Waves, Chapter 20 (PS 8 & 9)
advertisement
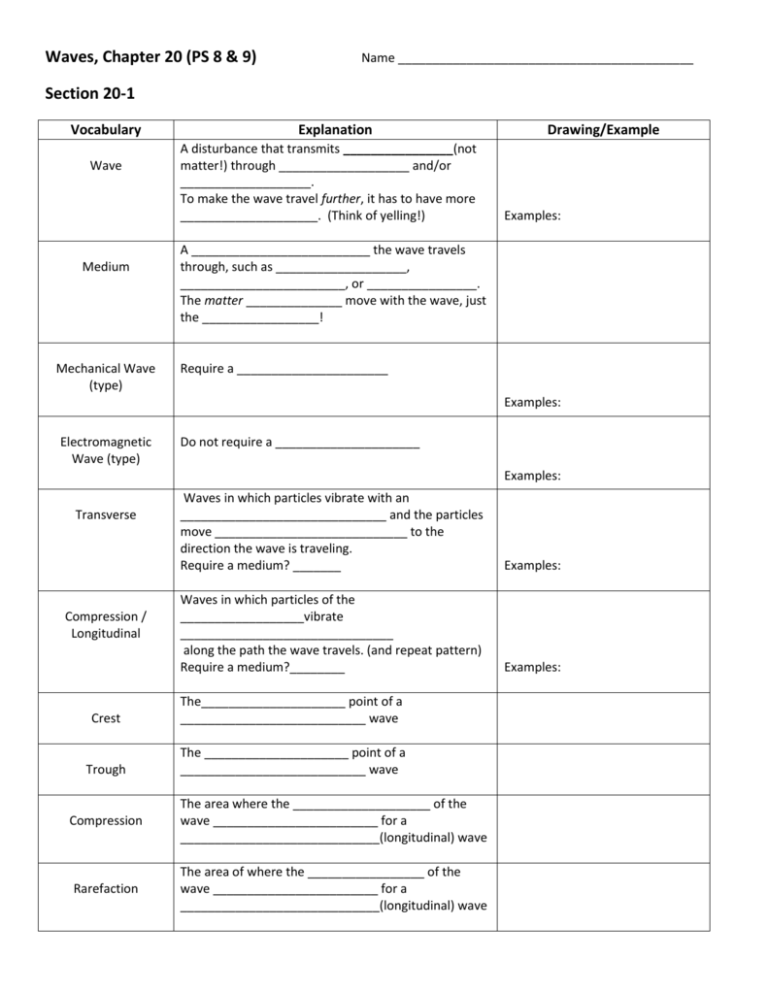
Waves, Chapter 20 (PS 8 & 9) Name ___________________________________________ Section 20-1 Vocabulary Wave Medium Mechanical Wave (type) Explanation A disturbance that transmits ________________(not matter!) through ___________________ and/or ___________________. To make the wave travel further, it has to have more ____________________. (Think of yelling!) Drawing/Example Examples: A __________________________ the wave travels through, such as ___________________, ________________________, or ________________. The matter ______________ move with the wave, just the _________________! Require a ______________________ Examples: Electromagnetic Wave (type) Do not require a _____________________ Examples: Transverse Compression / Longitudinal Waves in which particles vibrate with an ______________________________ and the particles move ____________________________ to the direction the wave is traveling. Require a medium? _______ Examples: Waves in which particles of the __________________vibrate _______________________________ along the path the wave travels. (and repeat pattern) Require a medium?________ Examples: Crest The_____________________ point of a ___________________________ wave Trough The _____________________ point of a ___________________________ wave Compression The area where the ____________________ of the wave ________________________ for a _____________________________(longitudinal) wave Rarefaction The area of where the _________________ of the wave ________________________ for a _____________________________(longitudinal) wave Section 20-1 Review A wave is a ___________________ that carries ___________________. A wave can travel through ___________________ or _______________________. There are two kinds of waves we’ve discussed: waves that require a medium called___________________________ or waves that do not require a medium called ______________________________. The _____________________ waves have crests and troughs and are the _______________________ waves. The _______________________ waves have compressions and rarefactions are the _________________________ waves. Section 20-2 Vocabulary Wave Velocity/Speed (v) Frequency (f) Hertz (Hz) Wavelength (λ) Unit: meters Amplitude Explanation Measured in _____________. Velocity depends on the _______________________ for a compression wave. Drawing/Example V= λx f The number of ___________________ produced in a given amount of ___________________ (how many _________________ pass each __________________) Count the number of ____________or _____________ for a transverse wave or the number of _______________ or __________________ for a compression/longitudinal wave that pass by each second. The higher the frequency, the ____________________ the wavelength and the ( less / more ) energy. The unit used to measure _______________________: 1 Hz = 1 _____________/_____________________ The __________________ between two adjacent ___________ or_____________ for a transverse wave or the distance between two adjacent ____________________ or ____________________ for a compression/longitudinal wave λ and f have ________________ relationship The ___________________________ distance a wave vibrates from the ______________________________. (The “height” of the wave) The larger the amplitude, the ( less / more ) energy. Section 20-2 Review There are four properties of waves: wave velocity measured by _________________, frequency measured in ___________________, wavelength measured in _______________________ and amplitude measured in _____________________. The speed of a wave is determined by the ___________________________ the wave is traveling through. If wavelength increases, frequency _______________________________. Section 20-3 Vocabulary Explanation Reflection The ___________________________ of a wave after it hits a ______________ or an object Drawing/Example Example: Refraction The ___________________ of a wave as it passes at an _______________from one __________________ to another due to the difference in ___________________ in the mediums. Example: Diffraction Interference Constructive Interference Destructive Interference The ________________________ of waves around a ___________________ or through an _____________________ and is determined by the __________________________ and/or the size of the _______________________. (= new waves produced) The result of two or move waves ________________________ (as a result of diffraction). 3 Types: When one wave ___________________ another wave. This results in (smaller/larger) amplitudes, which means _______ energy or __________ sounds. When one wave __________________ another wave. This results in (smaller/larger) amplitudes, which means _______ energy or __________ sounds. Example: Example: Example: Example: Two waves with identical amplitudes will _____________________________. Resonance What occurs when an object vibrating at or near the _____________________________________ of a second object causes the second object to _______________________________. (They vibrate at maximum amplitude at certain frequencies.) Example: Section 20-3 Review There are four wave interactions: ______________________________, ________________________________, ___________________________________ and ________________________________. Seeing myself in the mirror is an example of ______________________ and seeing light come into a dark room from a hallway is an example of _________________________________. When waves overlap and become louder, we call it _____________________________ interference. When one object vibration causes another object to vibrate, we call that _____________________________________.






