Learning Outcomees Chart Biology BS (8-15
advertisement

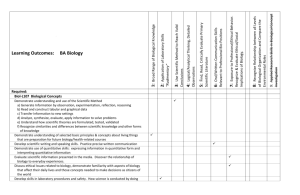
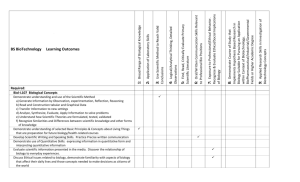
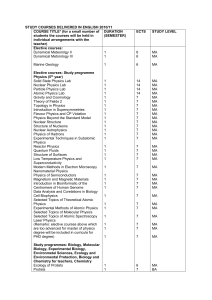
Required: Biol-L107 Biological Concepts Demonstrate understanding and use of the scientific method a) Generate Information by observation, experimentation, reflection, reasoning b) Read and construct tabular and graphical data c) Transfer information to new settings d) Analyze, synthesize, evaluate, apply information to solve problems e) Understand how scientific theories are formulated, tested, validated f) Recognize similarities and differences between scientific knowledge and other forms of knowledge Demonstrate understanding of selected basic principles & concepts about living things that are preparation for future biology/health-related courses Develop scientific writing and speaking skills. Practice precise written communication Demonstrate use of quantitative skills: expressing information in quantitative form and interpreting quantitative information Evaluate scientific information presented in the media. Discover the relationship of biology to everyday experiences. Concept Investigation 9: Applied Research Skills in Biological of Biological Organization and Compare the Environmental Roles 8: Recognize Relationship between all Levels Recognize & Evaluate Ethical/Social Implications of Biology. 7: Exposure to Professional/Ethical Behavior. Relevant to Professional Bio Positions 6: Oral/Written Communication Skills Scientific Literature 5: Find, Read, Critically Evaluate Primary Observations 4: Logical/Analytical Thinking, Detailed Conclusions 3: Use Scientific Method to Reach Valid 2: Application of Laboratory Skills Learning Outcomes: BS Biology 1: Broad Range of Biological Knowledge Draft 08/15/2011 Discuss ethical issues related to biology, demonstrate familiarity with aspects of biology that affect their daily lives and those concepts needed to make decisions as citizens of the world Develop skills in laboratory procedures and safety. How science is conducted by doing some activities that scientists do. Develop skills working in groups to clarify course concepts, solve problems, complete writing assignments. Complete semester-long Research Project Biol-L315 Cell Recognize and describe what tissues, cells and cell organelles are Recognize and describe the structure, function and regulation of the various components of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including macromolecules, membranes and cell organelles Describe how cells communicate and interact with each other and the environment Describe how energy is generated and utilized in cells Describe on introductory level the concept of gene expression and regulation Evaluate the various techniques used to study cell biology Apply knowledge of cell biology to read, understand and present scientific articles related to the field. Biol-B301 Introduction to Plant Kingdom Describe an introduction to botany: what it is, how it was developed and how it relates to everyday life. Describe the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells as well as plant and animal cells. Identify the various organs and tissues of plants. Identify their morphology, development, function and economic importance. Identify and compare dicots and monocots. Recognize the structure and parts of flowers, fruits and seeds. Describe their development. Describe an introduction of plant physiology, plant metabolism, including photosynthesis and respiration, and plant growth. Compare sexual and asexual reproduction, identify the stages of mitosis and meiosis, and describe alternation of generations. Describe a brief introduction to plant genetics. Describe plant breeding and propagation. Identify plant names and classification, including the Binomial System of Nomenclature and the six-kingdom classification. Recognize and describe the characteristic features and economic importance of all kingdoms and corresponding phyla. Classify plants to the various kingdoms and their phyla based on key features. Use various experiments in class to understand topics such as osmosis, plant growth and the effect of light or various chemicals on plant germination. Biol-Z301 Introduction to Animal Kingdom Demonstrate scientific method by a)generating information by observation and discerning patterns b)transfer biological concepts to new settings c)analyzing, evaluating, applying information to problem-solving. Describe basic molecular, physiological, developmental mechanisms that unite animals Explain forces that shape animal form and function Describe diversity of animals and interrelationships that unite them Demonstrate critical thinking skills through observation, experimentation, reviewing scientific literature and writing Demonstrate empirical basis of scientific ideas with lab experiences Demonstrate relationships between biological structures and their functional capabilities with lab experiences Biol-L325 Ecological Principles Delineate modes of energy transfer in biological systems Explore factors regulating community organization, stability, complexity Use mathematics to model population genetics Demonstrate critical thinking skills through observation, experimentation, reviewing scientific literature, writing Demonstrate improved writing skills by summarizing technical information, and converting it to an article for general reading Biol-L314 Genetics Use scientific method of evaluating experiments Write/communicate with scientific language and in standard scientific methods Apply critical assessment and analysis to experimental work Use cellular genetic material basis to differentiate media hype and quality medical discovery Biol-L452 Capstone Demonstrate ability to think