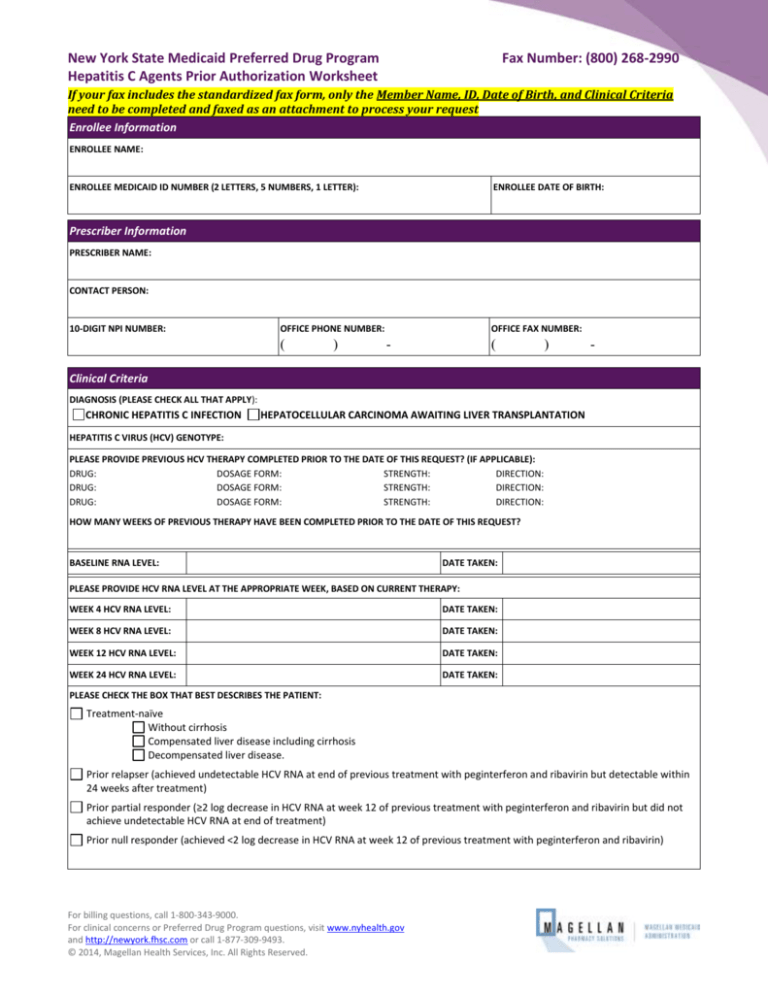
New York State Medicaid Preferred Drug Program
Hepatitis C Agents Prior Authorization Worksheet
Fax Number: (800) 268-2990
If your fax includes the standardized fax form, only the Member Name, ID, Date of Birth, and Clinical Criteria
need to be completed and faxed as an attachment to process your request
Enrollee Information
ENROLLEE NAME:
ENROLLEE MEDICAID ID NUMBER (2 LETTERS, 5 NUMBERS, 1 LETTER):
ENROLLEE DATE OF BIRTH:
Prescriber Information
PRESCRIBER NAME:
CONTACT PERSON:
10-DIGIT NPI NUMBER:
OFFICE PHONE NUMBER:
(
)
OFFICE FAX NUMBER:
-
(
)
-
Clinical Criteria
DIAGNOSIS (PLEASE CHECK ALL THAT APPLY):
CHRONIC HEPATITIS C INFECTION
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA AWAITING LIVER TRANSPLANTATION
HEPATITIS C VIRUS (HCV) GENOTYPE:
PLEASE PROVIDE PREVIOUS HCV THERAPY COMPLETED PRIOR TO THE DATE OF THIS REQUEST? (IF APPLICABLE):
DRUG:
DOSAGE FORM:
STRENGTH:
DIRECTION:
DRUG:
DOSAGE FORM:
STRENGTH:
DIRECTION:
DRUG:
DOSAGE FORM:
STRENGTH:
DIRECTION:
HOW MANY WEEKS OF PREVIOUS THERAPY HAVE BEEN COMPLETED PRIOR TO THE DATE OF THIS REQUEST?
BASELINE RNA LEVEL:
DATE TAKEN:
PLEASE PROVIDE HCV RNA LEVEL AT THE APPROPRIATE WEEK, BASED ON CURRENT THERAPY:
WEEK 4 HCV RNA LEVEL:
DATE TAKEN:
WEEK 8 HCV RNA LEVEL:
DATE TAKEN:
WEEK 12 HCV RNA LEVEL:
DATE TAKEN:
WEEK 24 HCV RNA LEVEL:
DATE TAKEN:
PLEASE CHECK THE BOX THAT BEST DESCRIBES THE PATIENT:
Treatment-naïve
Without cirrhosis
Compensated liver disease including cirrhosis
Decompensated liver disease.
