Reasoning and Explaining - Transition to Common Core
advertisement

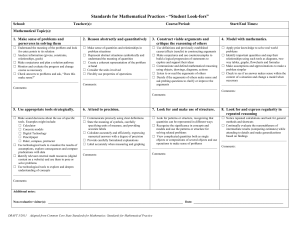
9-4-13 Name of Teacher: School: HCPSS Student Learning Objective Mathematical Practices 2 & 3: Reasoning and Explaining Component Student Learning Objective (SLO) Description 100% of students will demonstrate growth in Common Core State Content Standards for Mathematics with connections to the Standards for Mathematical Practice (Practices 2 and 3: Reasoning and Explaining), as evidenced by performance on worthwhile mathematical tasks and/or high quality formative assessment items1 and participation in effective classroom discourse. The task selection checklist can be used to support identification of worthwhile mathematical tasks and/or high quality formative assessment items. 1 Population Learning Content Instructional Interval Evidence of Growth Baseline Rationale for Student Learning Objective (insert grade) grade mathematics students Common Core State Standards: 2. Reason Abstractly and Quantitatively. (SMP2) 3. Construct Viable Arguments and Critique the Reasoning of Others. (SMP3) School year 2013-14 Pre/post teaching data collected through the Student Performance Rubric. Analyze pre-teaching data collected through Student Performance Rubric (attached) Attach class roster to share students’ scores of pre-teaching data. The 8 Standards for Mathematical Practice (SMP) describe the behaviors of mathematically proficient students. These are the behaviors that mathematics teachers should seek to develop in their students. Together, practices 2 and 3 (below) can be described as reasoning and explaining. 2. Reason Abstractly and Quantitatively. (SMP2) 3. Construct Viable Arguments and Critique the Reasoning of Others. (SMP3) The behaviors are described in the Student Performance Rubric (attached). The rubric is a tool to measure student performance. With teacher guidance, student proficiency will progress from the baseline to more advanced proficiency levels. Target The chart shows growth targets for all students. Values are based on the Student Performance Rubric. Students scoring this value2 on the Will increase to this score on the pre-assessment: post-assessment. 0-2 3-5 3-5 6-7 6-7 8-9 8-9 8-9 2 Multiple tasks can be measured with the rubric and an averaged performance can be used as a performance value. *Please note: Students identified by IEP teams as having significant cognitive disabilities will have individual targets. This SLO is a sample. Targets need to be adjusted based on your students’ data. Student growth should be achieved for all students. 9-4-13 Evidence of Growth Pre/post teaching data collected through the Student Performance Rubric. Criteria for Effectiveness Full Attainment of Target More than 90% of students meet agreed upon learning targets identified in the chart in the Target section above. Mathematics Content Standards and Mathematical Practices Standards 2 & 3 Strategies Partial Attainment of Target Between 75% and 90% of students meet agreed upon learning targets identified in the chart in the Target section above. Insufficient Attainment of Target Less than 75% of students meet agreed upon learning targets identified in the chart in the Target section above. Be purposeful when planning lessons to include challenging mathematical tasks that elicit the Mathematics Practices in their students. (SMP2 and 3) Monitor instructional progress. (SMP2 and 3) Ask students to explain their thinking regardless of accuracy (SM2) Highlight flexible use of numbers (SMP2) Facilitate discussion through guided questions and representations. (SMP2) Accept varied solutions/representations (SMP2). Provide opportunities for students to listen to or read the conclusions or arguments of others (SMP3) Establish and facilitate a safe environment for discussion. (SMP3) Ask clarifying and probing questions. (SMP3) Avoid giving too much assistance (e.g., providing answers or procedures). (SMP3) Pose rich problems and/or ask open ended questions (SMP3) Provide wait-time for processing/finding solutions (SMP3) Embrace diverse solutions and/or justifications (SMP3) Recognize and model efficient strategies for computation (SMP2) Model to develop student oral and written communication in mathematics (SMP3) This SLO is a sample. Targets need to be adjusted based on your students’ data. Student growth should be achieved for all students. Student Performance Rubric Reason and Explain • Standards for Mathematical Practices 2 and 3 Reasoning about Problems Reasoning about Numbers Explaining • Uses symbols/equations to solve problems. • Represents problems with tools, drawings, or equations. • Understands reasonableness of the solution. • Interprets solutions including remainders. • Represents problems with tools, drawings, equations. • Uses symbols/equations to solve problems. • Represents problems. Representations are flawed or inaccurate. • Uses symbols/equations incorrectly or inconsistently. • Does not represent problems. • Does not use symbols/equations. 3 2 1 0 • Estimates answer before calculating to determine reasonableness of answer. • Uses numbers flexibly, does not use standard algorithms for all computation situations • Computes accurately. • Relies on procedural methods for computation in inappropriate situations. • Computes accurately. • Relies on procedural methods for computation in inappropriate situations • Computation is flawed. • Cannot apply a procedure for computation. • Procedure is flawed. • Computation is flawed. 3 2 1 0 • Explanation is clear and complete. • Uses examples in explanation or describes mathematical concept not just procedure. • Uses representations in explanation. • Uses correct math vocabulary in explanation. • Explanation is clear and complete. • Uses representation in explanation. • Uses correct mathematics vocabulary. • Partial explanation • Some/partial use of math vocabulary. • Vocabulary is not consistently correct. • Missing explanation • Explanation is irrelevant or unrelated • Explanation simply restates prompt. • Missing math vocabulary or used incorrectly. 3 2 1 0 Task Selection Checklist This checklist supports the identification of worthwhile mathematical tasks and/or high quality formative assessment tasks. All 3 elements are present in such tasks. The task/item explicitly requires students to communicate their reasoning and understanding. The task/item allows for multiple solutions/strategies but not necessarily multiple correct answers. The task/item requires student engagement in the overarching habits of mind of a productive mathematical thinker. For example, the task/item MAY require students to: Make sense of quantities and relationships in problem situations Represent abstract situations/problems symbolically and understand the meaning of quantities Create a coherent representation of the problem Consider the units involved Flexibly use properties of operations Use definitions and previously established causes/effects (results) in constructing arguments Make conjectures and use counter examples to build a logical progression of statements to explore and support their ideas Communicate and defend mathematical reasoning using objects, drawings, diagrams, and/or actions Listen to or read the arguments of others Decide if the arguments of others make sense and ask probing questions to clarify or improve the arguments.