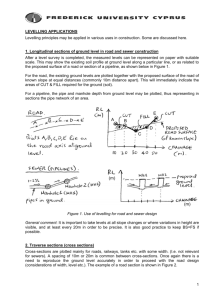
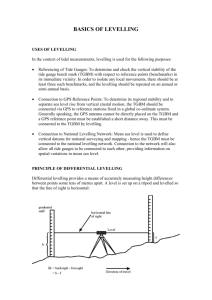
Advanced Setting out and site surveying
advertisement

Finchley College Advanced Setting out, site surveying and site engineering course syllabus and practical exercises list Theory and practice learning to use surveying instruments History of Total stations and their development Practice sessions with the aim of learning to; Creating jobs, folders, naming jobs memory management, types of memory, their capacity and differences entering, editing, searching and deleting data as well as naming points Distance measurement, slope, horizontal and vertical distances Applications and benefits of distance measurement in real life situations Calculating distance from instrument to one or more points Measuring distance between remote objects Measuring angles and distances using automatic levels Using automatic levels for rough setting out and surveys Levelling using distance measurement Using total stations for levelling through coordinate system Using dumpy, automatic and laser levels for levelling Testing equipment for accuracy and calibration Levelling with automatic levels using standard format Inverted and negative levels Drawing contour lines in a levelling survey Measuring angles using Total station and automatic levels Practical exercises using Total stations Topographic survey of a road Survey of internal and external features of a building Plotting surveys using Auto Cad or drawing on graph paper Total station programs and Setting out methods and technique 1 Site engineering practical tasks Site engineering practical tasks (cont.) Reading and understanding construction drawings including; Architects, engineers and reinforcement drawings Understanding sequence of operations in ground works Knowing what is going to happen next and what is required of you as an engineer Establishing control networks Creating your own grid systems from scratch Working on large projects with global coordinate systems Working on very small projects were no control points are provided Understanding global and local grid systems and how to manipulate them Traversing Types of traverse, open and closed networks Planning a traverse and adjustment methods Checking an existing traverse Using part of a closed traverse as an open traverse Using spread sheet programs to adjust raw data of a traverse Carrying out site surveys Surveying façade of a building for line and level Levelling Using dumpy level, reading staff, Setting out and calculating distances using dumpy levels Calculating areas and volumes 2 Checking dumpy level, laser level and total stations for accuracy and calibration Testing total stations for horizontal angle, vertical angle and levelling Adjusting levelling bubbles on levels and total stations Plumbing lift shafts and building facades using string lines and plumb lasers Using a local coordinate system for plumbing Checking a column for plumb Checking beams and ceilings for level Controlling verticality and plumb of a building during construction Deciding on number, size and location of plumbing holes Safety measures when using plumb lasers Checking if two walls are parallel Calculating internal angle between two walls Setting out lines and 90 degrees and other acute angles Setting out ramps, slopes and calculating falls Drawing contour lines of a field survey Transferring points through a building Checking if two lines are parallel Calculating intersection coordinate of two lines Using a programmable calculator for free station or resection program Using a Programmable calculator Calculating coordinate of a point Global Local coordinate transformation