Prior relapser (achieved undetectable HCV RNA at end of previous treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin but detectable within
24 weeks after treatment)
Prior partial responder (≥2 log decrease in HCV RNA at week 12 of previous treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin but did not
achieve undetectable HCV RNA at end of treatment)
Prior null responder (achieved <2 log decrease in HCV RNA at week 12 of previous treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin)
For billing questions, call 1-800-343-9000.
For clinical concerns or Preferred Drug Program questions, visit www.nyhealth.gov
and http://newyork.fhsc.com or call 1-877-309-9493.
© 2014, Magellan Health Services, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Magellan Medicaid Administration
Hepatitis C Agents Prior Authorization Fax Form
Answer the following if requesting a nonpreferred Ribavirin product (Form Cannot be Processed without
Required Explanation):
Patient has experienced a treatment failure with a preferred drug.
Yes
No
Patient has experienced an adverse drug reaction with a preferred drug.
Yes
No
There is a documented history of successful therapeutic control with a nonpreferred drug and transition
to a preferred drug is medically contraindicated.
Yes
No
Other (Please specify the clinical reason the patient is unable to use a preferred agent in the same drug class. If
necessary, fax additional pages):
YOU WILL NEED TO COMPLETE ALL QUESTIONS IN ONLY ONE OF THE FOLLOWING SIX BOXES, and
then sign the attestation that follows.
TRIPLE THERAPY: INCIVEK, PEGINTERFERON, & RIBAVIRIN
Incivek
Pegasys
Ribavirin
STRENGTH:
DIRECTION:
Pegintron STRENGTH:
DOSAGE FORM:
STRENGTH:
Other
QUANTITY:
REFILLS:
DIRECTION:
DIRECTION:
QUANTITY:
QUANTITY:
REFILLS:
REFILLS:
Has the patient previously failed therapy with Incivek, Olysio, or Victrelis?
Yes
No
Has the patient previously failed therapy with Sovaldi?
Yes
No
Will the patient be on peginterferon and ribavirin in combination with Incivek?
Yes
No
Is HCV RNA ≤1000 IU/mL at week 4?
Yes
No
Is HCV RNA ≤1000 IU/mL at week 12?
Yes
No
Is HCV RNA undetectable at both week 4 and week 12?
Yes
No
Is HCV RNA detectable but ≤1000 IU/mL at either week 4 or week 12?
Yes
No
TRIPLE THERAPY: OLYSIO, PEGINTERFERON, & RIBAVIRIN
Olysio
Pegasys
Ribavirin
STRENGTH:
DIRECTION:
Pegintron STRENGTH:
DOSAGE FORM:
STRENGTH:
Other
QUANTITY:
REFILLS:
DIRECTION:
DIRECTION:
QUANTITY:
QUANTITY:
REFILLS:
REFILLS:
Has the patient previously failed therapy with Incivek, Olysio, or Victrelis?
Yes
No
Has the patient previously failed therapy with Sovaldi?
Yes
No
Will the patient be on peginterferon and ribavirin in combination with Olysio?
Yes
No
Is HCV RNA ≤25 IU/mL at week 4?
Yes
No
Is HCV RNA ≤25 IU/mL at week 12?
Yes
No
Please note: Olysio efficacy in combination with peginterferon & ribavirin is substantially reduced in patients infected with
HCV genotype 1a with an NS3 Q80K polymorphism. Screening for NS3 Q80K polymorphism is strongly recommended prior
to initiation of therapy; alternative therapy should be considered in patients with the polymorphism.
TRIPLE THERAPY: SOVALDI, PEGINTERFERON, & RIBAVIRIN
Sovaldi
STRENGTH:
Pegasys
Pegintron STRENGTH:
Ribavirin
Other
STRENGTH:
DIRECTION:
DOSAGE FORM:
DIRECTION:
QUANTITY:
DIRECTION:
QUANTITY:
REFILLS:
QUANTITY:
REFILLS:
Will the patient be on peginterferon and ribavirin in combination with Sovaldi?
Revision Date: April 2014
REFILLS:
For billing questions, call 1-800-343-9000.
For clinical concerns or Preferred Drug Program questions, visit
www.nyhealth.gov and http://newyork.fhsc.com or call 1-877-309-9493.
Yes
No
Page 2
Magellan Medicaid Administration
Hepatitis C Agents Prior Authorization Fax Form
TRIPLE THERAPY: VICTRELIS, PEGINTERFERON, & RIBAVIRIN
Victrelis
Pegasys
Ribavirin
STRENGTH:
DIRECTION:
Pegintron STRENGTH:
DOSAGE FORM:
STRENGTH:
Other
QUANTITY:
DIRECTION:
REFILLS:
DIRECTION:
QUANTITY:
QUANTITY:
REFILLS:
REFILLS:
Has the patient previously failed therapy with Incivek, Olysio, or Victrelis?
