KIT S1 P7 DUE DATE
advertisement
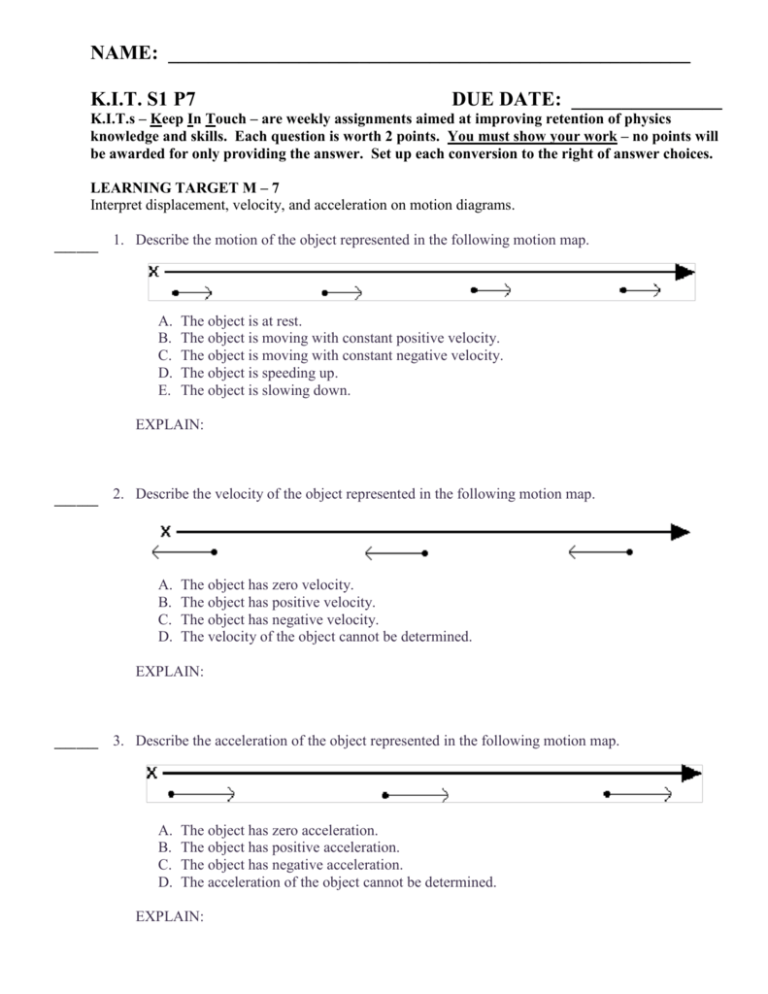
where each image revealed the position of the car at one-second intervals. NAME: ____________________________________________________ K.I.T. This S1 P7 is the motion map that represents the car. DUE DATE: _______________ We model the position of the object with a small K.I.T.s – Keep In Touch – are weekly assignments aimed at improving retention of physics point. At each position, the object’s velocity is represented by a vector. knowledge and skills. Each question is worth 2 points. You must show your work – no points will be awarded for only providing the answer. Set up each conversion to the right of answer choices. LEARNING TARGET M – 7 Interpret displacement, velocity, and acceleration on motion diagrams. If the car were traveling at greater velocity, the strobe photo might look like this: ________ 1. Describe the motion of the object represented in the following motion map. The corresponding motion map has the points spaced farther apart, and the velocity vectors are A. The object is at rest. longer, implying that the car is moving faster. B. The object is moving with constant positive velocity. C. The object is moving with constant negative velocity. D. The object is speeding up. E. The object is slowing down. If the car were moving to the left at constant velocity, the photo and motion map might look like EXPLAIN: this: ________ 2. Describe the velocity of the object represented in the following motion map. A. The object has zero velocity. More complicated motion can be represented as well. B. The object has positive velocity. C. The object has negative velocity. D. The velocity of the object cannot be determined. EXPLAIN: Here, an object moves to the right at constant velocity, stops and remains in place for two seconds, then moves to the left at a slower constant velocity. ________ 3. Describe the acceleration of the object represented in the following motion map. 'Modeling Workshop Project 2002 A. B. C. D. 1 The object has zero acceleration. The object has positive acceleration. The object has negative acceleration. The acceleration of the object cannot be determined. EXPLAIN: Unit II Reading-Motion Maps v2.0 ________ 4. Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding the motion of the object represented in the following motion map? A. B. C. D. The object moves with a greater negative velocity then positive velocity. The object moves with constant positive velocity for 4 seconds. The object remains at rest for 2 seconds. The object moves with constant negative velocity for 4 seconds. EXPLAIN: Consider the interpretation of the motion map below. At time t = 0, cyclist A starts moving to the right at constant velocity, at some position to the right of the origin. ________ 5. Which of the following statements regarding the motions of objects A and B is true? A. Object withand a greater than at Object B Cyclist B startsAatmoves the origin travelsvelocity to the right a constant, though greater velocity. B. Object B moves with a greater velocity than Object A At t = 3 s, B overtakes A (i.e., both have the same position, but B is moving faster). C. Object A and B move with the same velocity. D. The relative velocities of Objects B cannot beBdetermined. A graphical representation of the behaviorAofand cyclists A and would like this: EXPLAIN: LEARNING TARGET M-7 Interpret displacement, velocity, and acceleration on motion diagrams. Questions Correct Points Explanation 5 4.0 Complex content 4 3.5 Target and some complex 3 3.0 Target goal 2 2.5 Simple and some target You could algebraically as follows: 1 also represent the behavior 2.0 Simple/Foundational 0, butxshowed 1.0 = vAt + work x0 , forfor A all where vB > vA = vshow for for B all Bt , 0, did xnot work 0.5 With help, partial success at 2.0 & 3.0 content With help, partial success at 2.0 content Throughout this semester, you will be representing the behavior of objects in motion in multiple ways: diagramatically (motion maps), graphically and algebraically.








