11.4 Notes (Completed) - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
advertisement

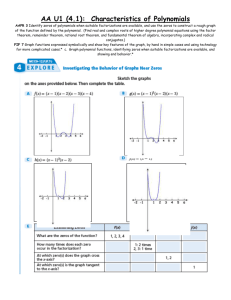
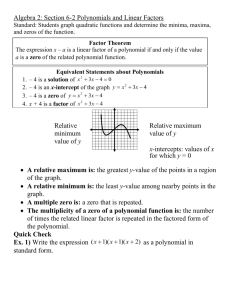
P.o.D. – Factor each of the following: 1.) 𝑥 2 + 10𝑥 + 21 2.) 𝑡 2 − 3𝑡 − 4 3.) 𝑥 2 − 15𝑥 + 54 4.) 𝑝2 + 12𝑝 + 32 5.) 𝑥 2 − 100 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) (x+3)(x+7) (t-4)(t+1) (x-6)(x-9) (p+8)(p+4) 5.) (x+10)(x-10) 11-4: The Factor Theorem Learning Target(s): I can find zeros of polynomial functions by factoring; apply the zeroproduct theorem and the factor theorem; graph polynomial functions; estimate zeros using graphs. Zero(s) of a Polynomial: - Places where the graph crosses the x-axis - Solutions to the equation - Also known as a root Zero Product Theorem: For all a and b, ab=0 if and only if a=0 or b=0. EX: An open box has sides of length x, (24-2x), and (24-2x). Thus, its volume is given by V(x)=x(24-2x)(24-2x). Find the zeros of V. The Zero-Product Theorem says that in order for an equation to equal zero, each of its factors could equal zero. X=0 24-2x=0 24-2x=0 24=2x 24=2x 12=x 12=x Solutions: 0,12,12 12 is a double root Factor Theorem: (x-r) is a factor of P(x) if and only if P(r)=0. In other words, r is a zero of P. EX: Find the roots of 𝑃(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 4 − 𝑥 3 − 20𝑥 2 by factoring. Begin by taking out a common factor. 𝑃(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 2 (𝑥 2 − 𝑥 − 20) Now factor the trinomial by un-FOILing. 𝑃(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 2 (𝑥 − 5)(𝑥 + 4) Use the Zero-Product Property to set each factor equal to zero and solve. X+4=0 𝑥 2 = 0 x-5=0 X=-4 𝑥 = +0, −0 x=5 The zeros are x=0,0,5,-4. O is a double root. EX: Find the roots of 𝑃(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 4 − 14𝑥 2 + 45 Since this has 3 terms, we should try to un-FOIL. 𝑃(𝑥 ) = (𝑥 2 − 9)(𝑥 2 − 5) Notice that one of these factors is the difference of squares. 𝑃(𝑥 ) = (𝑥 − 3)(𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 2 − 5) Apply the zero-product property. x-3=0 x=3 x+3=0 x=-3 𝑥2 − 5 = 0 𝑥2 = 5 𝑥 = ±√5 The roots are 3, -3, √5, −√5. This is an example of the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. The FTA states that you will have the same number of roots as the highest exponent. EX: A polynomial function p with degree 4 and leading coefficient 1 is graphed below. Find the factors of p(x) and use them to write a formula for p(x). This graph crosses the x-axis, or has zeros, at -7, -4, 0, and 3. Therefore, it has factors of (x+7), (x+4), x, and (x-3). Expand these factors to find the polynomial. 𝑃(𝑥 ) = 𝑥(𝑥 + 7)(𝑥 + 4)(𝑥 − 3) = (𝑥 2 + 7𝑥)(𝑥 + 4)(𝑥 − 3) = (𝑥 3 + 4𝑥 2 + 7𝑥 2 + 28𝑥)(𝑥 − 3) = (𝑥 3 + 11𝑥 2 + 28𝑥)(𝑥 − 3) = 𝑥 4 + 11𝑥 3 + 28𝑥 2 − 3𝑥 3 − 33𝑥 2 − 84𝑥 = 𝑥 4 + 8𝑥 3 − 5𝑥 2 − 84𝑥 EX: Find the equation of a polynomial whose zeros are -4, 7/2, and 5/3. The factors are (x+4), (x-7/2), and (x-5/3). 7 5 𝑃(𝑥 ) = (𝑥 + 4) (𝑥 − ) (𝑥 − ) 2 3 Or 𝑃(𝑥 ) = (𝑥 + 4)(2𝑥 − 7)(3𝑥 − 5) 7 5 = (𝑥 − 𝑥 + 4𝑥 − 14) (𝑥 − ) 2 3 1 5 2 = (𝑥 + 𝑥 − 14) (𝑥 − ) 2 3 2 1 2 5 2 5 70 = 𝑥 + 𝑥 − 14𝑥 − 𝑥 − 𝑥 + 2 3 6 3 3 7 2 89 70 =𝑥 − 𝑥 − 𝑥+ 6 6 3 Or 𝑃(𝑥 ) = 6𝑥 3 − 7𝑥 2 − 89𝑥 + 140 3 Upon completion of this lesson, you should be able to: 1. Find zeros of a polynomial. 2. Find the roots of a polynomial by factoring. 3. Use ZoomMath (not on ACT). For more information, visit http://www.purplemath.com/modules/from zero2.htm HW Pg.756 2-12, 14-27 Quiz 11.1-11.4 tomorrow