Yes
No
Has the patient previously failed therapy with Sovaldi?
Yes
No
Will the patient be on peginterferon and ribavirin in combination with Victrelis?
Yes
No
Did the patient complete four consecutive weeks of therapy with ribavirin and peginterferon within 30 days of
the initial request?
Yes
No
Is HCV RNA undetectable at week 8 (= week 8 of peginterferon and week 4 of Victrelis)?
Yes
No
Is HCV RNA <100 IU/mL at week 12 (= week 12 of peginterferon and week 8 of Victrelis)?
Yes
No
Is HCV RNA undetectable at week 24 (= week 24 of peginterferon and week 20 of Victrelis)?
Yes
No
Will the patient be on ribavirin in combination with Sovaldi?
Yes
No
Is the patient ineligible for interferon therapy?
Yes
No
DUAL THERAPY: SOVALDI & RIBAVIRIN
Sovaldi
Ribavirin
Other
STRENGTH:
DIRECTION:
QUANTITY:
REFILLS:
STRENGTH:
DIRECTION:
QUANTITY:
REFILLS:
DUAL THERAPY: PEGINTERFERON & RIBAVIRIN
Pegasys
Ribavirin
Pegintron
STRENGTH:
Other
DOSAGE FORM:
STRENGTH:
DIRECTION:
DIRECTION:
QUANTITY:
QUANTITY:
REFILLS:
REFILLS:
Will the patient be on ribavirin in combination with the Injectable Hepatitis C Agent?
Yes
No
Please check the box that demonstrates the patient’s response at week 12:
No early virologic response (EVR) [HCV RNA decreased < 2 log]
Partial EVR [HCV RNA decreased ≥2 log]
Complete EVR [HCV RNA negative]
Please check the box that demonstrates the patient’s response at week 24:
HCV RNA negative
HCV RNA positive
If requesting Injectable Hepatitis C treatment for genotype 2 or 3 beyond 24 weeks, please answer the following:
Does the patient have a comorbidity requiring adjustment to the expected duration of therapy for patients with genotype 2 and 3?
Yes
No
If yes, list comorbid condition(s):
If requesting Injectable Hepatitis C treatment beyond 48 weeks, please answer the following:
Has the patient demonstrated a delayed virologic response (partial EVR at week 12 and HCV RNA negative at week 24)?
Yes
No
I attest that this is medically necessary for this patient and that all of the information on this form is accurate to
the best of my knowledge. I attest that documentation of the above diagnosis and medical necessity is available
for review if requested by New York Medicaid.
PRESCRIBER’S SIGNATURE
Revision Date: April 2014
DATE
For billing questions, call 1-800-343-9000.
For clinical concerns or Preferred Drug Program questions, visit
www.nyhealth.gov and http://newyork.fhsc.com or call 1-877-309-9493.
Page 3
Boceprevir (Victrelis®)
Boceprevir is the first direct-acting antiviral (DAA) to be approved for treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) genotype 1
infection. A member of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease inhibitor class, boceprevir was approved by the Food and Drug
Administration (FDA) in 2011 for use in combination with peginterferon and ribavirin (PR) in treatment-naïve and
treatment-experienced adult patients with compensated liver disease, including cirrhosis.1
Advantages of adding boceprevir to therapy
Boceprevir was designed to inhibit HCV NS3/4A protease which prevents the cleavage of viral polyproteins during HCV
replication. It is a complementary therapy to PR that together enhances host defenses against the virus. It has been shown
to increase sustained virologic response (SVR) rates in both treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients when
compared to using standard treatment with only PR.
Trial
Subjects
Treatment arm
including lead-in*
Overall SVR rate (%)
SVR rate (%)
Non-black patients
SVR rate (%)
Black patients
SPRINT-21
1,097
treatmentnaïve
B24 + PR28 or 48
63 (p<0.001)
67 (p<0.001)
53 (p<0.001)
B44 + PR48
66 (p<0.001)
68 (p<0.001)
42 (p=0.004)
PR48 (Control)
38
40
23
403
treatmentexperienced
Treatment arm
including lead-in*
Overall SVR rate (%)
SVR rate (%)
Prior relapsers
SVR rate (%)
Prior partial responder
B32 + PR36 or 48
59 (p<0.001)
69 (p<0.001)
40 (p<0.001)
B44 + PR48
66 (p<0.001)
75 (p<0.001)
52 (p<0.001)
PR48 (Control)
21
29
7
RESPOND-22
*By weeks on each component; B=boceprevir; PR=peginterferon + ribavirin; lead-in=4 weeks of PR prior to adding B or placebo;
p values are in reference to the statistical significance as compared to the control group
Cautions
Boceprevir should not be used as monotherapy due to rapid development of resistance mutations. Resistance is also
seen in patients that do not achieve SVR with combination therapy.
