Plate Tectonics/Earthquakes/Volcanoes Study Guide
advertisement
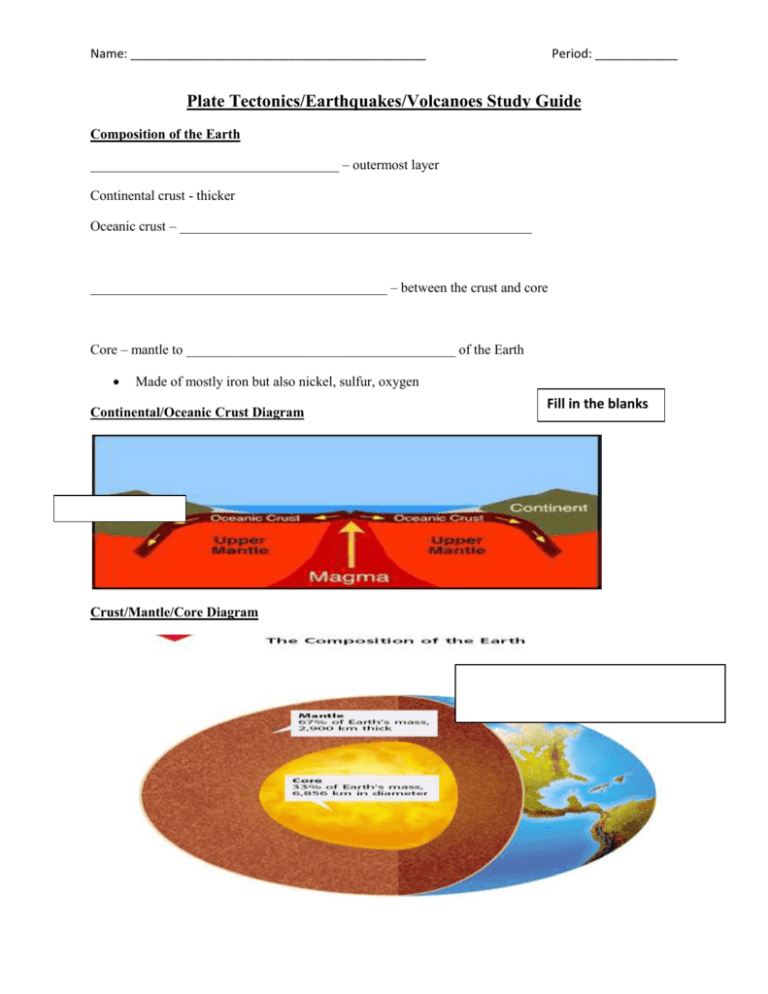
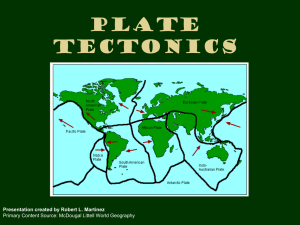
Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ Plate Tectonics/Earthquakes/Volcanoes Study Guide Composition of the Earth ____________________________________ – outermost layer Continental crust - thicker Oceanic crust – ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________ – between the crust and core Core – mantle to _______________________________________ of the Earth Made of mostly iron but also nickel, sulfur, oxygen Continental/Oceanic Crust Diagram Crust/Mantle/Core Diagram Fill in the blanks Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ Structure of the Earth 5 main physical layers (breaks down crust, mantle, and core into more specific layers) _________________________________ – outermost layer (crust and upper part of mantle) “rock sphere” (1st 60 miles down) Rigid Divided into tectonic plates Asthenosphere – “_____________________________________ sphere” (60-430 miles) Hot, flowing, soft layer of mantle where pieces of the lithosphere moved. _________________________________ – “middle sphere” (430-1800 miles) Hot, rigid, strong, lower part of mantle (pressure keeps it from flowing) Extends to core Lithosphere/Asthenosphere/Mesosphere Diagram Fill in the blanks Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ Outer Core – ________________________________________ 1,800 to 3,200 miles Average temp. is 9000 degrees F ____________________________________ Core - solid, dense center of the Earth 3,200 to 3,960 miles Avg. temp is 12,000 F Inner Core and Outer Core Diagram Wegener’s Continental Drift Theory _________________________________ drift is a theory, by Alfred Wegener, that continents can drift apart from one another. He didn’t take into account the ________________________________ __________________________. He just thought the continents moved. Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ Pangaea – all _____________________________________ as one Greek for “all Earth” Pangaea Picture Fill in the blank Tectonic Plates Plate Tectonics Theory: The theory that the Earth’s ___________________________________________ is divided into tectonic plates that move. Think jig saw puzzle. Each plate fits into another one. Sea floor spreading – process by which new ______________________________________ lithosphere is created as older materials are pulled away (the sea floor spreads apart). Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ _________________________________________ form when the tectonic plates collide and they push the continental crust upward. Tectonic Plates Diagram Earthquakes Seismology is the study of _____________________________________. Seismos means “to _________________________________________” in Greek. Earthquakes occur near tectonic plate boundaries or faults. Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ The most ____________________________________________ activity (earthquakes and volcanoes) occurs along the Ring of Fire, the area that surrounds the Pacific Plate. Ring of Fire Diagram A ________________________________________ is a break in the Earth’s crust along which blocks of the crust slide. This sliding along the fault is an earthquake. Types of Motions and Faults Motions _________________________________ motion occurs where two plates slip past each other Convergent motion occurs where two plates ___________________________________ together. _______________________________ motion occurs where two plates pull away from each other. Faults Strike slip faults are caused by ___________________________ motion. Blocks of crust slide horizontally. ______________________________ faults are caused by convergent motion. Blocks of crust slide vertically. Normal faults are caused from divergent motion. Blocks of crust move ____________________. Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ Motion and Fault Chart Plate Motion Prominent fault type Earthquake characteristics Strike-slip fault Moderate, shallow _______________________ Convergent Strong, deep ________________ fault Divergent Normal fault _______________, shallow Earthquake Fault/Motion Video What did the geologist use to demonstration the 3 types of plate motions? _________________________ At the end of the video, in the pot, what did he use to represent the crust of the Earth? _____________________________________________________ Earthquake Waves Seismic waves are waves of ________________________ that travel through the Earth from earthquakes. ___________ Waves (primary/pressure) travel through solids, liquids, and gases and are the fastest. (think push and pull) ________________ Waves (secondary/shear) waves are created when the rock springs back to its original position after being deformed. (think side to side) Surface waves move the ground _____________ and _____________________ in circles. (think up and down like a roller coaster.) Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ Earthquake Measurement Seismographs are ____________________________________________located at or near the surface of the Earth that record seismic waves. _______________________________________ is a tracing of earthquake motion created by a seismograph. Epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above an earthquakes starting point. A ____________________________ is the point inside the Earth where the earthquake begins. Epicenter Picture Fill in the blanks Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ Richter Scale The __________________________________________Scale is used to measure an earthquakes strength Named after Charles Richter. Goes from 1 (weakest) to 10 (strongest) Each time the magnitude increases by 1 unit, the amount of energy released becomes 31.7 times larger. Earthquakes Study Jams Video Quiz Score: __________ / 7 Volcanoes What is a volcano? A volcano is a ____________________________ that forms when magma is forced to the Earth’s surface. ____________________________________ is magma that flows on the Earth’s surface. Types of eruptions Nonexplosive – ______________________ flows ___________________________________: clouds of hot debris and gases shoot out from the volcano Eruptions Volcanoes erupt with either lava or ________________________________________________ material. Lava–created by nonexplosive __________________________________________. ______________________________________: stiff, jumbled heaps of sharp chunks Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ Pahoehoe: slow forming, like __________________________________ dripping Aa - pours quickly and has a jagged and brittle crust. ______________________________________________: rounded lumps that form underwater Pyroclastic material is rock ______________________________________ created by explosive volcanic eruptions. Types of Volcanoes _______________________________________: built out of layers of lava from repeated nonexplosive eruptions. (wide base, not steep) Cinder cone: small volcanic cones made entirely of ____________________________________ material from moderately explosive eruptions. (narrow base, steep) Composite (stratovolcanoes): most ________________________________________ that form by explosive eruptions of pyroclastic material followed by quieter outpourings of lava. (wide base, gets steeper towards the top) Types of Volcanoes Picture Name: ___________________________________________ Period: ____________ What causes a volcano? Rock melts and forms magma when the temperature of the rock increases or when the pressure on the rock decreases. Temperature is usually constant (doesn’t change) so _______________________________ usually causes magma to form. Magma ______________________________________ because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. The tectonic plate ___________________________ are where most volcanoes are formed (Ring of Fire). Formation of Magma Picutre Earthquakes Study Jams Video Quiz Score: __________ / 7