DNA Extraction from Fresh or Frozen Tissues Phenol/Chloroform
advertisement

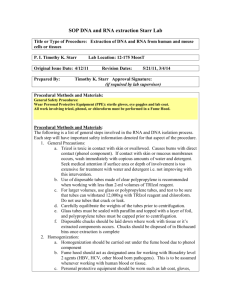
DNA Extraction from Fresh or Frozen Tissues 1. Phenol/Chloroform Extraction of DNA That the DNA is soluble in water whereas lipids are soluble in phenol. In these protocols, tissues are disaggregated and then treated with detergent to lyse cell membranes followed by proteinase to digest proteins. Phenol, an organic solvent, is added to help separate the lipids and protein remnants from the DNA. Chloroform is then used to facilitate the removal of phenol. DNA is subsequently concentrated and further purified by precipitation in a cold mixture of salt and ethanol. Finally, DNA is resolubilized in Tris-EDTA buffer. Sample Preparation 1. Mince fresh, solid tissue up to 3 mm3 into small pieces (1–2 mm) with a sterile scalpel blade. Process the tissue within 2 h of collection, or freeze at –20°C or colder until the time of DNA extraction. 2. Place the tissue in a clean mortar filled with liquid nitrogen, for cleaning instructions, and work under a hood to protect yourself from aerosolized powder. The procedure: 1. Add an equal volume of equilibrated phenol (TRIzol) , close the cap tightly, and mix gently by inversion for 1 min. 2. Spin the tube at 1700g in a swinging bucket rotor at room temperature for 10 min. 3. With a plastic pipet, aspirate the upper clear aqueous layer and transfer it to another clean labeled tube. 4. Repeat the phenol extraction (steps 1–3) one more time. 5. Next, extract with an equal volume of chloroform instead of phenol, and save the supernatant to another clean tube after centrifugation. 6. Repeat the chloroform extraction; this helps eliminate all of the phenol from the DNA sample. TRIzol is a chemical solution used in RNA/DNA/protein extraction, The correct name of the method is Guanidinium thiocyanate-phenolchloroform extraction. The use of TRIzol can result in DNA and RNA yields comparable to other extraction methods. An alternative method for RNA extraction is phenol extraction and TCA/acetone precipitation. Chloroform should be exchanged with 1-bromo-3-chloropropane when using the new generation TRI Reagent. TRIzol is light sensitive and is often stored in a dark-colored, glass container covered in foil. It must be kept below room temperature. When used, it resembles cough syrup, bright pink. The smell of the phenol is extremely strong. TRIzol works by maintaining RNA integrity during tissue homogenization, while at the same time disrupting and breaking down cells and cell components. 2. Solid Extraction Cell Lysis and Digestion: 1. For solid tissue, add 920 μL of DNA extraction buffer to the tissue powder in the mortar, and gently mix with the pestle. Then transfer the fluid to a 1.5-mL microfuge tube by gentle pipeting. For a mononuclear cell pellet, resuspend the cells in 920 μL of DNA extraction buffer and mix well by gentle pipeting. 2. Add 50 μL of 10% SDS to the mixture and mix well; the solution should become viscous. 3. Add 30 μL of proteinase K solution to the viscous mixture. Close the cap tightly and mix vigorously by vortex. 4. Incubate in a 37°C water bath for at least 6 h or as long as 2 d, or at 55°C for 3 h; gently invert the tube a few times during incubation. 8 Fan to drying. 5. The lysed sample should be viscous and relatively clear. This sample may be stored at 4°C for up to 1 wk before subjecting. 3. Genomic DNA Extract from Bacteria. Procedure: 1. Allow the bacterial cell pellet collection tube to thaw at room temperature. 2. Add 180 μl of Lysis Solution I and resuspend the pellet by gentle pipetting. 3. Add 20 μl of Proteinase K solution to the above collection tube, vortex thoroughly for 10-15 seconds, and incubate for 30 minutes at 55oC. 4. Add 20 μl of RNase A solution to the above collection tube, vortex thoroughly for 10-15 seconds, and incubate for 5 minutes at room temperature (15-25°C). NOTE: This step helps in getting RNA-free genomic DNA. 5. Add 200 μl of Lysis Solution II, vortex thoroughly for about 15 seconds, and incubate at 55oC for 10 minutes. 6. Add 200 μl of ethanol (95-100%) to the lysate and mix thoroughly by gentle pipetting. 7. Transfer the entire lysate obtained from step 5 into the spin column for binding the DNA, and Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 1 minute. Discard the flow-through liquid and place the spin column in the same 2.0 ml collection tube. Spin column tube 8. Add 500 μl of Solution to the Spin column and centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 1minute. Discard the flow-through liquid and re-use the same collection tube with the column. 9. Add 500 μl of Wash Solution to the column and centrifuge for 3 minutes at 14,000 rpm to dry the column. 10. Pipette 200 μl of the Elution Buffer directly into the column without spilling to the sides. Incubate for1 minute at room temperature. Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 1 minute to elute the DNA. For long-term storage, -20oC or lower temperature (-80oC) is recommended. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing of the sample which may cause denaturing of DNA. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZvuhJaiMrdU https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JNl1kjw9ZDQ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xv9hWBEzFxc https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lGTUEM9t0m4