Boceprevir should not be used if a patient has previously failed treatment with another HCV protease inhibitor (e.g.,
simeprevir or telaprevir) due to cross-resistance within the class.
Most common adverse reactions with boceprevir are fatigue, anemia, nausea, headache, and dysgeusia.
Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with use of boceprevir in combination with PR. If an acute
reaction occurs, treatment must be discontinued and urgent care obtained.
Boceprevir is a substrate and strong inhibitor of CYP3A4/5 and p-glycoprotein. Coadministration with potent CYP3A4/5
inducers is contraindicated. Coadministration with CYP3A4/5 substrates that produce serious or life threatening events
at elevated plasma concentrations is also contraindicated.
Where does boceprevir fit into therapy and how should it be used?
In January 2014, The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and Infectious Diseases Society of America, in
collaboration with the International Antiviral Society – USA, launched www.hcvguidelines.org for the purpose of
disseminating expert opinion on management of CHC as newer HCV DAA become available and treatment evidence emerges.
There are no comparative efficacy data available to date among the HCV DAA, but it is likely that guidelines for optimal
regimens will continue to evolve and will need to integrate patient-specific as well as economic factors.
Many patient-specific factors must be considered when deciding to initiate therapy. The goal of treatment is SVR, defined by
an undetectable HCV RNA level 24 weeks after the end of treatment. Baseline genotype must be established as boceprevir is
only approved in HCV genotype 1. Effective use of boceprevir is dependent on response-guided therapy.1 Duration of
treatment is determined by response and previous treatment status. It is essential to assess response by testing HCV-RNA
viral load at critical points: after a 4 week lead-in period of PR (week 4 of treatment), and then at treatment weeks 8, 12, and
24. Boceprevir is dosed at 800 mg three times daily (every 7 – 9 hours) with food (meal or light snack).
References: 1. Boceprevir (Victrelis®) product information. Schering Corporation, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., 2013. 2. Poordad et al. NEJM 2011; 364: 1195-1206. 3. Bacon
et al. NEJM 2011; 364: 1207-1217.
Revision Date: 2/20/14
Boceprevir Initiation and Monitoring
Once patient readiness for chronic hepatitis C treatment has been determined, the algorithm below outlines key decision
points for initiating and monitoring combination therapy including boceprevir. This algorithm is available in interactive
format on the NYMPEP website at: http://nypep.nysdoh.suny.edu.
Note: Ribavirin is contraindicated in pregnancy therefore all female patients of childbearing age (or female partners of male
patients) should be sure they are not pregnant prior to beginning treatment and should use two methods of non-hormonal
birth control throughout treatment. Also note, HCV RNA testing should be conducted using a sensitive assay.
Has the patient been diagnosed with HCV genotype 1
and received quantitative HCV RNA testing?
No
Seek alternative treatment
options or conduct testing
prior to treatment.
Yes
Initiate a 4-week lead-in treatment period with
peginterferon alpha and ribavirin. Has the patient
completed 4 consecutive weeks of lead-in therapy?
No
Provide 4 consecutive weeks of
lead-in therapy prior to
initiating boceprevir.
Yes
At the end of treatment week 4, add boceprevir 800
mg three times daily to peginterferon alpha and
ribavirin and obtain quantitative HCV RNA. Repeat
quantitative HCV RNA at treatment weeks 8 and 12.
Is HCV RNA <100 IU/mL at week 12?
No
Stop treatment in all patients.
No further HCV RNA testing.
Yes
No
Repeat HCV RNA at week 24. Is HCV RNA
undetectable at week 24?
Yes
Is the patient
Is the patient
O
O
treatment-naïve
prior partial
R
without cirrhosis?
responder?* R
Is the patient
prior
relapser?+
No
Prior null O Treatment-naïve
responder?‡ R w/ compensated
cirrhosis?
Yes
Was HCV RNA undetectable at treatment week 8?
Yes
Continue triple therapy to the end
of week 28 in treatment naïve
patients. Continue triple therapy to
the end of week 36 in prior partial
responders or prior relapsers.
Yes
No
Continue triple therapy to the
end of week 36. Continue
peginterferon alpha & ribavirin
to the end of week 48.
Continue triple therapy to the
end of week 48.
Obtain HCV RNA 24 weeks after the end of treatment to
determine sustained virological response.
*Prior partial responder = achieved ≥2 log decrease in HCV RNA at week 12 of previous treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin but did not achieve
undetectable HCV RNA at end of treatment
+Prior relapser = achieved undetectable HCV RNA at end of previous treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin but detectable within 24 weeks after
treatment
‡Prior null responder = achieved <2 log decrease in HCV RNA at week 12 of previous treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin
Revision Date: 2/20/14
Telaprevir (Incivek®)
Telaprevir is the second direct-acting antiviral (DAA) to be approved for treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (CHC) genotype 1.