like a scientist: critical-thinking and problem-solving, quality of the thinking 15 Credit Hrs from the Following: Biol-L211/213 Molecular Biology (Will be Included January 2012) Biol-N212/213 Human Biology (N213 is optional lab course) Define: scientific method, homeostasis, feedback loop, and pH Demonstrate understanding of structure and function of each organ system studied in course Demonstrate scientific communication, written and/or orally, to explain the apparent structure and function of organ systems at the molecular, cellular, histological, organ, and systemic level. In N123, demonstrate skills in laboratory exercises Anat-A215 Human Anatomy Define: scientific method, homeostasis, feedback loop, and pH Demonstrate understanding of structure with some function of each organ system studied in the course Demonstrate effective communication, written and/or orally, to explain the structure of organ systems at the molecular, cellular, histological, organ, and systemic level. Being planned for future semesters: demonstrate skills in carrying our laboratory procedures Phsl-P215 Human Physiology Define: scientific method, homeostasis, feedback loop, and pH Demonstrate understanding of function with some structure of each organ system studied in the course Demonstrate effective communication, written and/or orally, to explain the function of organ systems at the molecular, cellular, histological, organ, and systemic level. Being planned for future semesters: demonstrate skills in carrying our laboratory procedures Biol-B364 Summer Flowering Plants Demonstrate understanding of the diversity of organisms within the world of flowering plants Demonstrate knowledge of several of the major plant families, their structures, distribution, and human significance Demonstrate the skills in use of a technical key to identify native species of flowering plants Biol-L303 Field Biology Demonstrate basic understanding of ecosystem in which the course takes place Identify common organisms and relate their structure to ecological function Outline relationship on common organisms to habitat Apply basic physical, chemical, biological forces affecting organisms Describe impact of humans on ecosystem presently and historically Demonstrate sensitivity to culture if the region of the course Biol-L318 Evolution Explain/describe scientific theories and principles of origin of life, origin of species Scientifically analyze, evaluate, apply information to evolutionary problems Scientifically describe major patterns in fossil record Use population genetics to explain biological diversity Relate history of life to phylogenetic relatedness Biol-L321 Immunology Identify & understand elements of the immune system (barriers, adaptive response, etc) State and define antibody structures and how they are generated Understand and identify how antigens are recognized by T lymphocytes Describe and interpret how T cells and B cells develop Differentiate and describe T cell-mediated and B cell-mediated immunity Describe innate versus adaptive immune response Describe how the immune system can fail or over-react, including recognition of immunodeficiencies Describe examples of autoimmune disorders Describe mechanisms by which scientists can manipulate immune response Biol-L333 Introduction to Environmental Science Discuss scientific principles that underlie environmental issues Explain modern landfills, wastewater treatment facilities, water treatment processes and how they protect humans from disease and pollution Discuss environmental impact of high-tech food production & ways of minimizing damage Explain provisions of major environmental regulations Discuss cultural definition of environmental issues, influence of ethnic/cultural/gender perspectives Describe methods of sustainability Research/summarize environmental issues Biol-L340 Biological Basis of Sex Differences Understand and describe the processes (internal, external, hormonal) of biological sex differentiation Identify, describe and appreciate sex, gender, gender identity, gender attraction, gender roles Understand and be able to discuss current evolutionary theory, especially sexual selection as it applies across taxa but especially as it pertains to sexual and reproductive behavior in humans Understand and describe the concept of reproductive effort and apply its two forms (mating effort and parental effort) across taxa. Understand and describe kin selection (inclusive fitness). Understand and be able to discuss the hypothesis that humans evolved in a much different environment than our current one, and that our brains may not be “designed” to solve modern problems. Understand and be able to discuss that most of human sexual behavior is indeed nonreproductive in outcome. Appreciate and be able to discuss the relatively new discipline of evolutionary psychology in general, but especially as it applies to sexual/reproductive behavior Biol-L376 Biology of Birds Identify locally abundant species by sight and sound Use features of birds to place birds in taxonomic groups (Order, Family) Identify unique physical and behavioral traits and relate these to the life history of birds Describe the adaptations that birds have made for flight in an explanation of how birds fly Explain how birds communicate with each other Outline how individuals can enhance local and world-wide environment for bids Biol-L391 Special Topics Variable Based Upon Topic Biol-M310/315 MicroBiology Describe criteria of modern cell theory, describe characteristics, morphology, organelles of the major lineages of cellular life: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell archetypes Describe microbial cellular systems as mechanistic processes, compare systems and structures