _____________________________, or fertilize themselves. Pea plants can also reproduce by _____________________________, when pollen from one flowers is carried to another flower. Mendel’s first experiments Mendel’s first experiments had three steps. First, he produced a true-breeding _____ or _____________________________ generation. Second, he crossed two P generation plants with different traits and called the offspring the _____ or _____________________________ generation. Third, he allowed the F1 generation to self-pollinate and produce new plants. This created the _____ or _____________________________ generation. Mendel’s results For each character that Mendel studied, he found a _____________________________ ratio of contrasting traits in the F2 generation. Reading Check 12.2 Complete this outline while you read section 12.2 of your textbook. You do not need to answer in complete sentences. Chapter 12, Section 2: Mendel’s theory Explaining Mendel’s results Mendel’s hypotheses about inheritance were basically correct but have been _____________________________ with newer terms and more complete knowledge. Before Mendel’s experiments, many people though that traits of offspring were always a _____________________________ of the traits from parents. Mendelian theory explains patterns of inheritance, where different traits result from different versions of genes. Today, each version of a gene is called an _____________________________. Each individual has two alleles for a given _____________________________. A single _____________________________ carries only one of the two alleles. Mendel noticed that some traits always seemed to “win” over the others. The expressed allele is called _____________________________, while the allele that is not expressed when the dominant allele is present is called _____________________________. The law of _____________________________ holds that when an organisms produces _____________________________, each pair of alleles is separated and each gamete has an equal chance of receiving either allele. Mendel’s findings in modern terms The set of alleles an individual has for a character is called the _____________________________, while the trait that results from a set of alleles is the _____________________________. Mendel’s second experiments A _____________________________ cross examines two characters at the same time. If an individual has two of the same alleles of a certain gene, the individual is _____________________________ for the character. On the other hand, if an individual has two different alleles for a certain gene, the individual is _____________________________. The law of _____________________________ _____________________________ holds that when gametes are formed, the alleles of each gene separate independently. Reading Check 12.3 Complete this outline while you read section 12.3 of your textbook. You do not need to answer in complete sentences. Chapter 12, Section 3: Modeling Mendel’s laws Using Punnett squares A Punnett square shows all of the _____________________________ that could result from a given cross. Fill in the offspring genotypes in the following crosses: In the left Punnett square, both parents are _____________________________ for seed color. About one-____________________ of the offspring will be YY. About two-____________________ (or one-half) will be Yy. And about one-_______________________ will be yy. In the right Punnet square, both parents are _____________________________ for seed color, but one parent is yellow and the other is green. Here, _____________________________ is the dominant trait. All the offspring in this cross will be _____________________________ (Yy) and will express the dominant trait of _____________________________ seed color. Using probability _____________________________ is the likelihood that a specific event will occur. Using a pedigree A _____________________________ is a family history that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations. A genetic _____________________________ is a disease that can be inherited. _____________________________ have alleles for a disorder but do not show symptoms. They can pass the allele for the disorder to their _____________________________. A _____________________________ trait is located on either an X or Y chromosome. Reading Check 12.4 Complete this outline while you read section 12.4 of your textbook. You do not need to answer in complete sentences. Chapter 12, Section 4: Beyond Mendelian heredity Many genes, many alleles Not all genes have only two _____________________________. Not all characters are controlled by only one _____________________________. When several genes affect a character, it is called a _____________________________ character. An example is _____________________________ in humans. An inheritance pattern in which the offspring has a phenotype that is intermediate (or in between) the traits of its parents is called _____________________________ dominance. An example is when a red snapdragon is crossed with a white snapdragon, and their offspring all have _____________________________ flowers. Genes that have three or more possible alleles are said to have _____________________________ alleles. For some characters, two traits can appear at the same time. _____________________________ is a condition in which both alleles for the same gene are fully expressed. An example is human _____________________________ groups. Genes affected by the environment _____________________________ can be affected by conditions in the environment, such as _____________________________ and _____________________________. An example is the arctic fox, whose fur is __________________________ during the summer and __________________________ during the winter.