A member of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease inhibitor class, it was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2011
for use in combination with peginterferon and ribavirin (PR) in treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced adult patients with
compensated liver disease, including cirrhosis. 1
Advantages of adding telaprevir to therapy
Telaprevir was designed to inhibit HCV NS3/4A protease which prevents the cleavage of viral polyproteins during HCV replication. It
is a complementary therapy to PR that together enhances host defenses against the virus. It has been shown to increase the
sustained virologic response (SVR) in both treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients when compared to using only PR.
Trial
Subjects
Treatment arm*
ADVANCE2
1,088
treatment naïve
T12+PR24/48
Overall SVR rate (%)
75 (p<0.001)
T8+PR24/48
69 (p<0.001)
PR48 (control)
ILLUMINATE3
540
treatment naïve
44
T12+PR12 to start (all)
72
e-RVR T12+PR24
92 (non-inferior to e-RVR T12+PR48)
e-RVR T12+PR48
88
non-e-RVR T12+PR48
REALIZE4
662
treatment experienced
64
Overall
rate
Prior
relapsers
Prior partial
responders
Prior null
responders
T12+PR48
64 (p<0.001)
83 (p<0.001)
59 (p<0.001)
29 (p<0.001)
Lead-in T12+PR48
66 (p<0.001)
88 (p<0.001)
54 (p<0.001)
33 (p<0.001)
Treatment arm*
PR48 (control)
17
24
14
5
*By weeks on each component; T=telaprevir; PR=peginterferon + ribavirin; e-RVR=extended rapid virologic response (undetectable HCV RNA at weeks 4 & 12);
Lead-in=4 weeks PR prior to adding T; p values are in reference to the statistical significance as compared to the control group
Cautions
Telaprevir should not be used as monotherapy due to rapid development of resistance mutations. Resistance is also seen in
patients that do not achieve SVR with combination therapy.
Telaprevir should not be used if a patient has previously failed treatment with another HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor (e.g.,
boceprevir or simeprevir) due to cross resistance within the class.
Telaprevir labeling was updated in 2012 to include a boxed warning for serious fatal and non-fatal skin reactions, including
Stevens Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), and Toxic Epidermal
Necrolysis (TEN). Rash with systemic symptoms or progressive severe rash necessitates urgent medical care and discontinuation
of telaprevir and PR.
Telaprevir is a substrate and strong inhibitor of CYP3A and p-glycoprotein. Coadministration with potent CYP3A inducers is
contraindicated. Coadministration with CYP3A substrates that produce serious or life threatening events at elevated plasma
concentrations is also contraindicated.
Where does telaprevir fit into therapy and how should it be used?
In January 2014, The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and Infectious Diseases Society of America, in collaboration
with the International Antiviral Society – USA, launched www.hcvguidelines.org for the purpose of disseminating expert opinion on
management of CHC as newer HCV DAA become available and treatment evidence emerges. There are no comparative efficacy data
available to date among the HCV DAA, but it is likely that guidelines for optimal regimens will continue to evolve and will need to
integrate patient-specific as well as economic factors.
Many patient-specific factors must be considered when deciding to initiate therapy. The goal of treatment is SVR, defined by an
undetectable HCV RNA level 24 weeks after the end of treatment. Baseline genotype must be established as telaprevir is only
approved in HCV genotype 1. Effective use of telaprevir is dependent on response-guided therapy. Telaprevir should be given with
PR for the first 12 weeks and PR continued for 12-36 weeks thereafter, depending on response and previous treatment status. It is
essential to assess HCV RNA viral load at weeks 4 and 12 to determine duration of treatment. Telaprevir is dosed at 1125 mg twice
daily (10 – 14 hours apart) with food (not low fat).
References: 1. Incivek® product information. Vertex Pharmaceuticals, 2013. 2. Jacobson et al. NEJM 2011;364(25):2405-16. 3. Sherman et al. NEJM 2011;365(11):1014-24. 4. Zeuzem et al.
NEJM 2011;364(25):2417-28.
Revision Date: 2/20/14
Telaprevir Initiation and Monitoring
Once patient readiness for chronic hepatitis C treatment has been determined, the algorithm below outlines key decision points for
initiating and monitoring combination therapy including telaprevir. This algorithm is available in interactive format on the NYMPEP
website at: http://nypep.nysdoh.suny.edu.
Note: Ribavirin is contraindicated in pregnancy therefore all female patients of childbearing age (or female partners of male patients)
should be sure they are not pregnant prior to beginning treatment and should use two methods of non-hormonal birth control
throughout treatment. Also note, HCV RNA testing should be conducted with a sensitive assay.
Has the patient been diagnosed with HCV genotype 1
and received quantitative HCV RNA testing?
No
Seek alternative treatment options or
conduct testing prior to treatment
Yes
Begin treatment with telaprevir 1125 mg twice daily in
combination with peginterferon alpha and ribavirin.