found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes. Describe taxonomic relationships of microbial lineages and apply different methods to identify organisms to the genus level. Apply knowledge of microbial systems to medical, ecological, industrial applications Demonstrate critical thinking skills, problem solving skills, communication of scientific ideas and principles through written/oral presentation methods Biol-L490 Individual Study Biol-L498 Internship Independent Limited Instruction/Laboratory Work/Off-Campus Experience Biol-Z468 Limnology (freshwater ecology) Describe and understand the physical and chemical properties of water, especially in a fresh water context Identify groups of aquatic taxa (e.g. protists, plants and animals) and understand the ecological niches of each taxon Demonstrate field/laboratory ability to sample, test and evaluate fresh water Sample and process population members of a species and demonstrate the ability to use mark-recapture techniques to describe and compare populations Apply the “Watershed Approach” to understanding the status of fresh water systems Understand different classifications of aquatic systems (e.g. stream, lake) and be able to describe processes in aquatic system status (e.g. eutrophication) Be able to write a comprehensive scientific report on an aquatic system(s) using appropriate research and literature techniques. Support/Prerequisite Courses: Math-M215/Math-M119/MA221 Calculus Calculate and Interpret finite and infinite limits, derivatives, integrals Apply concepts of derivatives and integrals to solving application problems Analyze physical phenomena using derivatives and integrals Chem-C105/125 General Chemistry I Describe quantum-mechanical atomic model relative to periodic table Illustrate chemical bonding features with appropriate chemical formulas Compare/contrast VSEPR, valence bond, molecular orbital theories Apply nomenclature rules to molecular and ionic substances Determine empirical formula of a compound from experimental data Distinguish strong/weak electrolytes, including acids/bases Predict precipitation reactions from solubility rules Express solution concentration in appropriate unit Distinguish between chemical and physical changes Balance chemical equation and apply stoichiometry to problem solving Perform dimensional analysis of units of measurement Predict molecular shape and polarity from Lewis Structures Maintain Lab Notebook consistent with industry standards Chem-C106/126 General Chemistry II Apply log equations to appropriate relationships Apply thermodynamic/kinetic data to predict reaction course Distinguish between rate constants and equilibrium constants Sketch plots of rate laws Predict equilibrium shift of reaction with Le Chatelier’s Principle Identify conjugate acid-base pairs Rate acid strength and buffering capacity to pH, Ka and pKa Balance oxidation-reduction equations, determine oxidation states Distinguish between chemical reactions and nuclear reactions Identify seven most common organic functional groups Name four basic types of hydrocarbons Identify Chiral Center in a structural formula Maintain Lab Notebook consistent with industry standards Chem-C341/343 Organic Chemistry I Identify name of organic molecule by observing structure and vice versa, draw structure of organic molecule from appropriate common/systematic (IUPAC) name Predict outcome of given set of organic molecules and synthetic reagents using principles of basic patterns of reactivity and/or identify adequate starting materials to synthesize simple organic molecule containing one of the common functional groups Predict overall 3-D structure of organic molecules and ionic/radical species that contain common functional groups by applying principles of bonding, hybridization, conformation analysis. Use spectroscopic techniques to determine molecular structure. interpret physical characteristics of common organic functional groups Safely handle lab glassware, equipment, chemical reagents. know guidelines, basic knowledge about common hazards in lab. Interpret lab results/data correctly, report findings in notebook with appropriate notational/descriptive content, understandable, reproducible Demonstrate how thermodynamic and kinetic principles are used to characterize organic chemical reaction energy changes, mechanisms, reaction rates. Chem-C342/344 Organic Chemistry II See Chem-C341/343 Organic Chemistry I. Same outcomes but different topics. Phys-P201 Physics I Define basic physical quantities learned for topics covered the course, using proper symbols and units. Identify these quantities in various contexts. write them in proper mathematical form. Use physical laws and principles to describe connections between relevant physical quantities. Demonstrate ability to state these relationships in mathematical form. Demonstrate problem-solving skills in a variety of topics: list known quantities and equations, prepare and label a relevant diagram, use algebra tools to solve for unknown quantity. With defined laboratory procedure, observe physical phenomena, gather and tabulate data with traditional measuring instruments and with computerinterfaced sensors. Demonstrate ability to record, organize, label data obtained from the observed quantity. Demonstrate ability to group and analyze data and interpret observations verbally. Carry out statistical calculations to determine precision, accuracy, sources of error. Compare data gathered/calculated to predictions deduced by mathematical calculations from the learned physical laws and principles. Perform graphical computer analysis to verify proportionality relationships and functional relationships of physical variables. Phys-P201 Physics II See Phys-P201 Physics II. Same outcomes but different topics.