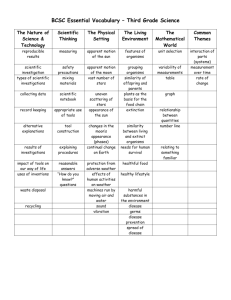
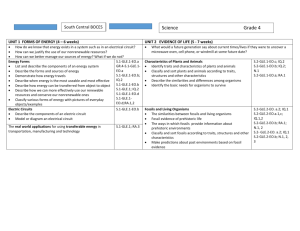
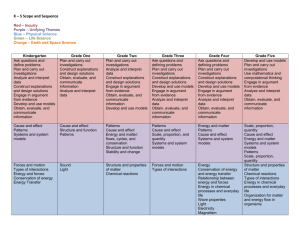
Side-By-Side 5th Grade
advertisement
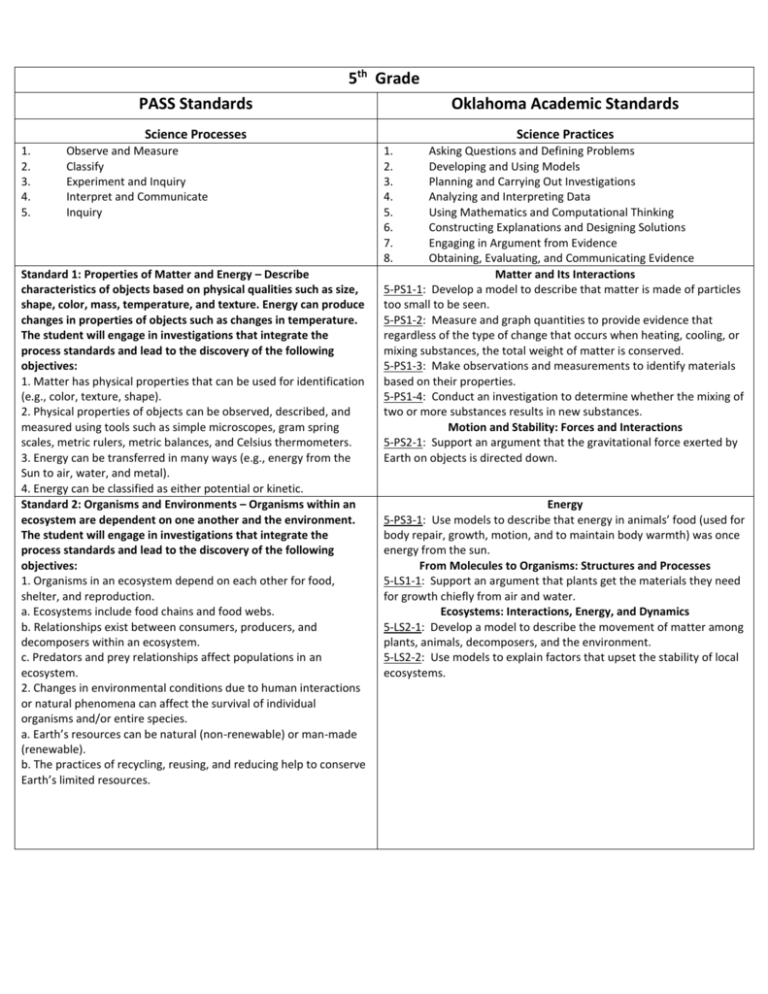
5th Grade PASS Standards Oklahoma Academic Standards Science Processes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Observe and Measure Classify Experiment and Inquiry Interpret and Communicate Inquiry Standard 1: Properties of Matter and Energy – Describe characteristics of objects based on physical qualities such as size, shape, color, mass, temperature, and texture. Energy can produce changes in properties of objects such as changes in temperature. The student will engage in investigations that integrate the process standards and lead to the discovery of the following objectives: 1. Matter has physical properties that can be used for identification (e.g., color, texture, shape). 2. Physical properties of objects can be observed, described, and measured using tools such as simple microscopes, gram spring scales, metric rulers, metric balances, and Celsius thermometers. 3. Energy can be transferred in many ways (e.g., energy from the Sun to air, water, and metal). 4. Energy can be classified as either potential or kinetic. Standard 2: Organisms and Environments – Organisms within an ecosystem are dependent on one another and the environment. The student will engage in investigations that integrate the process standards and lead to the discovery of the following objectives: 1. Organisms in an ecosystem depend on each other for food, shelter, and reproduction. a. Ecosystems include food chains and food webs. b. Relationships exist between consumers, producers, and decomposers within an ecosystem. c. Predators and prey relationships affect populations in an ecosystem. 2. Changes in environmental conditions due to human interactions or natural phenomena can affect the survival of individual organisms and/or entire species. a. Earth’s resources can be natural (non-renewable) or man-made (renewable). b. The practices of recycling, reusing, and reducing help to conserve Earth’s limited resources. Science Practices 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Asking Questions and Defining Problems Developing and Using Models Planning and Carrying Out Investigations Analyzing and Interpreting Data Using Mathematics and Computational Thinking Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions Engaging in Argument from Evidence Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Evidence Matter and Its Interactions 5-PS1-1: Develop a model to describe that matter is made of particles too small to be seen. 5-PS1-2: Measure and graph quantities to provide evidence that regardless of the type of change that occurs when heating, cooling, or mixing substances, the total weight of matter is conserved. 5-PS1-3: Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties. 5-PS1-4: Conduct an investigation to determine whether the mixing of two or more substances results in new substances. Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions 5-PS2-1: Support an argument that the gravitational force exerted by Earth on objects is directed down. Energy 5-PS3-1: Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun. From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes 5-LS1-1: Support an argument that plants get the materials they need for growth chiefly from air and water. Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics 5-LS2-1: Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment. 5-LS2-2: Use models to explain factors that upset the stability of local ecosystems. PASS Standards Standard 3: Structure of Earth and the Solar System – Interaction between air, water, rock/soil, and all living things. The student will engage in investigations that integrate the process standards and lead to the discovery of the following objectives: 1. Soil consists of weathered rocks and decomposed organic material from dead plants, animals, and bacteria. Soils are often found in layers. 2. Weather exhibits daily and seasonal patterns (i.e., air temperature, basic cloud types –cumulus, cirrus, stratus, and nimbus, wind direction, wind speed, humidity, precipitation). a. Weather measurement tools include thermometer, barometer, anemometer, and rain gauge. b. Weather maps are used to display current weather and weather predictions. 3. Earth is the third planet from the Sun in a system that includes the moon, the Sun, and seven other planets. a. Most objects in the solar system are in regular and predictable motion (e.g., phases of the moon). b. Objects in the Solar System have individual characteristics (e.g., distance from Sun, number of moons, and temperature of object). c. The Earth rotates on its axis while making revolutions around the Sun. Oklahoma Academic Standards Earth’s Place in the Universe 5-ESS1-1: Support an argument that differences in the apparent brightness of the sun compared to other stars is due to their relative distances from Earth. 5-ESS1-2: Represent data in graphical displays to reveal patterns of daily changes in length and direction of shadows, day and night, and the seasonal appearance of some stars in the night sky. Earth’s Systems 5-ESS2-1: Develop a model using an example to describe ways the geosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere, and/or atmosphere interact. 5-ESS2-2: Describe and graph the amounts and percentages of water and fresh water in various reservoirs to provide evidence about the distribution of water on Earth. Earth and Human Activity 5-ESS3-1: Obtain and combine information about ways individual communities use science ideas to protect the Earth’s resources and environment. Crosscutting Concepts Cause and Effect Cause and effect relationships are routinely identified, tested, and used to explain change. (5-PS1-4, 5-PS2-1) Energy and Matter Energy can be transferred in various ways and between objects. (5-PS3-1) Matter is transported into, out of, and within systems. (5-LS11) Systems and System Models A system can be described in terms of its components and their interactions. (5-LS2-1, 5LS2-2, 5-ESS2-1, 5-ESS3-1) Scale, Proportion, and Quantity Natural objects exist from the very small to the immensely large. (5-PS1-1, 5-ESS1-1) Standard units are used to measure and describe physical quantities such as weight, time, temperature, and volume. (5PS1-2, 5-PS1-3, 5-ESS2-2) Patterns Similarities and differences in patterns can be used to sort, classify, communicate and analyze simple rates of change for natural phenomena (5-ESS1-2)