Repeat quantitative HCV RNA at the end of treatment
week 4. Is HCV RNA ≤1000 IU/mL?
No
Stop treatment in all patients
No further HCV RNA testing
Yes
Continue telaprevir with peginterferon alpha and
ribavirin to the end of treatment week 12. Repeat
quantitative HCV RNA. Is HCV RNA ≤1000 IU/mL?
No
Yes
Is the patient treatment-naïve without cirrhosis
OR
a prior relapser?+
No
Is the patient treatment-naïve with
compensated cirrhosis? OR
a prior partial responder?* OR
a prior null responder?‡
Yes
Was HCV RNA undetectable at both weeks 4 and 12?
Yes
No
Continue peginterferon alpha and
ribavirin to the end of week 48
Yes
Continue peginterferon alpha and ribavirin to the end
of week 24
Obtain HCV RNA 24 weeks after the end of treatment to determine
sustained virological response
*Prior partial responder = achieved ≥2 log decrease in HCV RNA at week 12 of previous treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin but did not
achieve undetectable HCV RNA at end of treatment
+Prior relapser = achieved undetectable HCV RNA at end of previous treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin but detectable within 24 weeks
after treatment
‡Prior null responder = achieved <2 log decrease in HCV RNA at week 12 of previous treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin
Revision Date: 2/20/14
Simeprevir (Olysio™)
Simeprevir is a new treatment option for patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1. Approved by the Food and Drug
Administration (FDA) in November 2013, the drug represents the latest addition to the class of HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitors,
including boceprevir and telaprevir. Simeprevir is intended for use in combination with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin (PR) in HCV
genotype 1-infected patients with compensated liver disease, including cirrhosis. 1
Advantages of simeprevir
Simeprevir is taken once daily with food in combination with PR. Simeprevir directly interferes with the HCV life cycle by suppressing
viral replication. The drug was designed to inhibit HCV NS3/4A, which prevents the cleavage of viral polyproteins during HCV
replication. Thus, simeprevir is a complementary therapy to PR; together these drugs enhance host defenses against HCV. Use of
simeprevir in combination with PR has been shown to increase rates of sustained virologic response (SVR), in both treatment-naïve
and treatment-experienced patients compared to use of PR alone. In clinical trials, treatment duration was determined by responseguided-therapy criteria. Primary endpoint was defined as undetectable HCV RNA (<25 IU/mL) at 12 weeks post treatment (SVR12).
Phase III Trials:
Trial
Subjects
Treatment arm*
QUEST 1 and 22
(pooled analysis)
785
Treatment-naïve
PROMISE2
393
Treatment- experienced
SMV12+PR24/48
PR48 (control)
SMV12+PR24/48
PR48 (control)
Overall
SVR rate (%)
80%
50%
79%
37%
Genotype 1a
SVR rate (%)
Genotype 1b
SVR rate (%)
75%
47%
70%
28%
85%
53%
86%
43%
*By weeks on each component; SMV = simeprevir
Cautions
Simeprevir efficacy in combination with PR is substantially reduced in patients infected with HCV genotype 1a with an NS3 Q80K
polymorphism. Screening for NS3 Q80K polymorphism is strongly recommended prior to initiation of therapy; alternative
therapy should be considered in patients with the polymorphism due to reduced efficacy observed in clinical trials.
Simeprevir should be administered with PR and should not be used as monotherapy. Additionally the dose must not be reduced
nor should treatment be interrupted. Treatment with simeprevir must not be reinitiated in these patients.
Simeprevir should not be used if a patient has previously failed treatment with another HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor (e.g.,
boceprevir or telaprevir) due to cross resistance within the class.
If HCV RNA levels exceed 25 IU/mL at week 4, discontinuation of simeprevir and PR is recommended. If PR is discontinued
during the first 12 weeks of therapy, simeprevir must also be discontinued.
Higher rates of rash (including photosensitivity), pruritus and nausea occurred in simeprevir-treated patients vs. patients
receiving PR alone. If a severe rash develops, simeprevir should be discontinued and not restarted.
Simeprevir is metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A; co-administration with a moderate or strong inducer or inhibitor of
CYP3A is not recommended. Simeprevir inhibits organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1/3 and P-glycoprotein (P-gp)
transporters; therefore, co-administration of drugs that are substrates for OATP1B1/3 and P-gp transporters may result in
increased plasma concentration of those drugs.
Where does simeprevir fit into therapy and how should it be used?
In January 2014, The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and Infectious Diseases Society of America, in collaboration
with the International Antiviral Society – USA, launched www.hcvguidelines.org for the purpose of disseminating expert opinion on
management of CHC as newer HCV DAA become available and treatment evidence emerges. There are no comparative efficacy data
available to date among the HCV DAA, but it is likely that guidelines for optimal regimens will continue to evolve and will need to
integrate patient-specific as well as economic factors.
Many patient-specific factors must be taken into consideration when deciding to initiate therapy. Baseline genotype must be
established as simeprevir is only approved for HCV genotype 1. Simeprevir must be given with PR for the first 12 weeks; PR therapy
should be continued (alone) for an additional 12–36 weeks, depending on patient response and previous treatment status. It is
essential to assess HCV RNA viral load at treatment weeks 4, 12, and 24 to determine duration of treatment . The goal of treatment is
undetectable HCV RNA 12 weeks post-treatment (SVR12).
References: 1. Simeprevir (Olysio) product information. Janssen Corporation, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson (J&J); 2013. 2. Data on file. Janssen Corporation, subsidiary of J&J; 2013.
Revision Date: 2/20/14
Simeprevir Initiation and Monitoring
Once patient readiness for chronic hepatitis C treatment has been determined, the algorithm below outlines key decision points for
initiating and monitoring combination therapy including simeprevir.
Note: Ribavirin is contraindicated in pregnancy; therefore, all female patients of childbearing age (or female partners of male
patients) should be sure they are not pregnant prior to beginning treatment and should use two methods of non-hormonal birth
control throughout treatment. Also note, HCV RNA testing should be conducted with a sensitive assay.
Has the patient been diagnosed with HCV genotype 1 without
NS3 Q80K polymorphism and received quantitative HCV RNA
testing?
No
Seek alternative treatment options or
conduct testing prior to treatment
Yes
Begin treatment with simeprevir 150 mg once daily with food in
combination with peginterferon alpha and ribavirin
No
Repeat quantitative HCV RNA at the end of treatment week 4
Stop treatment in all patients
Is HCV RNA ≤25 IU/ ml?
No further HCV RNA testing
Yes
Continue simeprevir with peginterferon alpha and ribavirin to
the end of treatment week 12
No
Repeat quantitative HCV RNA. Is HCV RNA≤25 IU/ ml?
Yes
Is the patient treatmentnaïve, including those with
cirrhosis?
OR
Is the patient a prior
relapse, including those
with cirrhosis?*
No
Is the patient a prior non-responder
(including partial and null responders)
including those with cirrhosis?**
Yes
Yes
Continue peginteferon alfa and ribavirin for additional 12 weeks
for total treatment duration of 24 weeks
Continue peginterferon alfa and
ribavirin for additional 36 weeks for
total treatment duration of 48
weeks***
Obtain HCV RNA 12 weeks after the end of treatment to determine sustained
virological response (SVR12)
*Prior relapser: undetectable HCV RNA at the end of prior interferon-based therapy and detectable HCV RNA during follow-up
**Prior partial responder: prior on-treatment ≥2 log10 IU/ml reduction in HCV RNA from baseline at Week 12 and detectable HCV RNA at end of prior
interferon-based therapy. Prior null responder: prior on-treatment <2 log10 reduction in HCV RNA from baseline at Week 12 during prior interferonbased therapy.
***If HCV RNA ≥25 IU/ml discontinue peginterferon alfa and ribavirin for non-responders (including partial and null responders).
Revision Date: 2/20/14
Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi™)
Sofosbuvir is a new oral treatment option for patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1, 2, 3, or 4 infection, including
those with hepatocellular carcinoma meeting Milan criteria (awaiting liver transplant) and those with HCV/ human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- 1 co-infection. Approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 2013, sofosbuvir is
the first direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agent in the nucleoside/nucleotide polymerase inhibitor class. A nucleotide analog, sofosbuvir
interferes with the HCV life cycle by inhibiting HCV NS5B ribonucleic acid (RNA)-dependent RNA polymerase to prevent replication of
the HCV virus. Sofosbuvir is indicated for use in combination with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin (PR) for HCV genotypes 1 and 4
and in combination with ribavirin (RBV) for genotypes 2 and 3 as well as for genotype 1 in patients who are interferon ineligible.1
Advantages of sofosbuvir
Sofosbuvir is taken orally once daily with or without food as a component of an antiviral treatment regimen. The treatment regimen
and duration is dependent on both the HCV genotype and patient characteristics. Published phase 3 trials have demonstrated the
efficacy of sofosbuvir in combination with PR for patients with genotype 1 or 4 and in combination with RBV alone for patients with
genotype 2 or 3. Additionally, per unpublished data from the manufacturer, sustained virologic response (SVR) has been successfully
achieved in patients co-infected with HIV-1 and in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) awaiting liver transplantation. 1
Recommended treatment regimens are identical for patients with HCV mono-infection or HCV/HIV-1 co-infection. In clinical trials,
treatment duration was fixed and not guided by HCV RNA response. The primary endpoint was defined as HCV RNA less than the
lower level of quantification (<25 IU/mL) at 12 weeks post treatment (SVR12).
Published phase III trials:
Trial
Subjects
NEUTRINO1,2
327 treatment-naïve adults
FISSION1,2
499 treatment-naïve adults
POSITRON1,3
FUSION1,3
278 interferon intolerant, ineligible or
unwilling adults (81% no prior treatment)
201 adults with prior breakthrough,
relapse, or null response with interferon
Treatment arms
SOF + PR x 12 weeks
Adjusted historical control
SOF + RBV x 12 weeks
PR x 24 weeks
SOF + RBV x 12 weeks
Placebo x 12 weeks
SOF + RBV x 12 weeks
SOF + RBV x 16 weeks
Overall
SVR12 rate
90%
60%
67%
67%
78%
0%
50%
71%
SVR12 rate by genotype
2
3
4
96%
--NR
95%
56%
--78%
63%
93%
61%
--0%
0%
82%
30%
--89%
62%
1
89%
NR
SOF = sofosbuvir; PR = peginterferon + ribavirin; RBV = ribavirin; NR=not reported
Cautions
Sofosbuvir should not be used as monotherapy and only as a component of an antiviral regimen dependent on the patient’s
genotype and other conditions (see table below). Sofosbuvir dose must not be reduced nor should treatment be interrupted.
Sofosbuvir is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) drug transporters. Do not
coadminister sofosbuvir with potent P-gp inducers due to risk of reduced sofosbuvir concentrations and treatment failure.
For patients with severe renal impairment or with end stage renal disease, no dose recommendations are available.
Where does sofosbuvir fit into therapy and how should it be used?
In January 2014, The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and Infectious Diseases Society of America, in
collaboration with the International Antiviral Society – USA, launched www.hcvguidelines.org for the purpose of disseminating
expert opinion on management of CHC as newer HCV DAA become available and treatment evidence emerges. There are no
comparative efficacy data available to date among the HCV DAA, but it is likely that guidelines for optimal regimens will continue to
evolve and will need to integrate patient-specific as well as economic factors.
Many patient-specific factors must be taken into consideration when deciding to initiate therapy and baseline genotype must be
established to guide treatment regimen and duration as outlined below. Sofosbuvir is dosed 400 mg once daily with or without food.
The goal of treatment is undetectable HCV RNA 12 weeks post-treatment (SVR12).
Sofosbuvir treatment regimen and duration recommendations 1
HCV Mono-infected and HCV/HIV Co-infected
Genotype 1 or 4
Genotype 2
Genotype 1 interferon ineligible or Genotype 3
Treatment
SOF + PR
SOF + RBV
SOF + RBV
Duration
12 weeks
12 weeks
24 weeks
Note: For patients with HCC awaiting liver transplantation, the recommended treatment is SOF + RBV for up to 48 weeks or until transplant, whichever occurs first.
References: 1. Sovaldi™ product information. Gilead Sciences, 2013. 2. Lawitz et al. NEJM 2013;368(20):1878-87. 3. Jacobson et al. NEJM 2013;368(20):1867-77.
Revision Date: 2/20/14
Sofosbuvir Initiation and Monitoring
Once patient readiness for chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment has been determined, the algorithm below outlines
key decision points for initiating and monitoring combination therapy including sofosbuvir.
Note: Ribavirin is contraindicated in pregnancy therefore all female patients of childbearing age (or female partners of
male patients) should be sure they are not pregnant prior to beginning treatment and should use 2 methods of nonhormonal birth control throughout treatment. Also note, HCV RNA testing should be conducted using a sensitive assay.
Has the patient been diagnosed with HCV genotype 1, 2, 3 or 4
and received quantitative HCV RNA testing?
No
Seek alternative treatment options or
conduct testing prior to treatment
Yes
Does the patient have hepatocellular carcinoma and awaiting
liver transplantation?
No
Yes
Genotype 1 interferon ineligible
or genotype 2 or 3
or
Initiate sofosbuvir 400 mg once daily with
weight based ribavirin
Genotype 1 interferon eligible
or genotype 4
Initiate sofosbuvir 400 mg once daily with
peginterferon alpha and weight based ribavirin
Continue sofosbuvir 400 mg once daily as a component of antiviral
therapy to the end of treatment week 12
No
Repeat quantitative HCV RNA. Is HCV RNA ≤ 25 IU/ ml?
Evaluate patient adherence and
consider discontinuing therapy
If therapy is discontinued no further
HCV RNA testing is required
Yes
Hepatocellular carcinoma: continue
regimen for up to an additional 36
weeks or until liver transplantation,
whichever occurs first, for total
treatment duration of 48 weeks
Genotype 1 interferon ineligible or
genotype 3: continue regimen for an
additional 12 weeks for total
treatment duration of 24 weeks
Genotype 1 interferon eligible or
genotype 2 or 4: treatment is
complete
Obtain HCV RNA 12 weeks after the end of treatment to determine
sustained virological response (SVR12)
Revision Date: 2/20/14









